Small peptide with function of resisting against clinic multiple resistant bacteria, derivative and application thereof
A technology of multi-drug resistant bacteria and derivatives, applied to small peptides and their derivatives and application fields, can solve the problems of antibacterial peptide hemolytic side effects, low antibacterial activity, hemolytic side effects, etc. effect, the effect of improving the survival rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Solid Phase Synthesis of Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Derivatives
[0034] Antimicrobial peptides were synthesized by solid-phase synthesis using FMOC (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl) as a protecting group. It was cleaved from the resin with 95% trifluoroacetic acid, 2.5% water and 2.5% triisopropylsilane (TIA). After repeated precipitation with diethyl ether, the polypeptide was purified by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. A C18 reverse-phase column was used in the purification: 0%-60% acetonitrile containing 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid was used as the mobile phase, and gradient elution was performed at a flow rate of 3 mL / min. Then the peptide was dissolved in oxidation buffer (100 mmol / L ammonium acetate, pH 8.5) at a concentration of 1 mg / mL, and stirred continuously at room temperature for 3 days to fully oxidize and fold to form disulfide bonds. Finally, it was purified to over 95% by reverse-phase HPLC and freeze-dried for use. C-terminally...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Determination of Antibacterial Activity
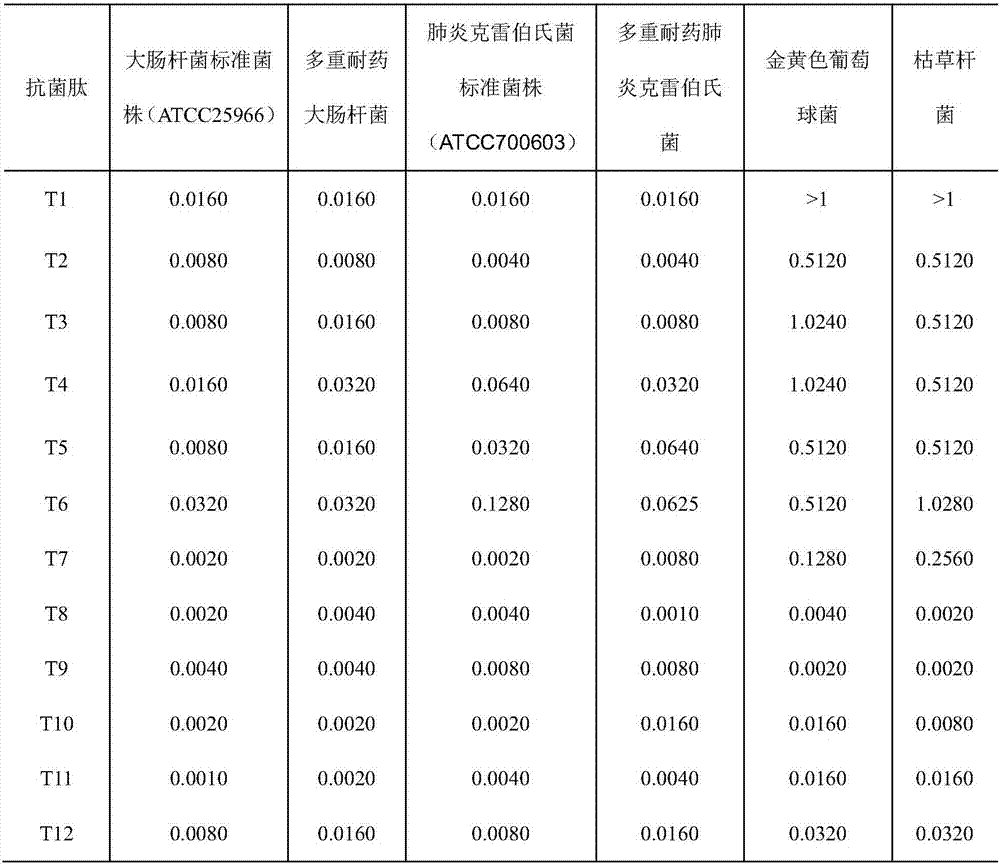
