Method for inducing coralline algae to improve exopolysaccharide secretion intensity
A technology of coralline algae and concentration, applied in botany equipment and methods, chemicals for biological control, biocides, etc., to achieve the effect of promoting physiological activity, improving environmental adaptability and adversity resistance, and enhancing resource utilization value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0021] One of the embodiments of the present invention relates to zinc methionine organic trace element chelate, and its preparation method comprises the following steps:
[0022] Dissolve methionine in distilled water, add methionine mass 2±0.5% of the mass of methionine, add 2% basic zinc carbonate in this example, stir and react at 70℃~85℃ for 4~6h; add 1mol / L hydrochloric acid solution, heat to methionine All dissolved, the solution was transparent and light yellow;
[0023] Adjust the pH value to 6.0-6.5, and filter while it is hot while stirring continuously;
[0024] Add absolute ethanol to precipitate the chelate, centrifuge, and then dry at 105-115°C to obtain a white product, that is, zinc methionine organic trace element chelate.
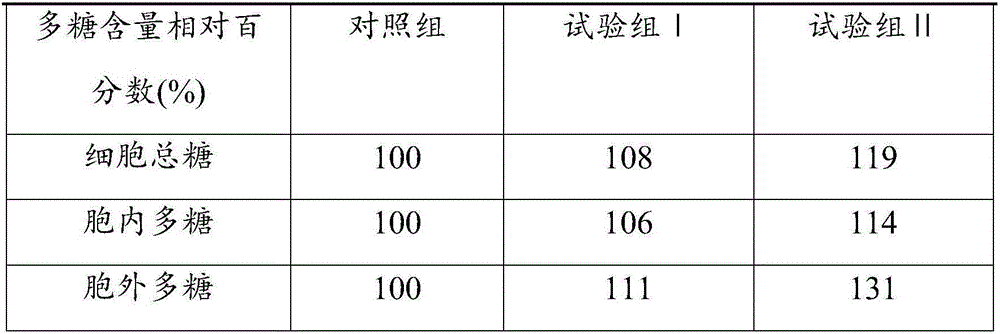
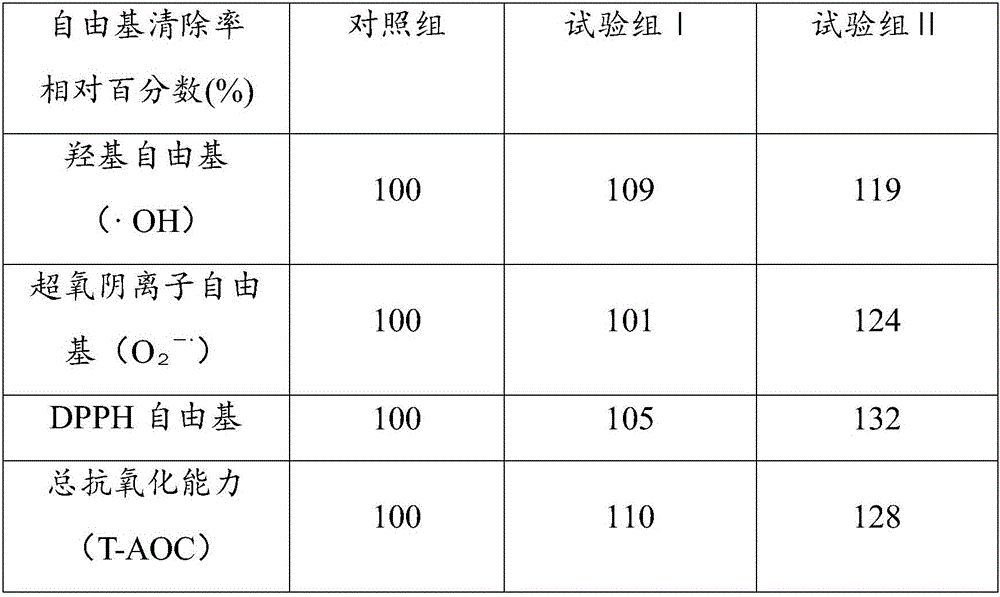
[0025] This embodiment also relates to a method for inducing coralline algae to increase the secretion intensity of exopolysaccharides, comprising the following steps: adding the methionine zinc organic trace element chelate prepared by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com