A low-temperature molten salt electrolytic clean metallurgy method and device for bismuth
A low-temperature molten salt and electrolysis device technology, applied in the direction of cells, can solve the problems of difficult expansion of processing capacity, small production scale, and heavy secondary pollution, so as to promote the progress of bismuth metallurgy technology, reduce the temperature of pyrometallurgy, and promote energy saving The effect of emission reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
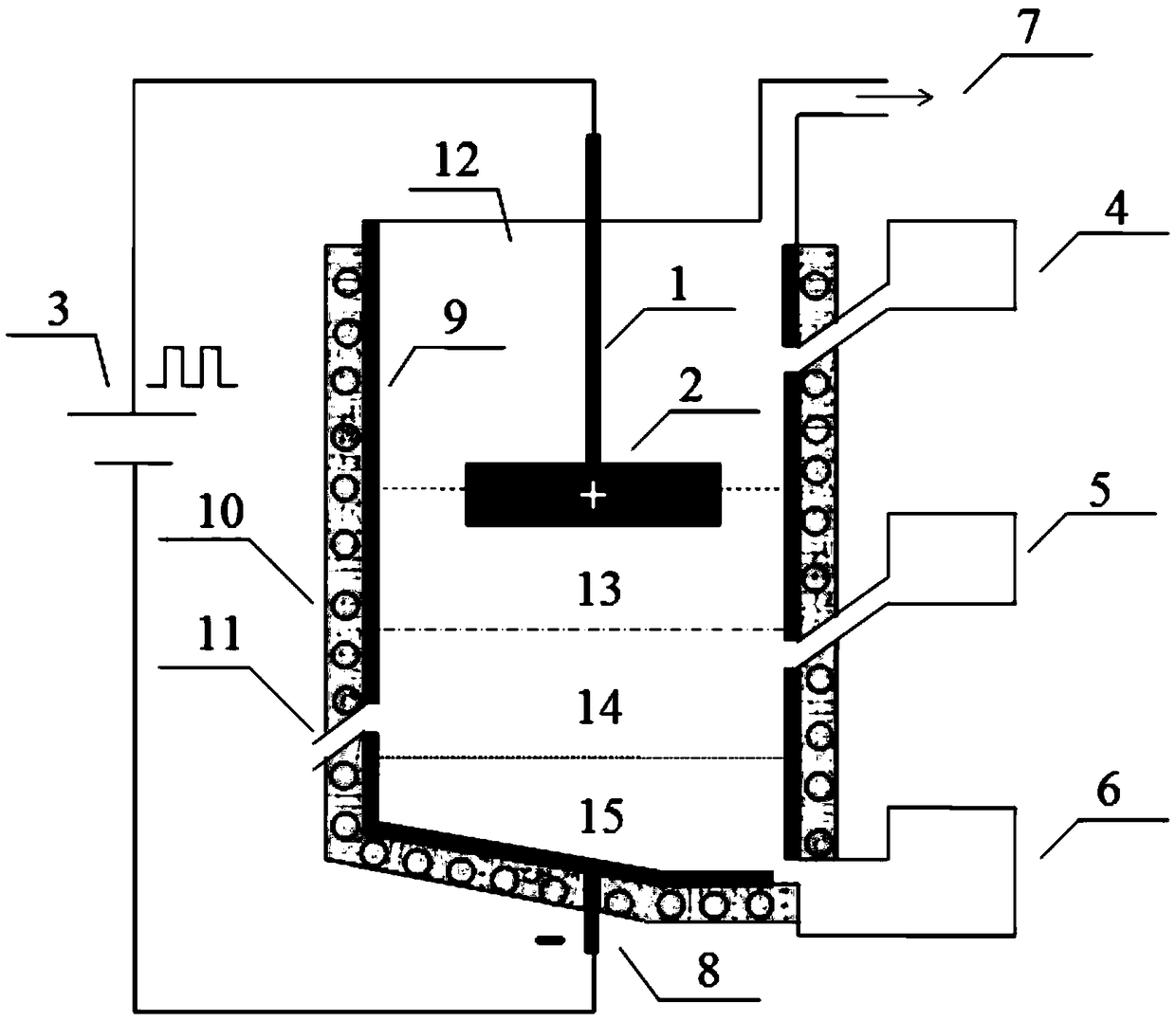
[0026] The chemical composition of bismuth concentrate A is (%): Bi 25.6, Fe 18.2, S 29.7, Cu 0.49, Pb 0.79, Mo2.2, As 0.29, SiO 2 8.80, CaO 5.22. Weigh 100g bismuth concentrate A, 20g Na 2 S, 79.1 g NaCl and 100.9 g KCl. First add 20g Na 2 S, 79.1g of NaCl and 100.9g of KCl were mixed evenly. Take out 80g and 100g bismuth concentrate A from this mixed molten salt afterwards and mix homogeneously. The mixed material was spread on the bottom of the hearth of the low-temperature molten salt electrolysis device through the bismuth-containing material feed port, and then the remaining 120g mixed molten salt was spread on the upper layer of the mixture through the inert molten salt feed port. Adjust the height of the anode guide rod so that the graphite anode is inserted into the upper layer of inert molten salt, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 5 cm. Turn on the power of the external resistance heating layer and raise the temperature to 850°C. Turn on t...
Embodiment 2
[0028] The chemical composition of bismuth concentrate B is (%): Bi 25.0, Mo 3.27, Fe 20.7, S 26.5, Cu 0.2, Pb 0.4, As 0.1, SiO 2 6.3, CaO 1.5, MgO 0.9. Weigh 200g bismuth concentrate B, 100g K respectively 2 S, 175.8g NaCl and 224.2g KCl. 100g K 2S, 175.8g of NaCl and 224.2g of KCl were mixed evenly. Take out 160g and 200g bismuth concentrate B from this mixed molten salt afterwards and mix homogeneously. The mixed material was spread on the bottom of the hearth of the low-temperature molten salt electrolysis device through the bismuth-containing material feed port, and then the remaining 240g mixed molten salt was spread on the upper layer of the mixture through the inert molten salt feed port. Adjust the height of the anode guide rod so that the graphite anode is inserted into the upper layer of inert molten salt, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 8cm. Turn on the power supply of the external resistance heating layer and raise the temperature to 90...
Embodiment 3
[0030] The chemical composition of bismuth concentrate C is (%): Bi 42.5%, Cu 5.2%, Pb 12.4%, Sb 9.5%, As3.9%, Ag 2215g / t. Weigh 100g bismuth concentrate C, 15g Na respectively 2 S, 48.3g NaCl and 61.7g KCl. First 15g Na 2 S, 48.3g of NaCl and 61.7g of KCl were mixed evenly. Take out 50g and 100g bismuth concentrate C from this mixed molten salt afterwards and mix homogeneously. The mixed material was spread on the bottom of the hearth of the low-temperature molten salt electrolysis device through the bismuth-containing material feed port, and then the remaining 75g mixed molten salt was spread on the upper layer of the mixture through the inert molten salt feed port. Adjust the height of the anode guide rod so that the graphite anode is inserted into the upper layer of inert molten salt, and the distance between the cathode and the anode is 6cm. Turn on the power supply of the external resistance heating layer and raise the temperature to 880°C. Turn on the pulse power s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com