A kit and method for separating free nucleic acid in peripheral blood using magnetic microspheres
A technology of magnetic microspheres and free nucleic acid, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological measurement/testing, DNA preparation, etc., can solve the problems of low degree of automation and high-throughput operation, low extraction efficiency of free nucleic acid, and difficulty in clinical use Large and other problems, to achieve the effect of high-throughput automatic operation, improve extraction and separation efficiency, efficient rinsing and elution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
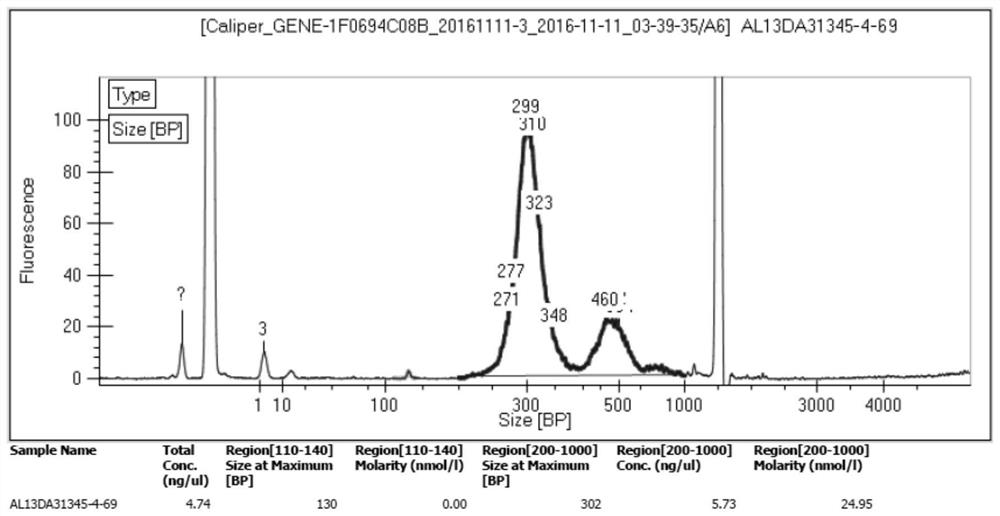
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1 Separation of Free Nucleic Acids in Plasma Samples Using Magnetic Microspheres
[0029] ① Add 200 μL plasma sample to a nuclease-free centrifuge tube, then add 450 μL lysis buffer to the centrifuge tube and mix well, then add 20 μL proteinase K, blow with a pipette or turn it upside down until fully mixed until uniform, And keep it for 10min to obtain the lysed sample;
[0030] ② Add 100 μL of binding buffer and 30 μL of nucleic acid binding reagent to the lysed sample, the nucleic acid binding reagent contains conjugated Oligo(dT) 25 Aqueous solution of magnetic microspheres and non-specific capture probes with Poly-A, which is coupled with Oligo(dT) 25 The concentration of magnetic microspheres is 0.1-5mg / mL, and Oligo(dT) is coupled to the magnetic microspheres 25 The amount is 50-200nmol / g, and the concentration of non-specific capture probes with Poly-A is 0.5-5nmol / mL. Use a pipette to blow or mix upside down. Let stand at room temperature for 20min. ...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2 Separation of Free Nucleic Acids in Serum Samples Using Magnetic Microspheres
[0035] ① Add 150 μL serum sample to a nuclease-free centrifuge tube, then add 400 μL lysis buffer to the centrifuge tube and mix well, then add 15 μL proteinase K, blow with a pipette or turn it upside down until fully mixed until uniform, And keep it for 6 minutes to get the lysed sample;
[0036] ② Add 100 μL of binding buffer and 35 μL of nucleic acid binding reagent to the lysed sample. The nucleic acid binding reagent is an aqueous solution containing magnetic microspheres coupled with Oligo(dT)25 and non-specific capture probes with Poly-A. Mix evenly by suction or upside down, and let stand at room temperature for 15 minutes. Place the centrifuge tube on the magnetic stand for 1 minute. At this time, the magnetic microspheres are enriched on the magnet and separated from the supernatant. The supernatant is discarded by suction. Obtain the magnetic bead-nucleic acid complex,...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3 Separation of Free Nucleic Acids in Plasma Samples Using Magnetic Microspheres
[0040] ① Add 100 μL plasma sample to a nuclease-free centrifuge tube, then add 400 μL lysis buffer to the centrifuge tube and mix well, then add 15 μL proteinase K, blow with a pipette or turn it upside down until fully mixed until uniform, And keep it for 10min to obtain the lysed sample;
[0041] ② Add 80 μL of binding buffer and 20 μL of nucleic acid binding reagent to the lysed sample, the nucleic acid binding reagent contains conjugated Oligo(dT) 25 The aqueous solution of the magnetic microspheres and the non-specific capture probes with Poly-A was mixed evenly with a pipette or upside down, and left to stand at room temperature for 15 minutes, and the centrifuge tube was placed on a magnetic stand for magnetic adsorption for 1 minute Aspirate and discard the supernatant to obtain the magnetic bead-nucleic acid complex, in which the sequence of the non-specific capture prob...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com