New use of rifamycin-quinolizidone dual-target molecule
A technology of rifamycin and quinazinone, which is applied in the field of medicinal chemistry, can solve the problem that no literature records the antibacterial activity of intestinal ammonia-producing flora and the like, and achieve the effects of low resistance frequency, strong antibacterial activity and good application prospect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
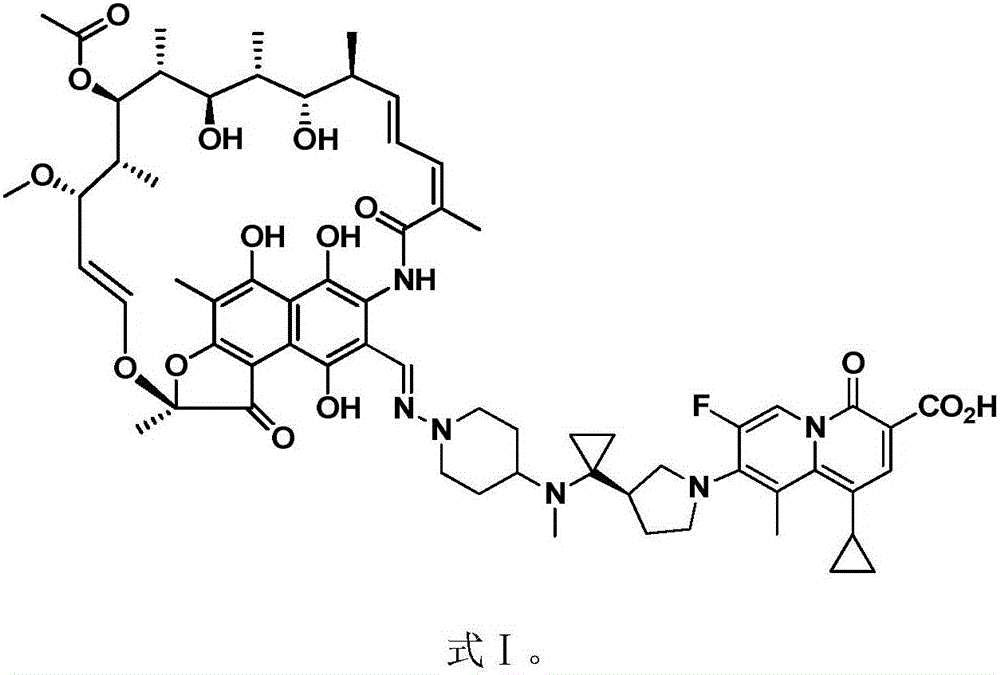
[0019] This embodiment provides the application of the rifamycin-quinazinone dual target molecule represented by formula I in inhibiting ammonia-producing bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract;
[0020]
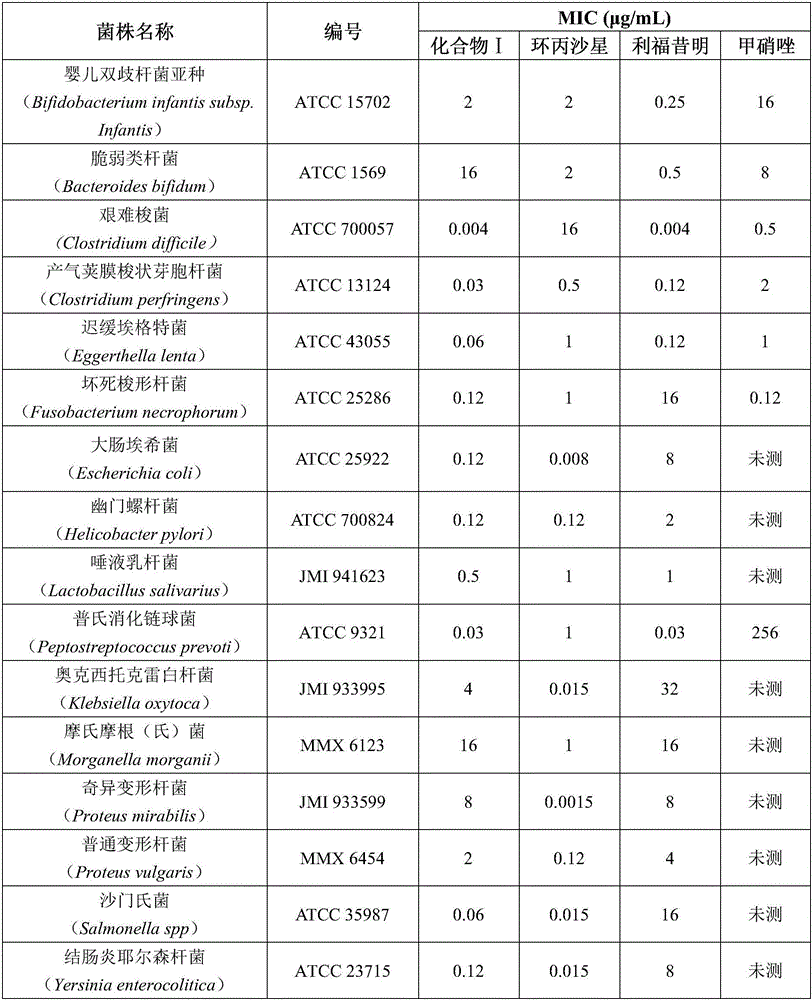
[0021] Wherein, the gastrointestinal ammonia-producing bacteria include Bifidobacterium infantis subsp. infantis, Bacteroides fragilis, Clostridium difficile, Clostridium perfringens, Escherichia lentus, Escherichia coli, Helicobacter pylori, Lactobacillus salivarius, Clostridium necrosis, Peptostreptococcus, Morganella morganii, Proteus vulgaris, Salmonella, and Yersinia colitis are a combination of one or more.
[0022] In this embodiment, compound I rifamycin-quinazinone dual target molecule has done a drug sensitivity test on pathogens related to hepatic encephalopathy, and the pathogens include the above-mentioned ammonia-producing bacteria group. Except for the liquid microdilution method for Haemophilus spp., the tests for other bacteria use the agar dilution method consis...
Embodiment 2
[0044] This embodiment provides a prescription and preparation method for a rapid-release oral preparation of the rifamycin-quinazinone dual target molecule represented by formula I.
[0045]
