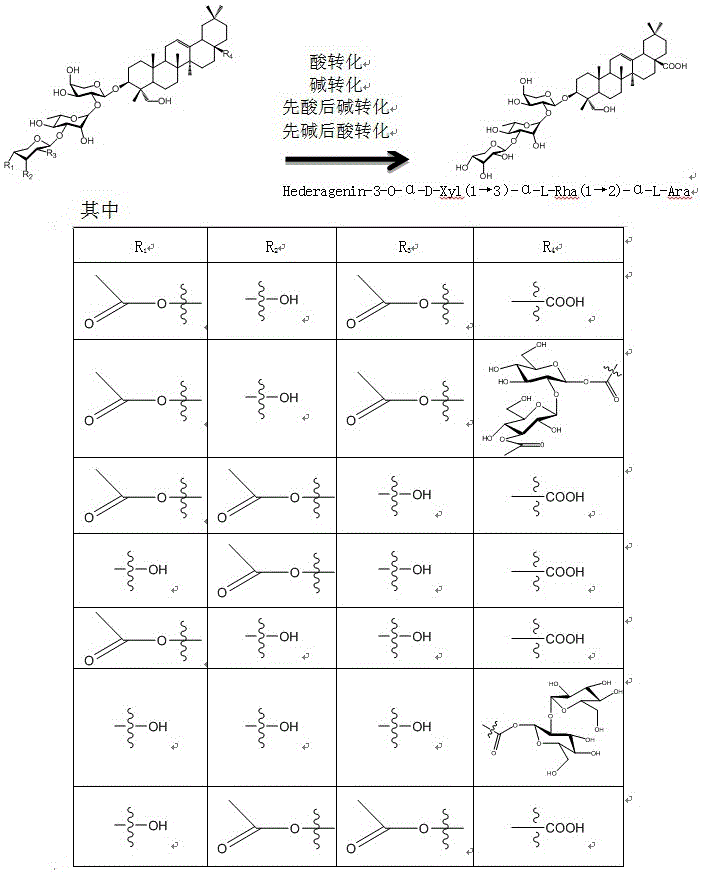
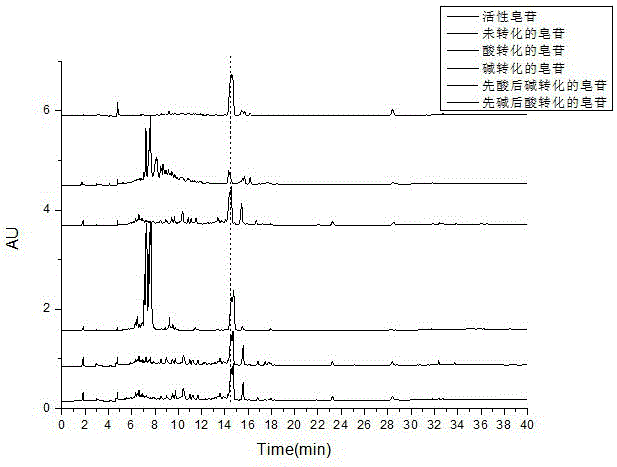
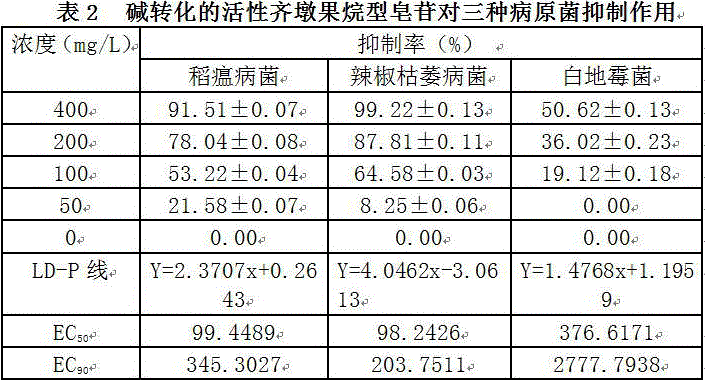
Method for preparing anti-pathogenic active oleanane glycoside through chemical conversion
An oleanane-type, anti-pathogenic technology is applied in the field of biocidal active substances to achieve the effects of good environmental compatibility, prevention of pathogen adhesion, and strong foaming.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029]1. Extraction of Sapindus crude saponin: remove the husk and core of Sapindia fruit, air-dry the mesocarp at room temperature, weigh 10kg, add 50kg of 70% ethanol aqueous solution to soak for 20 hours, extract in 70°C water bath for 5 hours, and suction filter. Recover the ethanol solvent under reduced pressure and concentrate to obtain about 6kg of crude saponin extract (standby);
[0030] 2. Acid-converted crude saponin extract: slowly add 10 mL of 2 M hydrochloric acid solution to 5 kg of crude saponin extract to obtain a mixed saponin aqueous solution, and adjust with water to obtain a final concentration of hydrochloric acid in the mixed saponin aqueous solution of 0.1 M. Hydrolyzed for 18 hours to obtain active oleanane triosyl saponins;
[0031] 3. Deacidification and concentration of active oleanane-type saponins: Pour the active oleanane trisaccharide-based saponins into the D101 macroporous resin column until the breakthrough point, let the D101 macroporous res...
Embodiment 2
[0035] 1. Crude saponin extraction of Sapindus chinensis: Sapindia chinensis fruit, shell and core removed, mesocarp air-dried at room temperature, weighing 20kg, adding 160kg of 80% ethanol aqueous solution to soak for 24 hours, leaching in 90℃ water bath for 10 hours, and suction filtration , recover the ethanol solvent under reduced pressure and concentrate to obtain about 8kg crude saponin extract (for standby);
[0036] 2. Alkali-transformed crude saponin extract: slowly add 10 mL of 2 M sodium hydroxide solution to 5 kg of crude saponin extract to obtain a mixed saponin aqueous solution, and adjust the final concentration of sodium hydroxide in the mixed saponin aqueous solution to 0.5 M with water. Hydrolyze at 90°C for 24 hours to obtain active oleanane triosyl saponins;
[0037] 3. Dealkalization and concentration of active oleanane-type saponins: Pour the active oleanane trisaccharide-based saponins into the D101 macroporous resin column until the breakthrough point,...
Embodiment 3
[0041] 1. Crude saponin extraction of Sapindus chinensis: Sapindia chinensis fruit, remove husk and core, air-dry mesocarp at room temperature, weigh 6kg, add 30kg of 60% ethanol aqueous solution to soak for 12h, leaching at 60°C for 3h, suction filtration, and decompression Recover the ethanol solvent and concentrate to obtain about 4kg crude saponin extract (standby);
[0042] 2. Convert the crude saponin extract to acid and then alkali: slowly add 0.5 mL of 2 M hydrochloric acid solution to 4 kg of crude saponin extract to obtain a mixed saponin aqueous solution, and adjust the final concentration of hydrochloric acid in the mixed saponin aqueous solution to 0.1 M with water, 60 After hydrolysis for 12 h at ℃, adjust the final concentration of sodium hydroxide in the mixed saponin aqueous solution to 0.5 M with 2 M sodium hydroxide solution, and hydrolyze for 12 h at 60 °C to obtain active oleanane triosyl saponin;
[0043] 3. Concentrated active oleanane triose-based sapon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com