Method for recovering nickel and vanadium from waste FCC (Fluid Catalytic Cracking) catalyst through molten chlorination volatilizing
A chlorination volatilization and catalyst technology, applied in the field of harmless treatment of waste FCC catalysts, can solve the problems of difficult and low-cost effective recycling, difficult iron solution treatment, high Si leaching rate, and achieves low environmental impact and high regeneration utilization rate. , the effect of strong regional adaptability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
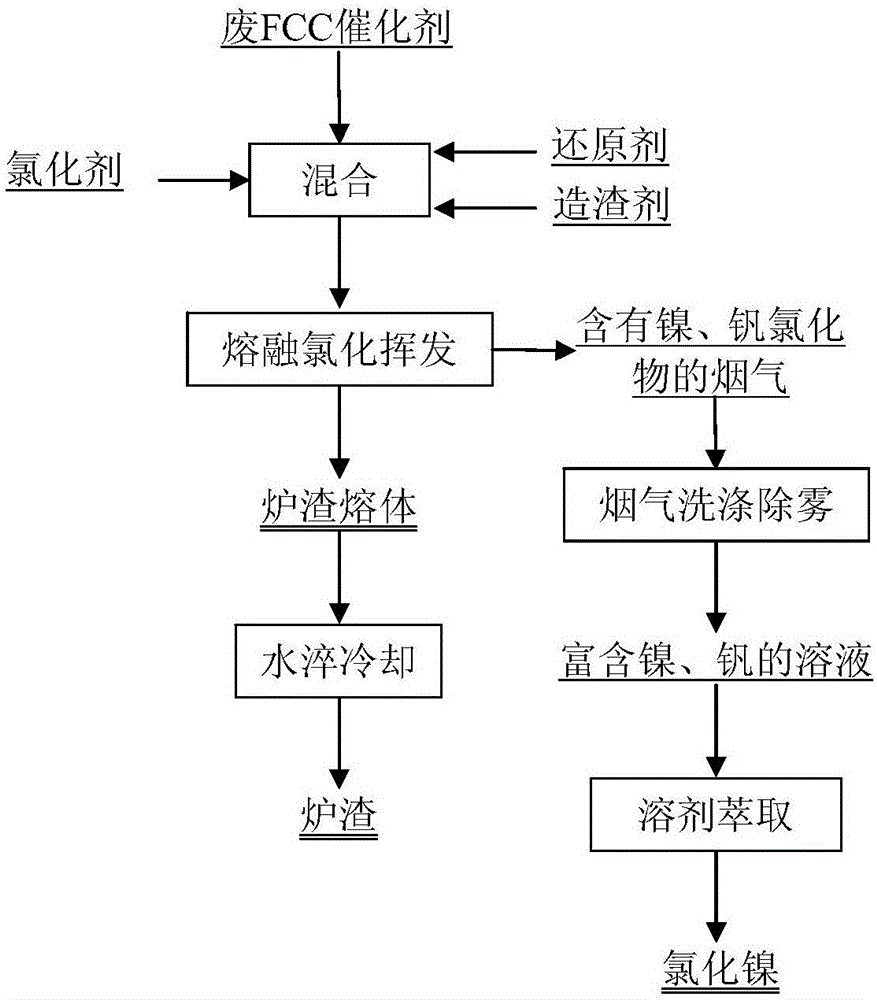
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A method for recovering nickel and vanadium from molten chlorination and volatilization from waste FCC catalysts, using waste FCC catalysts discharged from a petroleum cracking plant in Shandong as raw material, the main elemental components of the waste FCC catalysts are shown in Table 1 below:
[0047] Table 1:
[0048]
[0049]
[0050] The method comprises: taking 100g of the spent FCC catalyst (wherein, the spent FCC catalyst with a particle size less than 0.075mm accounts for 40% of the total spent FCC catalyst), and adding 7g of anhydrous calcium chloride, 1g of anthracite, and 20g of calcium oxide, and mixing uniformly , so as to obtain the mixed material to be smelted. Put the mixed material to be smelted into the corundum crucible, cover the crucible lid, put the crucible containing the mixed material to be smelted into a closed tubular heating furnace, cover the sealing end cover of the tubular furnace tightly, and connect the air inlet and the gas out...
Embodiment 2
[0053] A method for recovering nickel and vanadium by reducing smelting from waste FCC catalysts, using waste FCC catalysts discharged from a certain petroleum cracking plant in Hebei as raw material, the main elemental components of the waste FCC catalysts are shown in Table 2 below:
[0054] Table 2:
[0055] element Ni V al 2 o 3
SiO 2
Fe Sb Ca content / % 2.80 0.46 45.10 50.20 0.57 0.21 0.26
[0056] The method comprises: taking 100g of the spent FCC catalyst (wherein, the spent FCC catalyst with a particle size less than 0.075mm accounts for 45% of the spent FCC catalyst), and adding 10g of anhydrous magnesium chloride, 1g of coke powder, and 20g of quartz sand, and mixing evenly, Thus, the mixed material to be smelted is obtained. Put the mixed material to be smelted into the corundum crucible, cover the crucible lid, put the crucible containing the mixed material to be smelted into a closed tubular heating furnace, cover t...
Embodiment 3
[0059]A method for recovering nickel and vanadium by reduction smelting from waste FCC catalysts, using waste FCC catalysts discharged from a certain petroleum cracking plant in Gansu as raw material, the main elemental components of the waste FCC catalysts are shown in Table 3 below:
[0060] table 3:
[0061] element Ni V al 2 o 3
SiO 2
Fe Sb Ca content / % 2.16 0.36 45.47 51.05 0.43 0.18 0.23
[0062] The method comprises: taking 100g of the spent FCC catalyst (wherein, the spent FCC catalyst with a particle size less than 0.075mm accounts for 50% of the spent FCC catalyst), and adding 9g of anhydrous calcium chloride, 1g of charcoal, and 25g of limestone, and mixing evenly, Thus, the mixed material to be smelted is obtained. Put the mixed material to be smelted into the corundum crucible, cover the crucible lid, put the crucible containing the mixed material to be smelted into a closed tubular heating furnace, cover the seali...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com