A strain of Streptomyces albus and its application in pesticides
A technology of Streptomyces albicans and microbial pesticides, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of poor fermentation performance of strains and poor field test results, and achieve the effect of inhibiting germination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Isolation, Identification and Biological Characterization of Streptomyces microalbicans W68 for Controlling Soilborne Fungal Diseases
[0052] 1. Isolation and purification of Streptomyces microalbicans W68 for the control of soil-borne fungal diseases
[0053] In this experiment, several strains of actinomycetes were isolated from marine activated sludge. The process is as follows: add 1g of sample to a sterilized 300ml Erlenmeyer flask filled with small glass beads and 99ml of sterile saline, and incubate on a shaker at 28°C for 1h . Take 1 ml suspension and dilute to 10 by gradient dilution method -4 , take stock solution, 10 -2 Diluent and 10 -4 The dilution solution was coated with potassium dichromate at a final concentration of 50ug / ml Gaoshi No. 1 medium, and single colonies were picked on the 5th day, 7th day and 10th day, and then streaked on the PDA medium for purification and isolation.
[0054] The resulting purified strain was stored at -80°C with 20%...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Antifungal activity test of Streptomyces albus W68 isolated from deep-sea sludge to control soil-borne fungal diseases
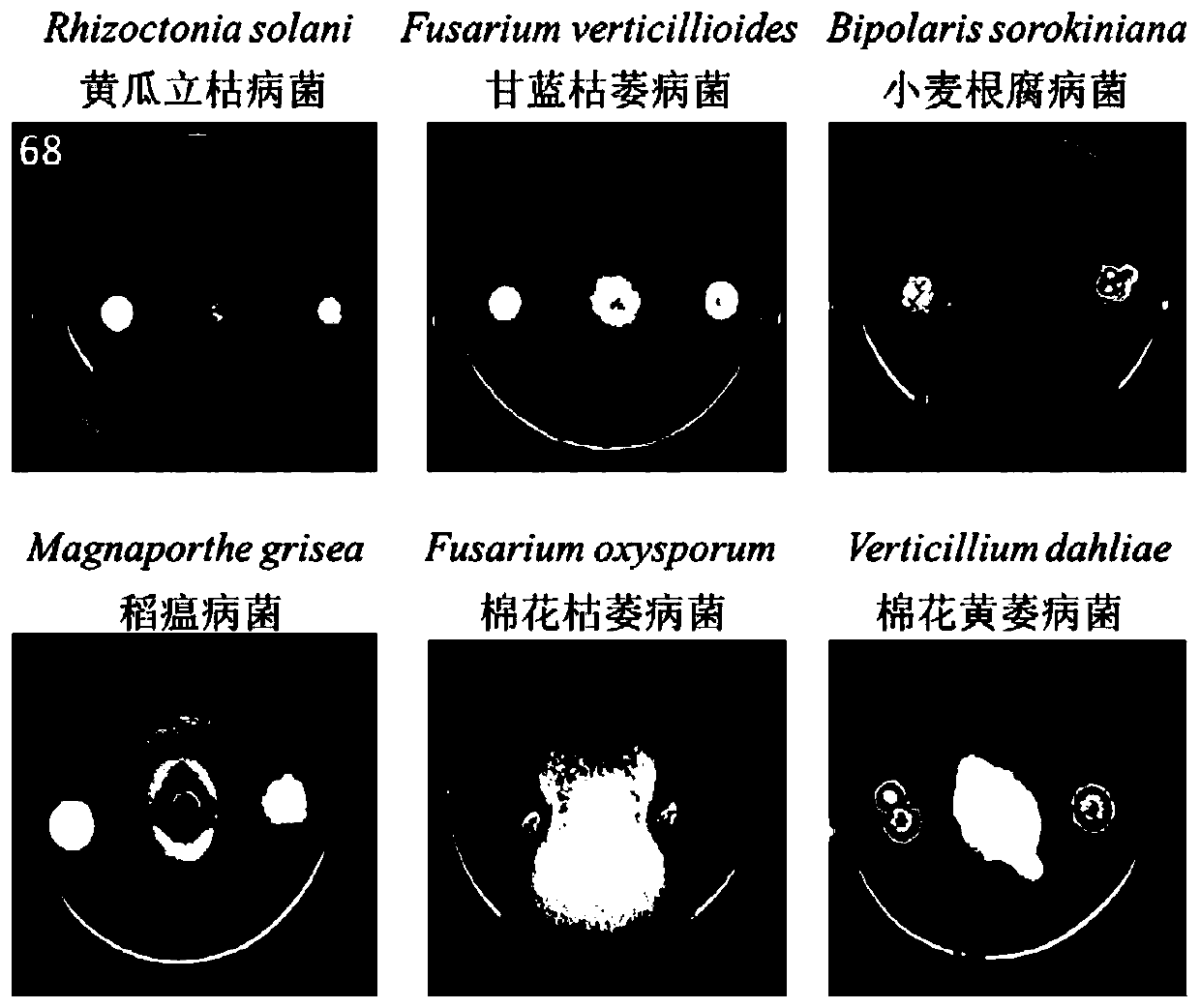
[0073] Determination of the antifungal activity of Streptomyces albus W68 for the control of soil-borne fungal diseases by plate confrontation method:
[0074] (1) Strain cultivation and collection: Streptomyces albiflous W68 for the prevention and treatment of soil-borne fungal diseases is inoculated on a PDA plate by streaking method, cultivated at 28°C for 5-7 days until sufficient spores are produced; scrape the spores into appropriate amount of sterile water Make a spore suspension for later use.
[0075] (2), the cultivation of pathogenic bacteria: inoculate cucumber blight, cabbage wilt, wheat root rot, rice blast fungus, cotton fusarium wilt, and cotton Verticillium dahliae on the PDA plate, and use it after cultivating for one week at 28°C.
[0076] (3), plate confrontation experiment: respectively inoculate the bacterial block of pathogenic...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Chitinase activity test of Streptomyces albus W68 isolated from deep-sea sludge to control soil-borne fungal diseases
[0079] (1) Preparation of colloidal chitin: Weigh 10 g of chitin sample, slowly add 200 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid (operated in a fume hood), and stir evenly while adding. After standing at 4 degrees for 24 hours, use glass wool to filter into 600ml of pre-cooled 50% ethanol, and continue to stand at 4 degrees for 24 hours. Next, centrifuge at 3000rpm for 20min*3 times, wash with water to neutral pH, and finally dissolve in 200ml of water. Made into 5% colloidal chitin, adjusted the pH to neutral with NaOH, sterilized under high temperature and high pressure at 115°C for 20min, and stored in the dark at 4°C.
[0080] (2) Determination of chitinase activity: Pick a single colony from the W68 strain that has been grown on PDA medium for 5-7 days, and inoculate it into 0.4% chitin with chitin as the only carbon source for screening On the petr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com