Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
A semiconductor and silicon carbide technology, which is applied to trench gate type silicon carbide semiconductor devices and their manufacturing fields, can solve the problems of high dielectric breakdown strength, electric field concentration, damage to gate insulating films, etc., so as to improve the avalanche breakdown voltage. , The effect of high device withstand voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
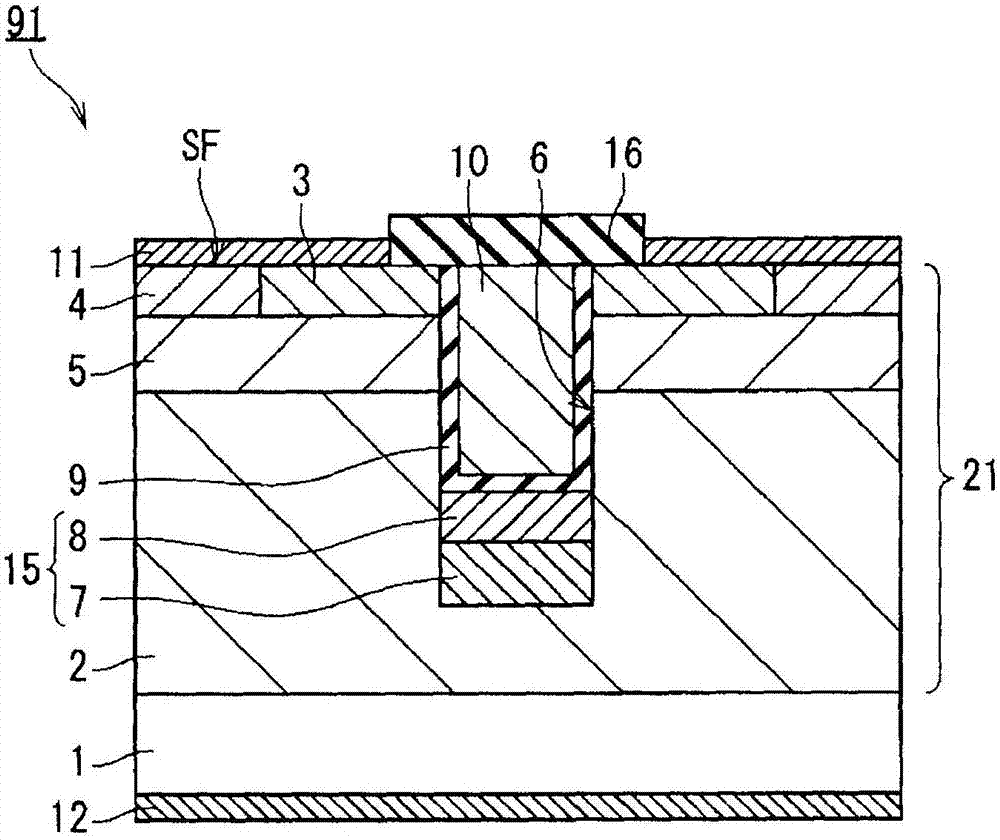
[0041] figure 1 It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing a cell structure of MOSFET 91 (silicon carbide semiconductor device) according to this embodiment. MOSFET 91 has substrate 1 (semiconductor substrate), semiconductor layer 21 , gate oxide film 9 (gate insulating film), gate electrode 10 , source electrode 11 , drain electrode 12 , and interlayer insulating film 16 .
[0042] The substrate 1 is an n-type (first conductivity type) silicon carbide semiconductor substrate. The plane orientation of the substrate 1 may be, for example, any plane orientation such as (0001) plane, (000-1) plane, or (11-20) plane. In addition, a substrate provided with an off angle (of angle) in each plane orientation may also be used.
[0043] The semiconductor layer 21 is formed of silicon carbide. The semiconductor layer 21 is an epitaxial layer on the substrate 1 . The semiconductor layer 21 has an n-type drift layer 2 provided on the substrate 1, a p-type (second conductivity t...
