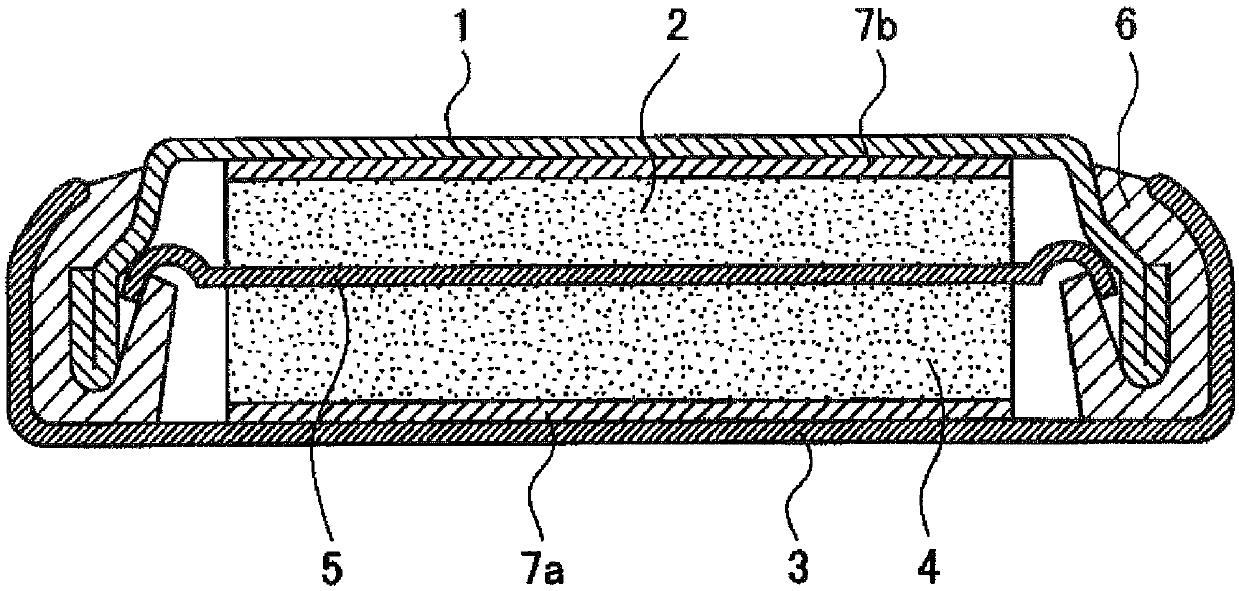
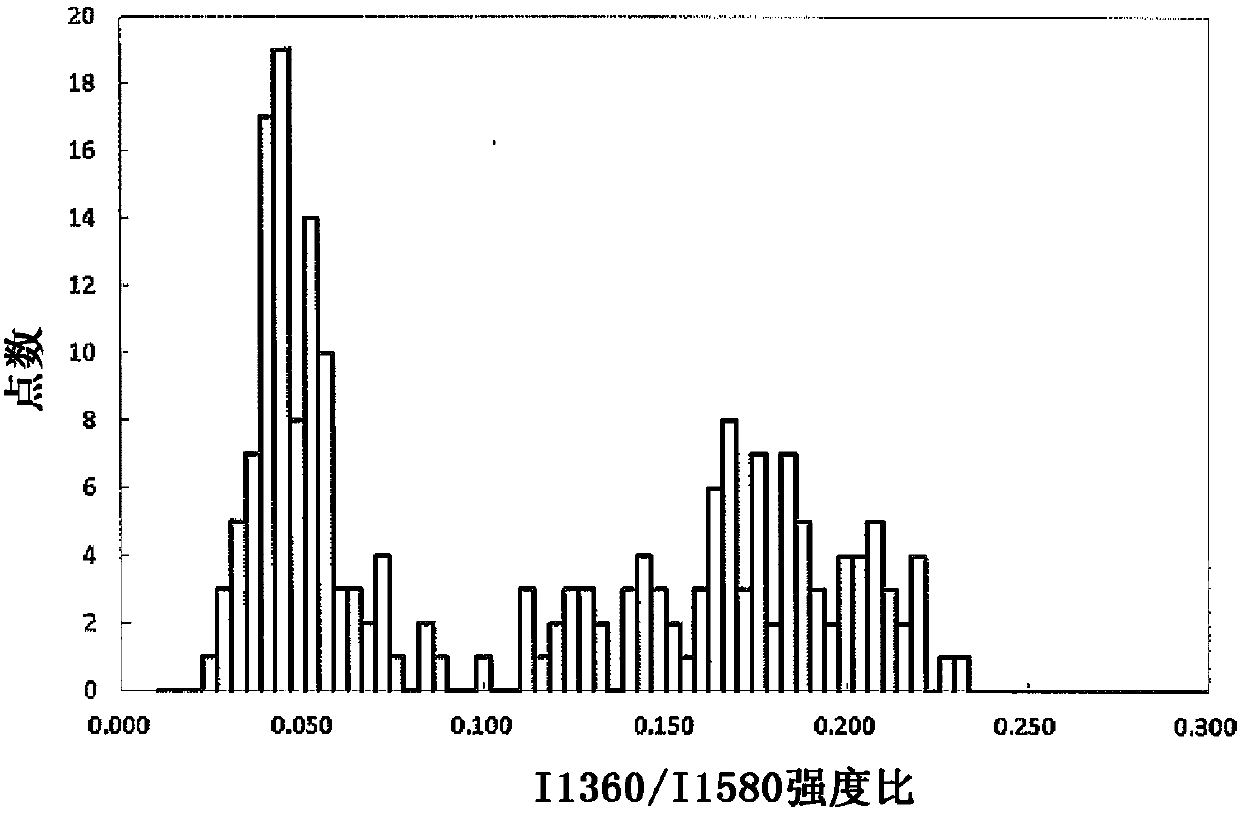
Graphite particles for lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode materials, lithium ion secondary battery negative electrode and lithium ion secondary battery
A secondary battery and negative electrode material technology, applied in the direction of secondary batteries, battery electrodes, graphite, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient fast charging, low initial charge and discharge efficiency, and insufficient discharge capacity, and achieve excellent initial charge and discharge efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0138] [Preparation of spheroidized graphitic particles (A)]
[0139] Flake natural graphite with an average particle diameter of 55 μm was pulverized, and folded while being rotated, shaped into a spherical shape, adjusted to an average particle diameter of 12 μm, and an average aspect ratio of 1.4, (d 002 ) is 0.3357nm, specific surface area is 7.0m 2 / g, and the volume of pores with a pore diameter of 0.5 μm or less obtained by mercury porosimetry is 0.12 ml / g.
[0140] Using a molding machine at 0.5 tons / cm 2 The pressure of this spherical graphitic particle is carried out compression treatment, is adjusted to be 12 μ m in average particle diameter, and average aspect ratio is 1.8, (d 002 ) is 0.3357nm, specific surface area is 6.5m 2 / g, and the volume of pores with a pore diameter of 0.5 μm or less obtained by mercury porosimetry is 0.08ml / g.
[0141] [Preparation of Composite Graphite Particles (C1)]
[0142] With 100 parts by mass of the above-mentioned spheroidiz...