[0037] A polypeptide sample solution with a concentration of 6 mg / mL was prepared with sterilized physiological saline. The bacteria used in the test were inoculated in the nutrient broth, cultured at 37°C for 24 hours, diluted 1:105 times with sterile saline before use, and 12 bacterial culture tubes were taken and numbered, and nutrient meat was added to the first tube Add 1.8mL broth, and add 1.0mL broth to the remaining 11 tubes. Add 0.2mL of polypeptide solution to the first tube, mix well, take out 1.0mL and add it to the second tube, repeat this process, and dilute to the 12th tube in turn, add 0.2mL of bacterial solution to each tube, shake gently, place at 37 Cultivate for 24 hours. The lowest concentration of peptides for sterile growth is the minimum sample concentration (MIC) that inhibits bacterial growth. Table 1 shows the minimum inhibitory concentrations of antimicrobial peptide derivatives prepared in Example...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Determination of polypeptide hemolytic activity:
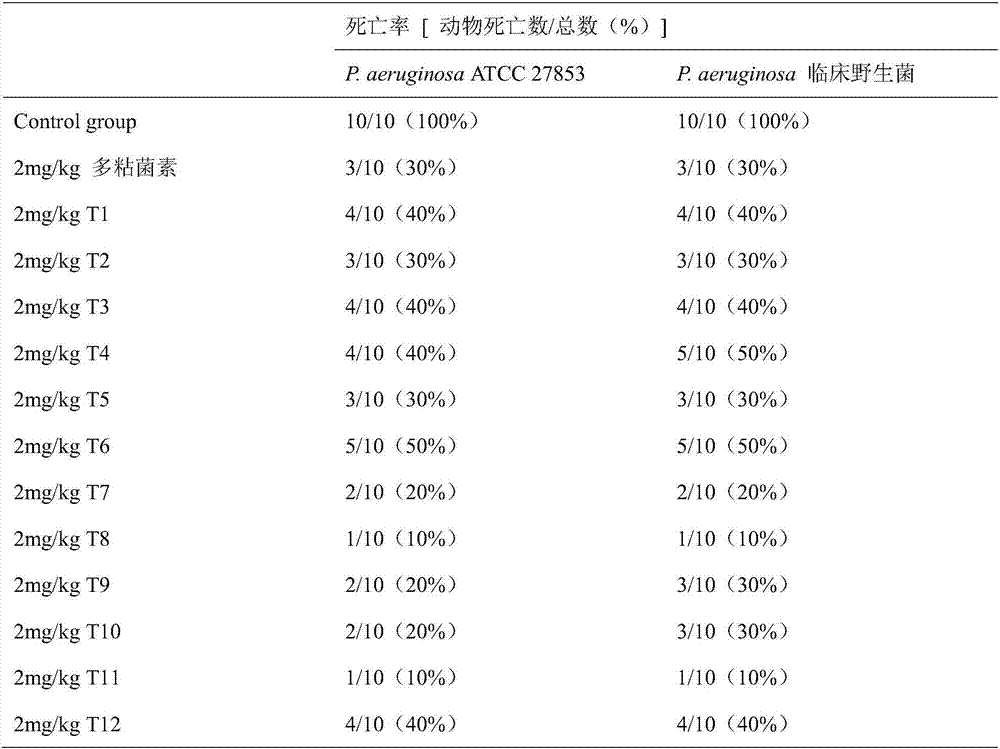
[0042]Human red blood cells were suspended in phosphate buffer (pH 7.4) to obtain red blood cell suspension (5% v / v). Dissolve the peptide in phosphate buffer to make about 5mg / mL stock solution, take 14 1.5mL centrifuge tubes, add 1mL peptide stock solution to the first centrifuge tube, add 0.5mL phosphate buffer to the other tubes solution, take 0.5mL peptide stock solution from the first tube and add it to the second tube, mix evenly with a micro mixer, then take 0.5mL solution from the second tube, add it to the third tube and mix evenly, and so on, That is, dilute to the 14th tube sequentially by doubling dilution method, discard 0.5mL, add 0.5mL prepared 5% red blood cell suspension to each tube until the final volume is 1.0mL, shake gently, and incubate in a 37°C incubator After 60 min, it was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 10 minutes, and the supernatant was taken for colorimetry at 414 nm. Red blood cells suspend...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com