[0046] Weigh the rifamycin-quinazinone dual target molecule and excipients shown in formula I according to the above-mentioned prescription amount. Dissolve povidone K30 (PVP K30) and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) in purified water, stir for 1 hour, and use as a binder for later use; use the rifamycin-quinazinone dual target shown in formula I The molecules, mannitol and sodium starch glycolate (DST) are passed through a 30-mesh sieve, and are added to the granulator, premixed, and the impeller stirring speed is 700 rpm for about 15 minutes. Then use a peristaltic pump to add an appropriate amount of purified water and binder to the granulator mixture at a fixed speed (145-165g / min). The impeller of the granulator stirs at 400rpm for about 1 to 2 minutes. After the binder is added , Contin...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This embodiment provides a method for preparing an injection of the rifamycin-quinazinone dual target molecule represented by formula I.
[0050]
[0051] Under the protection of nitrogen, add mannitol, sodium acetaldehyde sulfoxylate and Tween-80 to an appropriate amount of water for injection, add the rifamycin-quinazinone dual target molecule shown in formula I, and stir at medium speed for 10-15 minutes. Wetting the rifamycin-quinazinone dual target molecule shown in formula I, slowly dripping with 1N NaOH, which took about 175 minutes (fast before and slow afterwards), to the rifamycin-quinazinone shown in formula I The dual target molecules are completely dissolved, filtered by two 0.45+0.22μm microporous membranes, the filtrate is filled into 10mL glass bottles, each containing 3.5mL, the glass bottles are transferred to the freeze dryer for lyophilization, and the cap is ready to be prepared The freeze-dried powder injection of rifamycin-quinazinone dual target mol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com