Method for extracting wheat bran protein through two-step enzymolysis
A wheat bran and enzymatic hydrolysis technology is applied in the field of bioengineering, which can solve the problems of unsuitable large-scale production, high extraction process cost, and many protein impurities, and achieves the advantages of saving consumption, reducing energy consumption and reducing substrate concentration. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
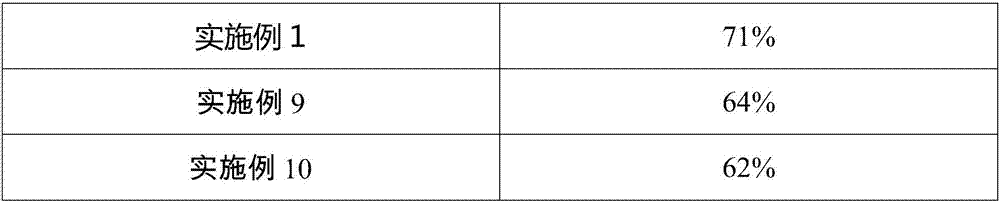
[0020] (1) Take the wheat bran residue after removing the starch, add deionized water to adjust the mash concentration to 15%, adjust the pH of the slurry to 5.5 and the temperature to 50°C with hydrochloric acid with a mass fraction of 5%, based on the weight of the wheat bran residue The total mass was added to the cell wall-breaking enzyme, and the added amount was 0.2%, and the pretreated wheat bran slurry was obtained after reacting for 2 hours.
[0021] (2) adding distilled water to the slurry obtained in step (1) in step (1) to adjust the slurry again until the mash concentration is 10%, and adjusting the pH to 8.0 with a mass concentration of 4% sodium hydroxide solution, setting the temperature At 80°C, based on the total weight of wheat bran, Novozymes’ Alcalase 2.4L FG was added in an amount of 2.0%, centrifuged after reaction 2, and the centrifugal speed was 4000rpm. The supernatant is concentrated and freeze-dried to obtain the gluten protein product.
Embodiment 2
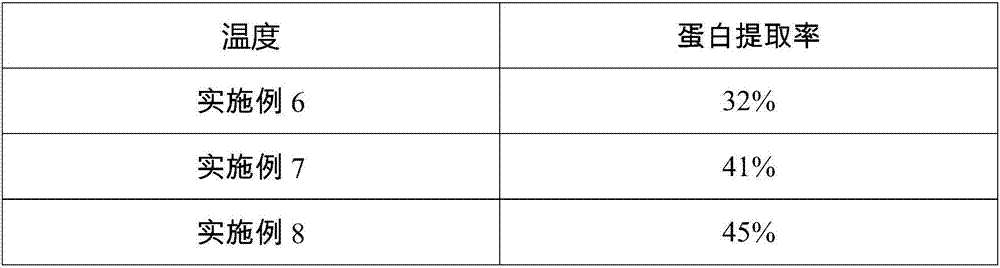
[0023] Except that the mash concentration in step (1) was set to 10%. Gluten was extracted in the same manner as in Example 1. The results are shown in Table 1, the protein extraction rate of step (1) was 3%.
Embodiment 3
[0025] Except that the mash concentration in step (1) is set to 20%. Gluten was extracted in the same manner as in Example 1. Result is as shown in table 1, and the protein extraction rate of step (1) is 4.7%
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com