Preparation process of ammonium ferric citrate
A kind of ferric ammonium citrate, the technology of preparation process, applied in the direction of carboxylate preparation, carboxylate preparation, organic compound preparation and other directions, can solve the problems of insoluble matter, dehydration difficulty, foaming and the like, and achieve the improvement of product yield, The effect of avoiding dehydration difficulty and improving solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
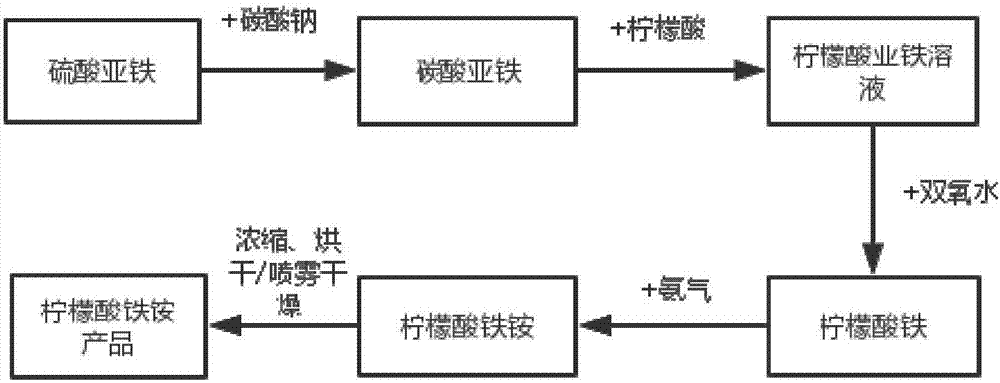
[0025] Step 1: 100g of ferrous sulfate is added to 500mL of water, stirred and dissolved to obtain ferrous sulfate aqueous solution,
[0026] Step 2: Slowly add 150mL aqueous solution containing 50g of sodium carbonate into the ferrous sulfate solution, fully react for 1-2h at room temperature, and react to generate ferrous carbonate.
[0027] Step 3: Suction filtration, wash the precipitate with water until no sulfate ion is detected, add water and stir evenly, then add 100g of citric acid to the above precipitate, stir for 1-2h,
[0028] Step 4: Add hydrogen peroxide to oxidize until there is no ferrous ion, then add ammonia water or pass through ammonia gas, stir the reaction to adjust the pH to 6-8, and then react for 0.5-1h,
[0029] Step 5: Heating and concentrating to 1 / 2 of the volume, cooling, adding ammonia water or introducing ammonia gas.
[0030] Step 6: drying at 130-150°C or spray-drying at 190-200°C to obtain ferric ammonium citrate product.
Embodiment 2
[0032] Step 1: 150g of ferrous sulfate is added to 800mL of water, stirred and dissolved to obtain ferrous sulfate aqueous solution,
[0033] Step 2: Then slowly add 150mL aqueous solution containing 50g of sodium carbonate into the ferrous sulfate solution, fully react for 1-2h at room temperature, and react to generate ferrous carbonate.
[0034] Step 3: Suction filtration, wash the precipitate with water until no sulfate ion is detected, add water and stir evenly, then add 150g citric acid to the above precipitate, stir for 1-2h,
[0035] Step 4: Add hydrogen peroxide to oxidize until there is no ferrous ion, add ammonia water or pass through ammonia gas, stir the reaction to adjust the pH to 6-8, and then react for 0.5-1h,
[0036] Step 5: Heating and concentrating to 1 / 3 of the volume, cooling, adding ammonia water or introducing ammonia gas.
[0037] Step 6: drying at 130-150°C or spray-drying at 190-200°C to obtain ferric ammonium citrate product.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Step 1: 110g of ferrous sulfate is added to 600mL of water, stirred and dissolved to obtain an aqueous solution of ferrous sulfate,
[0040] Step 2: Then slowly add 150mL aqueous solution containing 50g of sodium carbonate into the ferrous sulfate solution, fully react for 1-2h at room temperature, and react to generate ferrous carbonate.
[0041] Step 3: Suction filtration, wash the precipitate with water until no sulfate ion is detected, add water and stir evenly, then add 110g of citric acid to the above precipitate, stir for 1-2h,
[0042] Step 4: Add hydrogen peroxide to oxidize until there is no ferrous ion, add ammonia water or pass through ammonia gas, stir the reaction to adjust the pH to 6-8, and then react for 0.5-1h,
[0043] Step 5: Heating and concentrating to 1 / 4 of the volume, cooling, adding ammonia water or introducing ammonia gas.
[0044] Step 6: drying at 130-150°C or spray-drying at 190-200°C to obtain ferric ammonium citrate product.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com