Embodiment 2~5
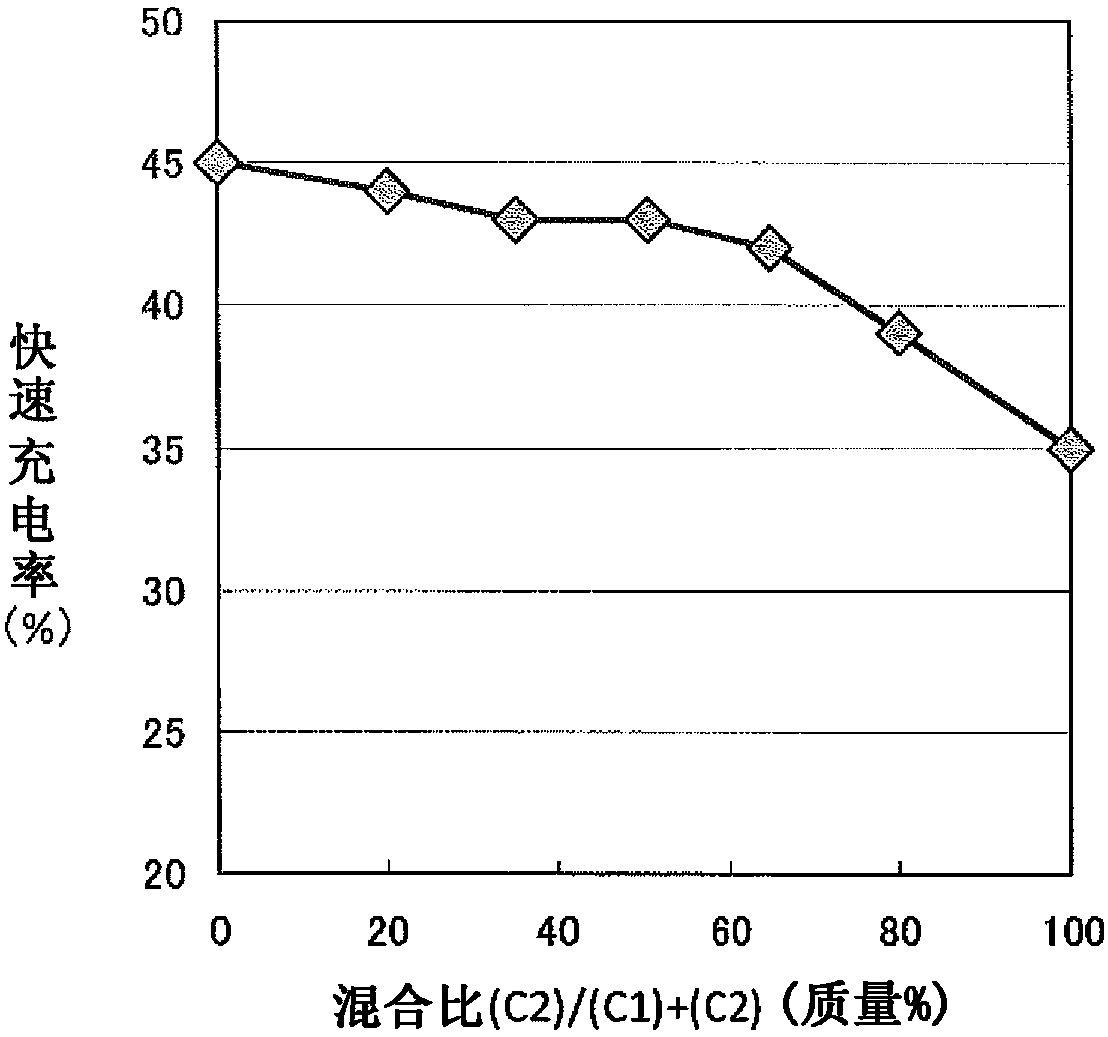
[0184] In Example 1, the mixing ratio of the composite graphite particles (C1) and the composite graphite particles (C2) was changed. In addition, the pressurized pressure was changed in the same manner as in Example 1, and the density of the negative electrode mixture layer was adjusted to 1.75. g / cm 3 , making the working electrode and making the evaluation cell. The same charge and discharge test as in Example 1 was performed, and the evaluation results of battery characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 6
[0189] In Example 1, the density of the negative electrode mixture layer was changed to 1.80g / cm 3 (Example 6) Except for this, a working electrode was produced in the same manner as in Example 1, and an evaluation cell was produced. The same charge and discharge test as in Example 1 was performed, and the evaluation results of battery characteristics are shown in Table 1.
[0190] The more you increase the density of the negative electrode mixture layer, the more the characteristics of each battery tend to decrease, but at a density of 1.80g / cm 3 maintained at a sufficiently high standard. On the other hand, if the density is increased too much, the deformation of the copper foil serving as the current collector and the decrease in battery characteristics will become significant.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pore volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com