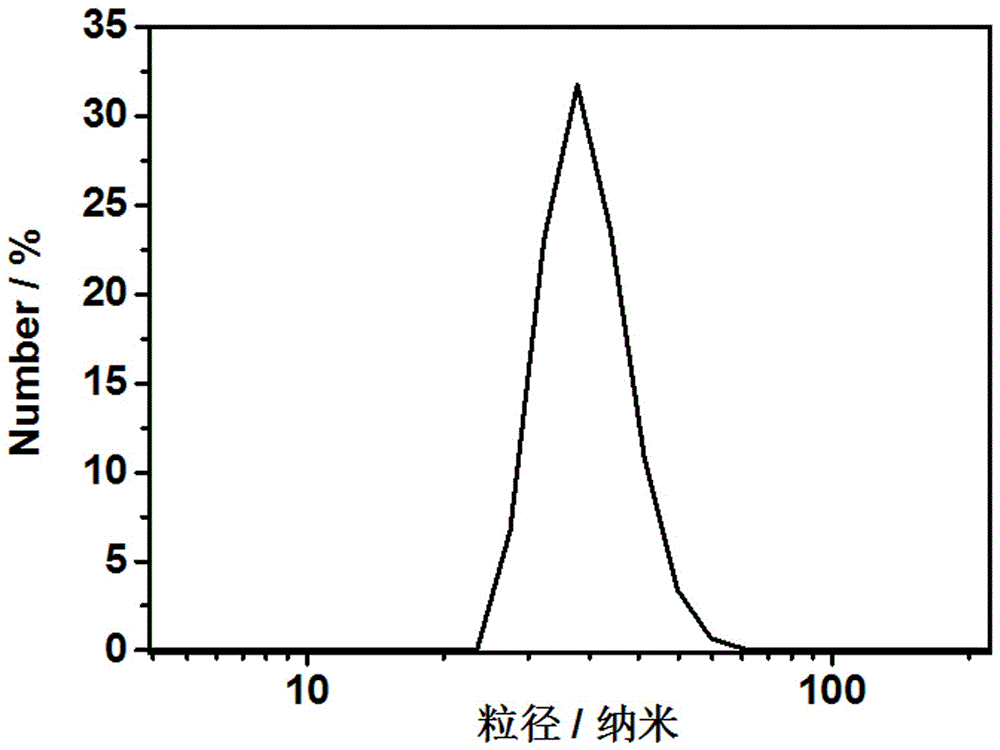
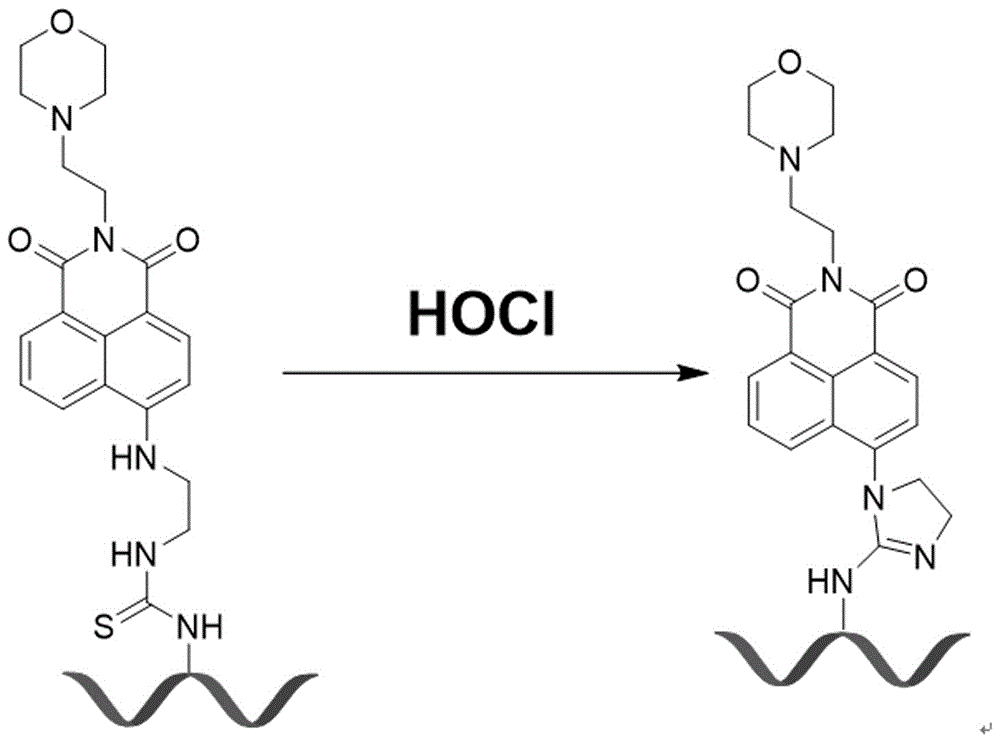
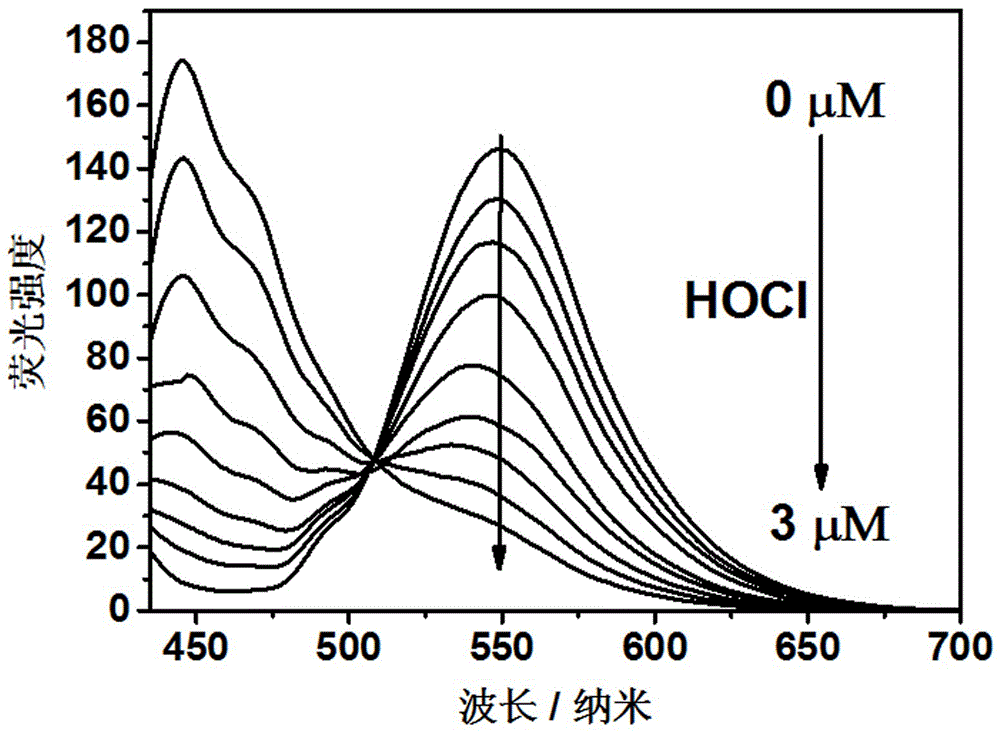
Polymer fluorescence sensor with hypochlorous acid ratio detection function and application of polymer fluorescence sensor
A fluorescent sensor and a technology for detecting hypochlorous acid, applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of reduced feasibility and limited applicability, and achieve convenient post-processing, obvious selectivity and fast response, and high The effect of selective rapid response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029]Embodiment 1: the preparation of a kind of fluorescent sensor that can ratio detect hypochlorous acid, concrete steps are as follows:
[0030] (1) Dissolve 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene dianhydride (10 mmol) and 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine (10 mmol) in ethylene glycol methyl ether (10 mL), placed in N 2 Under the conditions of protection and avoiding light, rapidly raise the temperature to 120°C and stir for 4 hours. After the reaction is completed, it is directly added to 40 mL of distilled water to precipitate, and the desired product is obtained by suction filtration, and vacuum-dried to obtain product 1;
[0031] (2) Dissolve the product 1 (3 mmol) synthesized in step (1) in 10 mL of ethylenediamine, and place the mixed solution in the dark and N 2 Stir at 80°C for 4 h under protected conditions, remove most (85-95%) of ethylene glycol methyl ether by rotary evaporation after the reaction, purify the product through a column, and dry it in vacuum to obtain product 2;
[0...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2: The preparation of a fluorescent sensor capable of ratiometrically detecting hypochlorous acid, the specific steps are as follows:
