Method for quickly screening high-yield astaxanthin phaffia rhodozyma strains
A technology of Phaffia rhodochrous and yeast strains is applied in the field of rapid screening of high-yielding astaxanthin strains of Phaffia rhodozyma, which can solve the problems of high cost, complicated chemical synthesis method of astaxanthin, etc. simple craftsmanship
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
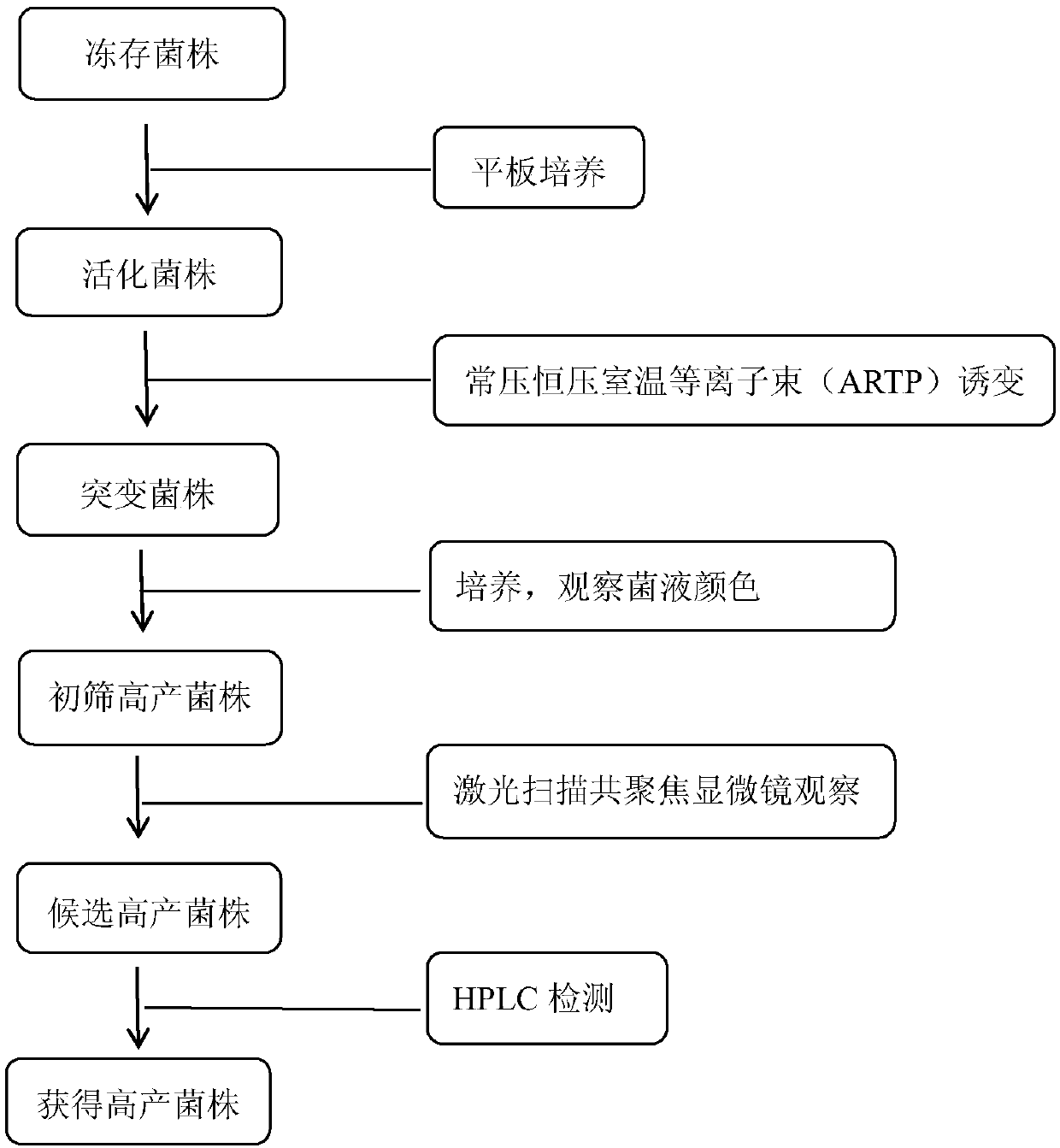
[0030] Activation: After activation, the wild-type Phaffia rhodozyma strain was cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 22°C for 125 hours at a speed of 120r / min;
[0031] Mutagenesis: Take the wild-type single colony strain and add it to the seed medium for 24 hours on a shaking table with a rotation speed of 120-130r / min and a temperature of 22-25°C. The time is 160s, the mutagenized bacterial solution is transferred to a centrifuge tube containing sterile saline, after gradient dilution, spread on a plate, and incubate at 22°C for 120h;
[0032] Preliminary screening: the single colony grown on the plate was transferred to a 24-well plate with 2mL of culture solution for shaking culture at a rotation speed of 125r / min, and the dark orange mutant strain was selected as the candidate strain;
[0033] Re-screening: the candidate strains are made into temporary mounts, observed with a laser scanning confocal microscope, and mutant strains with higher fluorescence intens...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Activation: activation of the wild-type Phaffia rhodozyma strain, cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 25°C and 125r / min for 120h;
[0041] Mutagenesis: Take a small amount of cultured strains and add them to the seed medium, culture them on a shaking table for 24 hours, and mutagenize the yeast with plasma beams at room temperature at normal pressure and constant pressure for 180 seconds. Transfer the mutagenized bacteria solution into a centrifuge tube containing sterile saline Spread the plate after serial dilution and incubate at 22°C for 120 hours;
[0042] Preliminary screening: the strains were transferred to a 24-well plate with 2mL of culture medium, cultured on a shaker at 120r / min for 46 hours, and dark orange mutant strains were selected as candidate strains;
[0043] Re-screening: the candidate strains are made into temporary slides, observed with a laser scanning confocal microscope, and mutant strains with higher fluorescence intensity are scre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com