Method for quantitatively detecting molds and saccharomycetes in eye masks
A qualitative detection and yeast technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of raw and auxiliary material production environment unable to meet sterility index, enterprise storage, transportation and production efficiency problems, long period from inspection to release, and achieve high specificity. , easy operation, low detection limit effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Specificity Verification
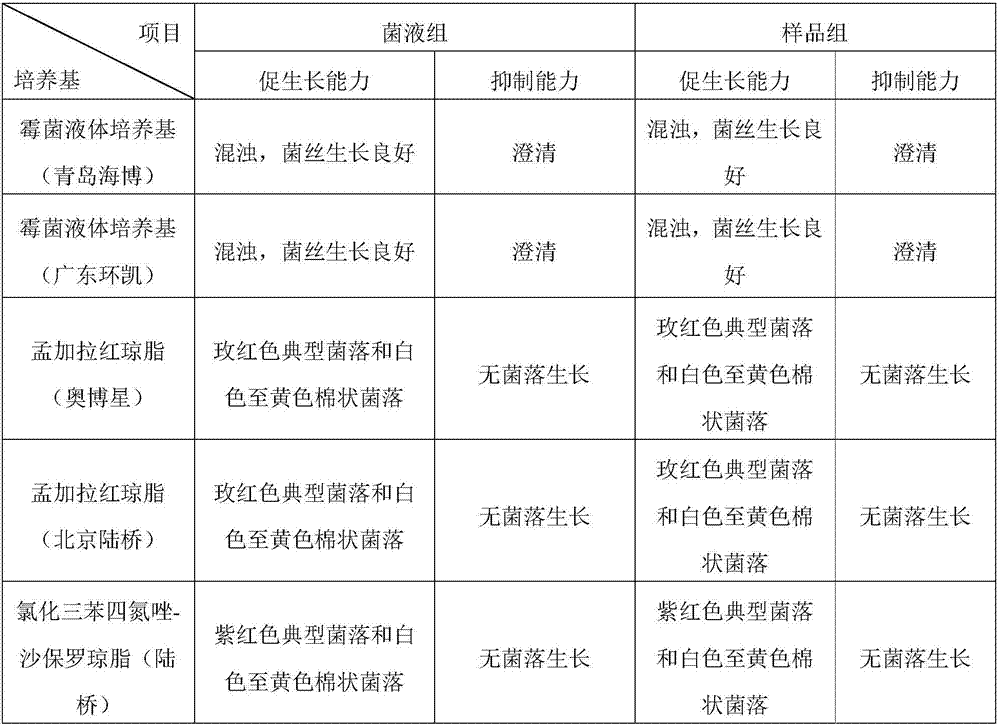
[0036] Take the freshly prepared Candida albicans solution and Aspergillus niger test bacteria solution not greater than 100cfu, and at the same time add Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Bacillus subtilis with a bacterial content greater than 100cfu and mix well. The growth-promoting ability and inhibitory ability of the mold liquid medium, Bengal red agar medium, and triphenyltetrazolium chloride-Sapauer agar medium were tested respectively. At the same time, add the sample and operate with the above method to investigate the influence of the sample. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0037] Table 1 The growth-promoting ability and inhibitory ability of the culture medium
[0038]
[0039] It can be seen from Table 1 that the target bacteria grew well in the selective medium, and the interfering bacteria did not grow, and the addition of samples for interference did not affect the results. It shows that the...
