Low-temperature sintering high-heat conduction ceramic paint suitable for metal base material and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of high thermal conductivity ceramics and low-temperature sintering, applied in the field of ceramic coatings, can solve problems such as the influence of heat transfer performance of heat exchangers, the inability to form ceramic coatings, and less research on ceramic coatings, so as to improve high-temperature oxidation resistance and improve Thermal shock resistance, anti-shedding and cracking effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] A low-temperature sintered high thermal conductivity ceramic coating suitable for metal substrates and a preparation method thereof:
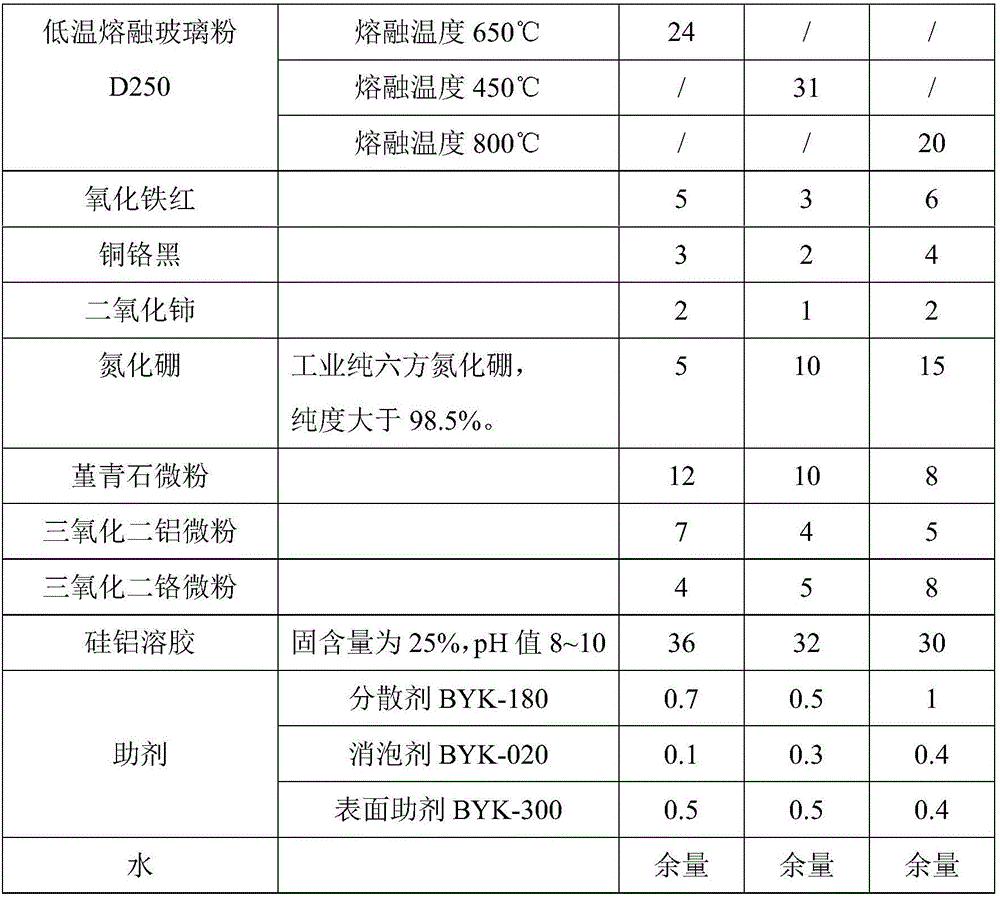
[0027] Weigh low-temperature molten glass powder, iron oxide red, copper chrome black, cerium dioxide, boron nitride, cordierite micropowder, aluminum oxide micropowder, chromium trioxide micropowder, silica-alumina sol and additives according to weight percentage, and initially After mixing evenly, use a high-energy ball mill to grind to a particle size of less than 5 μm to obtain a low-temperature sintered high thermal conductivity ceramic coating suitable for metal substrates. The contents of each component of the ceramic coating in this example are shown in Table 1.
[0028] Specific usage method:
[0029] 1) Grinding, cleaning, and removing oxides, grease and dust on the surface of the substrate for 0Cr25Ni4N heat-resistant steel;
[0030] 2) The ceramic coating prepared above is evenly coated on the surface of the metal substrate,...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The preparation process of the ceramic coating is the same as in Example 1, and the content of each component of the ceramic coating in this example is shown in Table 1.
[0034] Specific usage method:
[0035] 1) Grinding, cleaning, and removing oxides, grease and dust on the surface of the substrate for 1Cr18Ni9Ti heat-resistant steel;
[0036] 2) The ceramic coating prepared above is evenly coated on the surface of the metal substrate, and dried in the shade;
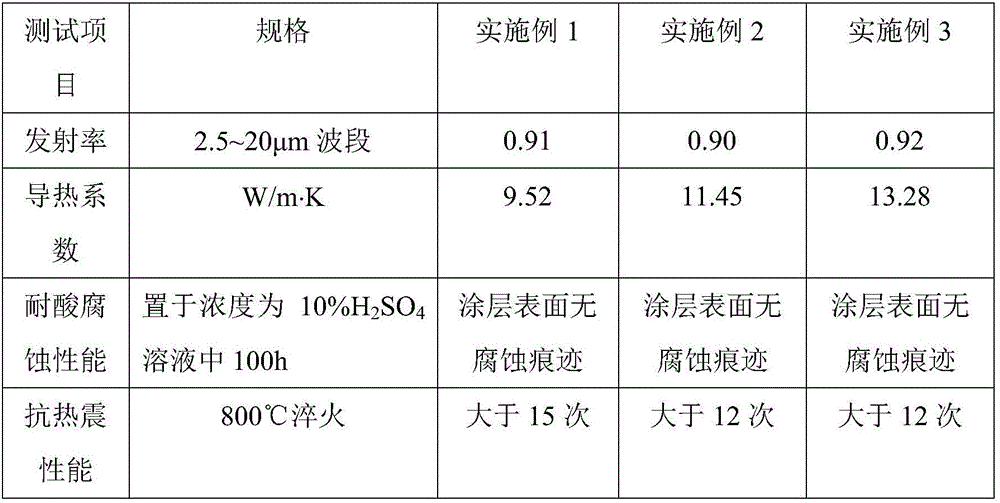
[0037] 3) Heating the coated metal substrate to 700°C, keeping it warm for 20 minutes, taking it out to form a low-temperature sintered high thermal conductivity ceramic coating on the metal surface. The performance of the coating was tested according to the general testing standards of the country or the industry, and the test results are shown in Table 2.
Embodiment 3
[0039] The preparation process of the ceramic coating is the same as in Example 1, and the content of each component of the ceramic coating in this example is shown in Table 1.
[0040] Specific usage method:
[0041] 1) Grinding, cleaning, and removing oxides, grease and dust on the surface of the substrate for 0Cr25Ni20 heat-resistant steel;
[0042] 2) The ceramic coating prepared above is evenly coated on the surface of the metal substrate, and dried in the shade;
[0043] 3) Heating the coated metal substrate to 900°C, keeping it warm for 20 minutes, taking it out to form a low-temperature sintered high thermal conductivity ceramic coating on the metal surface. The performance of the coating was tested according to the general testing standards of the country or the industry, and the test results are shown in Table 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com