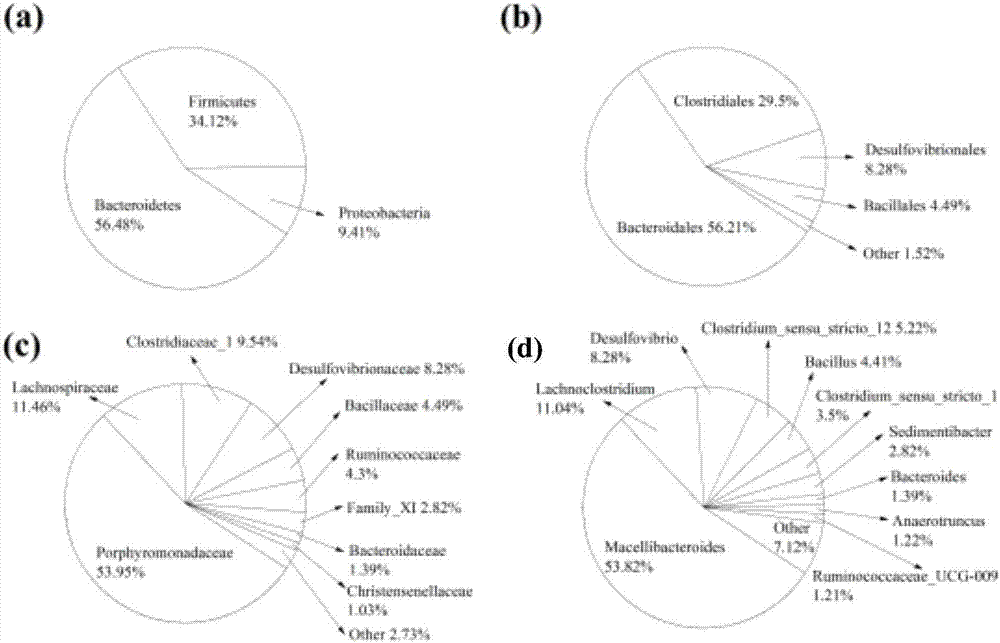
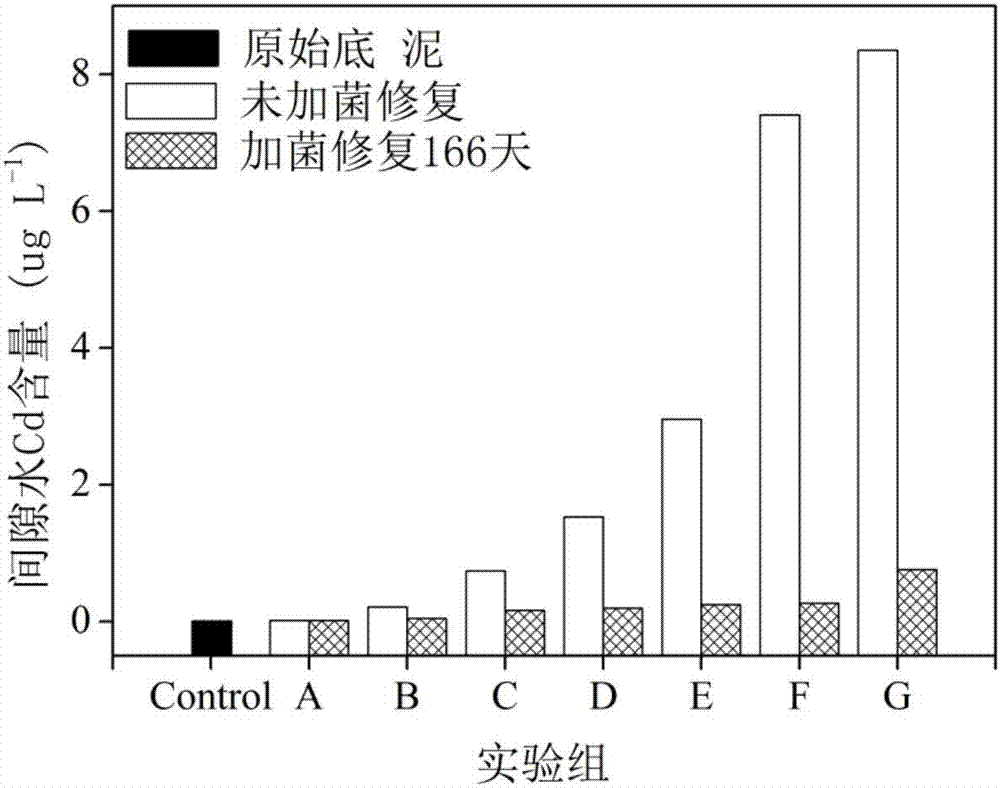
Microbial remediation method for cadmium-polluted bottom mud
A technology for microbial remediation and cadmium pollution, applied in the restoration of polluted soil, etc., can solve the problems of rare heavy metal pollution sediment restoration research, poor composite pollution restoration effect, and poor field test effect, etc. Small, low cost, low mobility effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The microbial remediation method of Cd polluted bottom mud is provided in the present embodiment, specifically comprises the following two steps:
[0043] Step 1: Enrichment, domestication and expansion of sulfate-reducing bacteria
[0044] (1) Medium: KH 2 PO 4 0.5g / L, NH 4 Cl 1g / L, CaSO 4 1g / L, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 2g / L, lactic acid 3.5g / L, yeast extract 1g / L, ascorbic acid 0.1g / L, thioglycolic acid 0.1g / L, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.5g / L, ultrapure water 1L, adjust the pH between 7.0 and 7.5.
[0045] (2) Strain enrichment: pick 2g of reservoir natural sediment samples, put them into a 50mL stoppered glass tube, add 9mL of 0.75% (mass percentage concentration) of normal saline to obtain 10 -1diluent. After shaking well, draw 2mL of the bottom mud dilution and add it into a sterilized Erlenmeyer flask containing 300mL of medium. Seal the Erlenmeyer flask with parafilm, and place it in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C for cultivation. After 2 to 3 days, it will be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com