[0036] (1) Dissolve 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene dianhydride (10 mmol) and 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine (10 mmol) in ethylene glycol methyl ether (10 mL), placed in N 2 Under the conditions of protection and avoiding light, rapidly raise the temperature to 120°C and stir for 4 hours. After the reaction is completed, it is directly added to 40 mL of distilled water to precipitate, and the desired product is obtained by suction filtration, and vacuum-dried to obtain product 1;
[0037] (2) Dissolve the product 1 (3 mmol) synthesized in step (1) in 10 mL of ethylenediamine, and place the mixed solution in the dark and N 2 Stir at 80°C for 4 h under protected conditions, remove most (85-95%) of ethylene glycol methyl ether by rotary evaporation after the reaction, purify the product through a column, and dry it in vacuum to obtain prod...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: the preparation of a kind of fluorescent sensor that can ratio detect hypochlorous acid, concrete steps are as follows:
[0042] (1) Dissolve 4-bromo-1,8-naphthalene dianhydride (10 mmol) and 4-(2-aminoethyl)morpholine (10 mmol) in ethylene glycol methyl ether (10 mL), placed in N 2 Under the conditions of protection and avoiding light, rapidly raise the temperature to 120°C and stir for 4 hours. After the reaction is completed, it is directly added to 40 mL of distilled water to precipitate, and the desired product is obtained by suction filtration, and vacuum-dried to obtain product 1;
[0043] (2) Dissolve the product 1 (3 mmol) synthesized in step (1) in 10 mL of ethylenediamine, and place the mixed solution in the dark and N 2 Stir at 80°C for 4 h under protected conditions, remove most (85-95%) of ethylene glycol methyl ether by rotary evaporation after the reaction, purify the product through a column, and dry it in vacuum to obtain product 2;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com