Embodiment 2
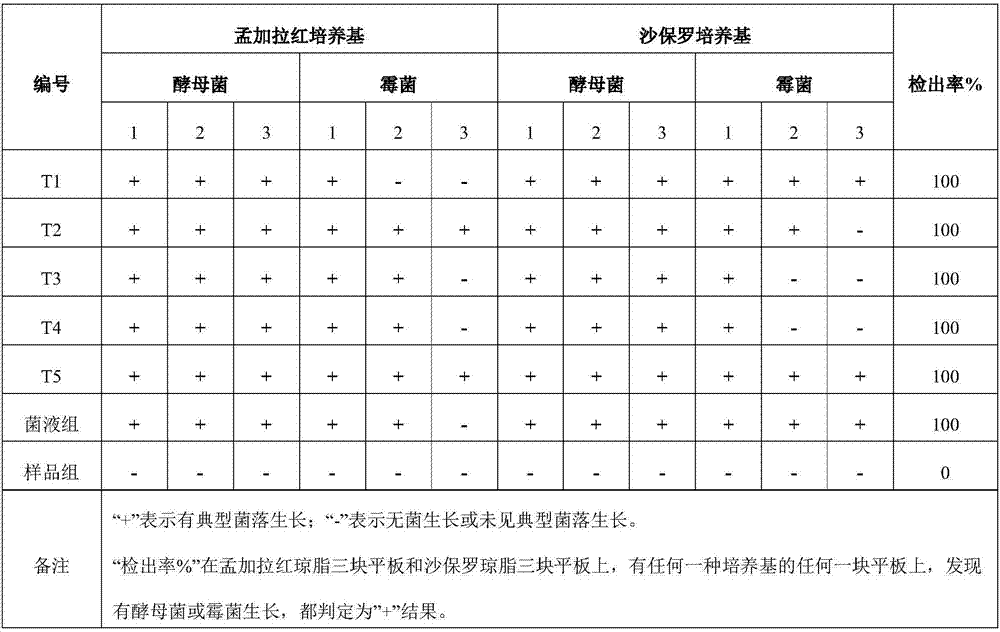
[0040] Embodiment 2: detection limit verification
[0041] Sample preparation: Test group: Weigh 10g sample, add 90mL 0.9% sterile sodium chloride solution, mix well, and make 1:10 (g / g) test solution. At the same time, the Candida albicans bacteria solution and the Aspergillus niger test bacteria solution with a bacterial content of not more than 5cfu (g / mL) were added respectively, and mixed evenly. Bacterial liquid control group: add Candida albicans bacterial liquid and Aspergillus niger test bacterial liquid with a bacterial content not greater than 5cfu (g / mL) to 90mL 0.9% sterile sodium chloride solution, and mix well. Sample group: Weigh 10g sample, add 90mL 0.9% sterile sodium chloride solution to make 1:10 (g / g) test solution.
[0042] Separation of bacteria enrichment: take 10mL of the above-mentioned homogeneous solution, add 90mL mold liquid culture medium, incubate at 28°C±1°C for 3 days, take 2mL of the homogeneous solution, mix thoroughly with a vortex mixer, ...
Embodiment 3
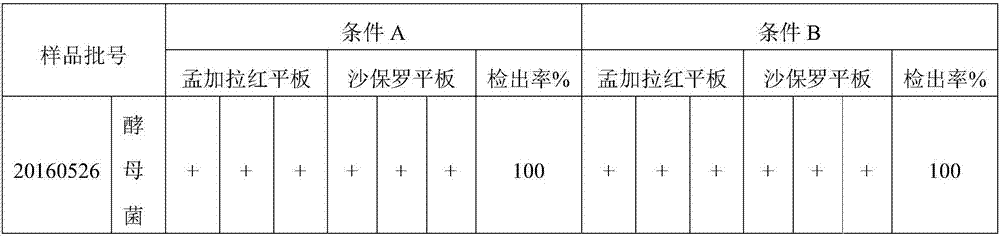
[0047] Example 3: Reproducibility Verification
[0048] Take samples of the same batch number, and change the experimental conditions (experimental location, experimenter, instrument, medium batch) for the test. At the same time, five batches of samples were selected for testing.
[0049] Condition A: Room 910, HFsafe-1200LC biological safety cabinet, Shanghai Lishen Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.; mold liquid culture medium, Qingdao High-tech Industrial Park Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch number: 20160730; Bengal red agar medium, Beijing Land Bridge Technology Co., Ltd., batch number: 160628; triphenyltetrazolium chloride-Sapauer culture medium, Beijing Land Bridge Technology Co., Ltd., batch number: 161009;
[0050] Condition B: Room 910, HFsafe 760S biological safety cabinet, Shanghai Lishen Scientific Instrument Co., Ltd.; mold liquid culture medium, Guangdong Huankai Biotechnology Co., Ltd., batch number: 3104619; Bengal red agar medium, Beijing Aoboxing Biotechno...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com