Embodiment approach 2
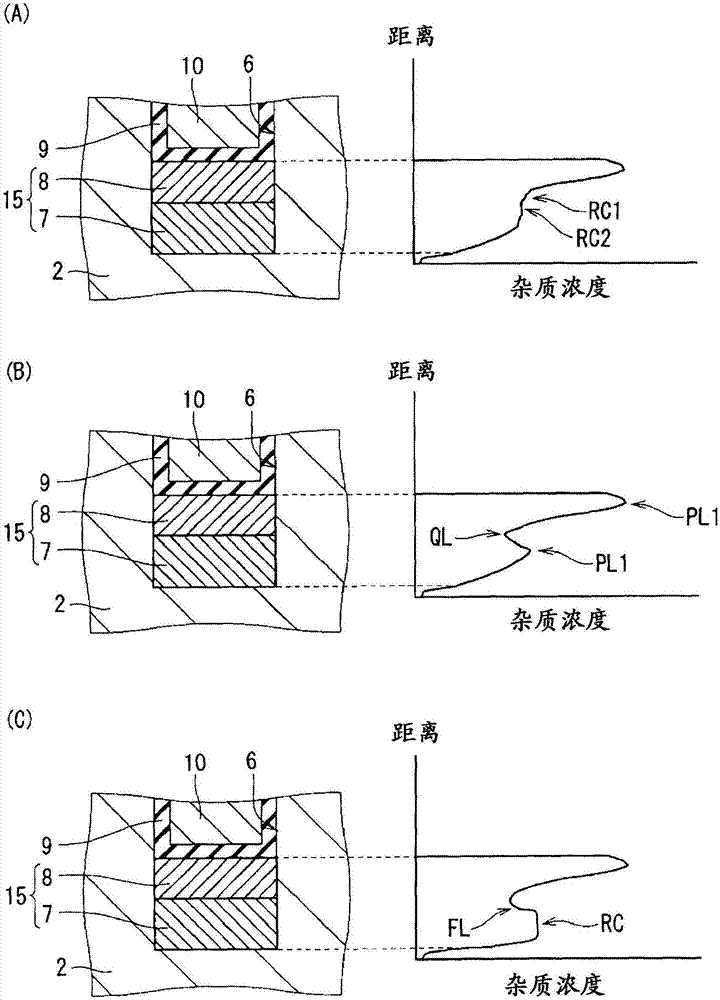
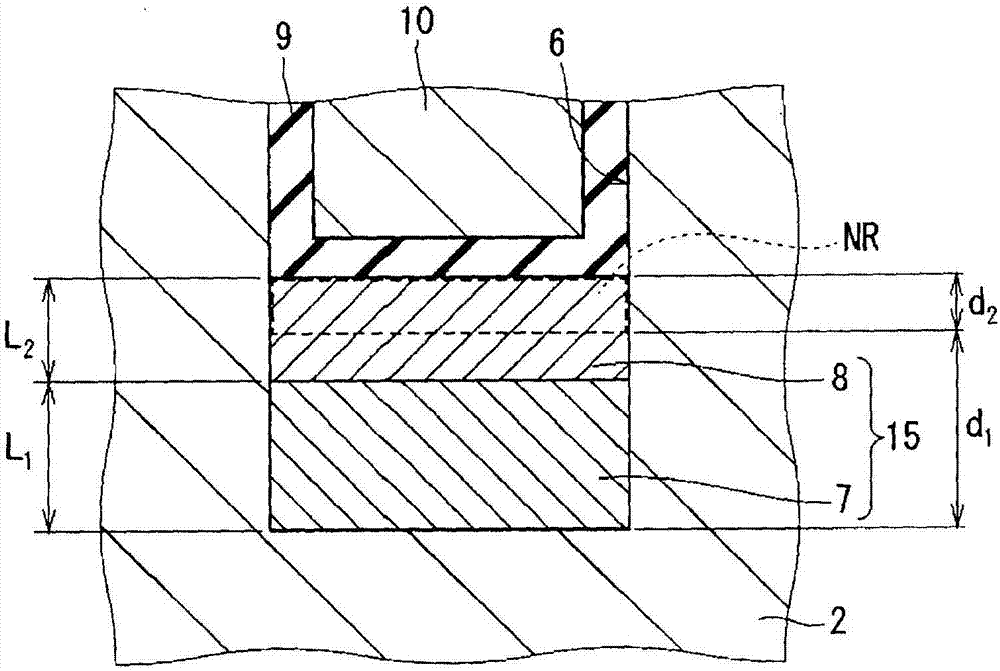
[0096] Figure 14 It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing a cell structure of MOSFET 92 (silicon carbide semiconductor device) according to this embodiment. In this embodiment, compared with Embodiment 1, the structure of trench bottom surface protection layer 15 is different. Specifically, in the trench bottom protective layer 15 of the MOSFET 92 , the width of the low-concentration protective layer 7 is smaller than the width of the high-concentration protective layer 8 . Therefore, the low-concentration protective layer 7 forms only a part of the bottom surface of the trench bottom surface protective layer 15 (in the figure, the central portion of the bottom surface), and the high-concentration protective layer 8 forms the other part of the bottom surface of the trench bottom surface protective layer 15 (in the figure). middle, both ends of the bottom surface). It should be noted that configurations other than those described above are substantially the same as...
Embodiment approach 3
[0105] Figure 16 It is a cross-sectional view schematically showing a cell structure of MOSFET 93 (silicon carbide semiconductor device) according to this embodiment. In this embodiment, compared with Embodiment 1, the structure of trench bottom surface protection layer 15 is different. Specifically, in the trench bottom protective layer 15 of the MOSFET 93 , the width of the low-concentration protective layer 7 is larger than the width of the high-concentration protective layer 8 . It should be noted that configurations other than those described above are substantially the same as those of Embodiment 1 described above, and therefore description thereof will not be repeated.
[0106] Next, a method of manufacturing MOSFET 93 will be described below.
[0107] refer to Figure 17A first drift layer 2 a (first layer) made of silicon carbide and having an n-type is formed on the substrate 1 . It should be noted that the method of forming the first drift layer 2a can be compa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com