Preparation method of MCNCs/PMAA magnetically-controlled Raman aptamer sensor for antibiotic residue detection
A technology of antibiotics and sensors, applied in Raman scattering, instruments, measuring devices, etc., to achieve high saturation magnetization, avoid interference from external environment, and excellent biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
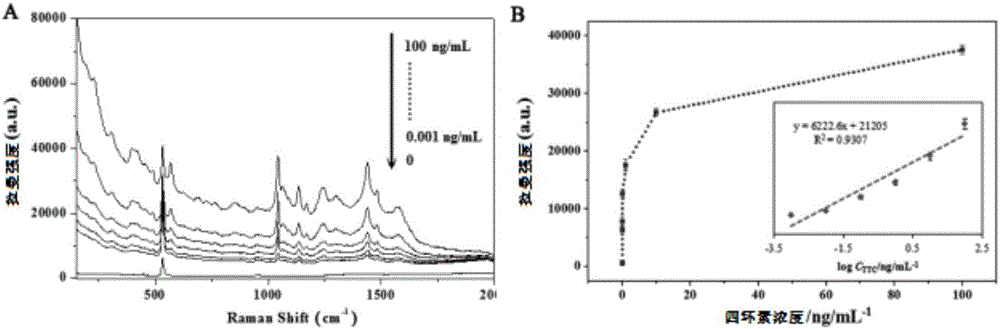
[0025] In order to further verify the effect of the prepared sensor of the present invention on the detection of antibiotic residues, in the example of the present invention, taking tetracycline (tetracycline) as an example, the specific operation steps are as follows:
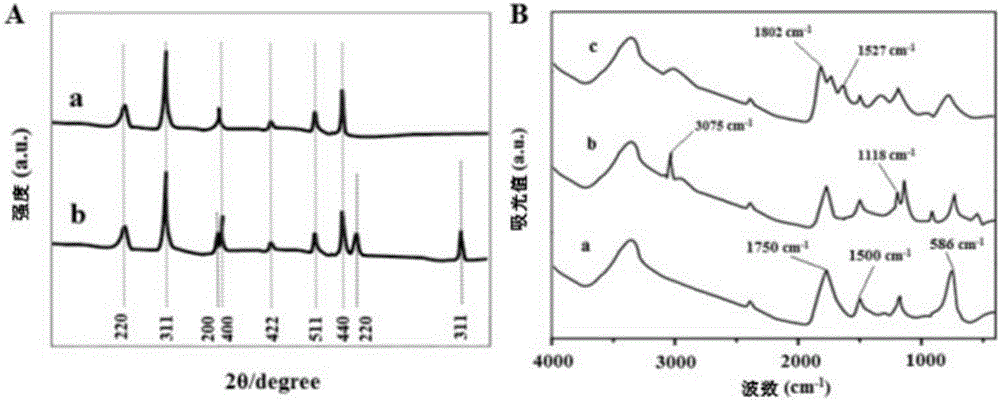
[0026] (1) Preparation of MCNCs / PMAA magnetic nanospheres: MCNCs were synthesized by solvothermal method. First, weigh 1.350g FeCl 3 .6H 2O, 3.854g of sodium acetate and 0.400g of sodium citrate were dissolved in a 250mL three-neck round-bottomed flask filled with 70mL of ethylene glycol. Subsequently, the above solution was heated to 300°C under the protection of argon, and the reaction was continued for 1h to form a uniform Black-red solution. After the solution was cooled to room temperature, it was transferred to a 100 mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel reactor, sealed and heated at 200°C for 17 hours. Finally, by magnetic separation and collection, wash with ethanol and ultrapure water sev...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Saturation magnetization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com