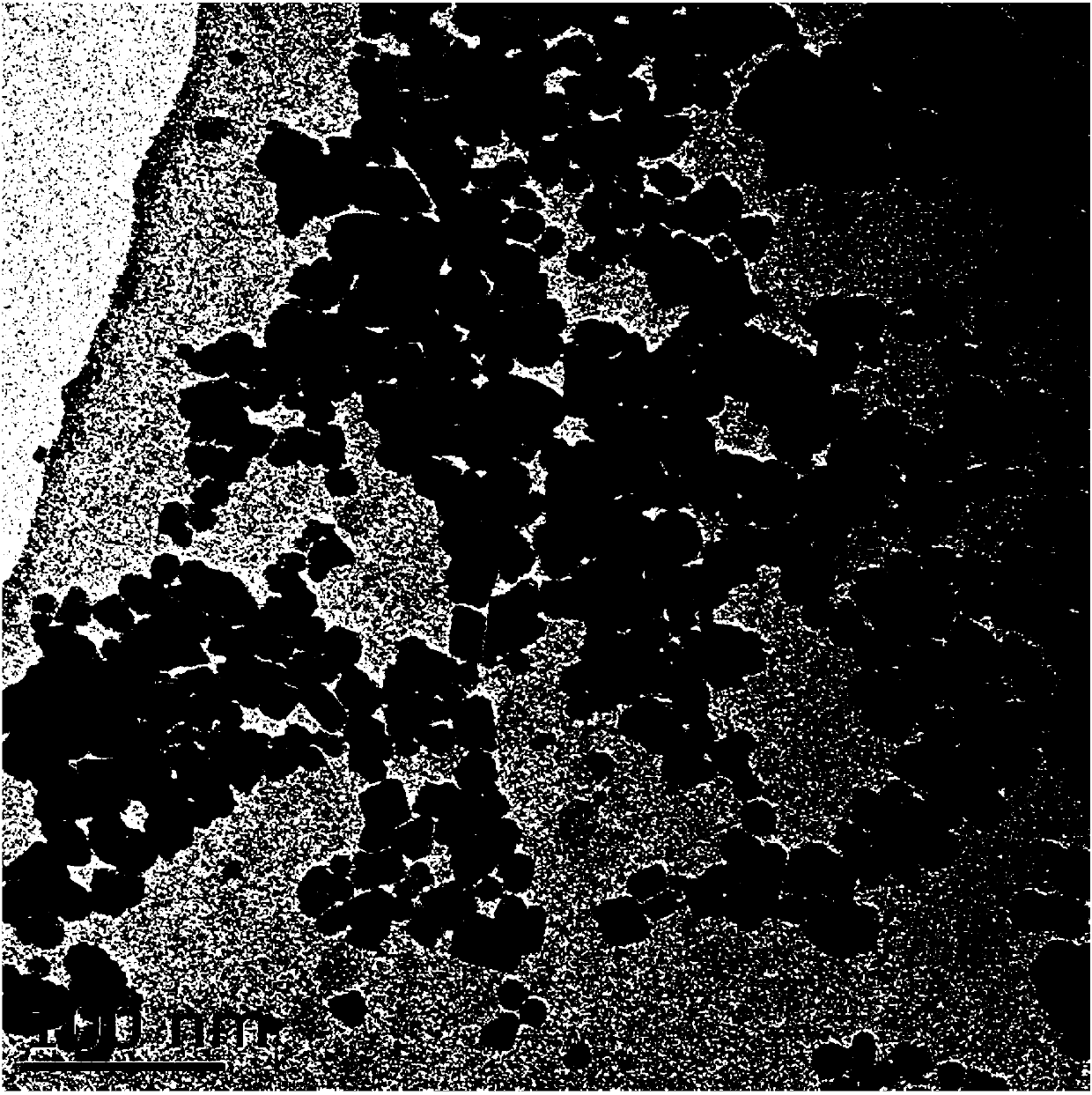
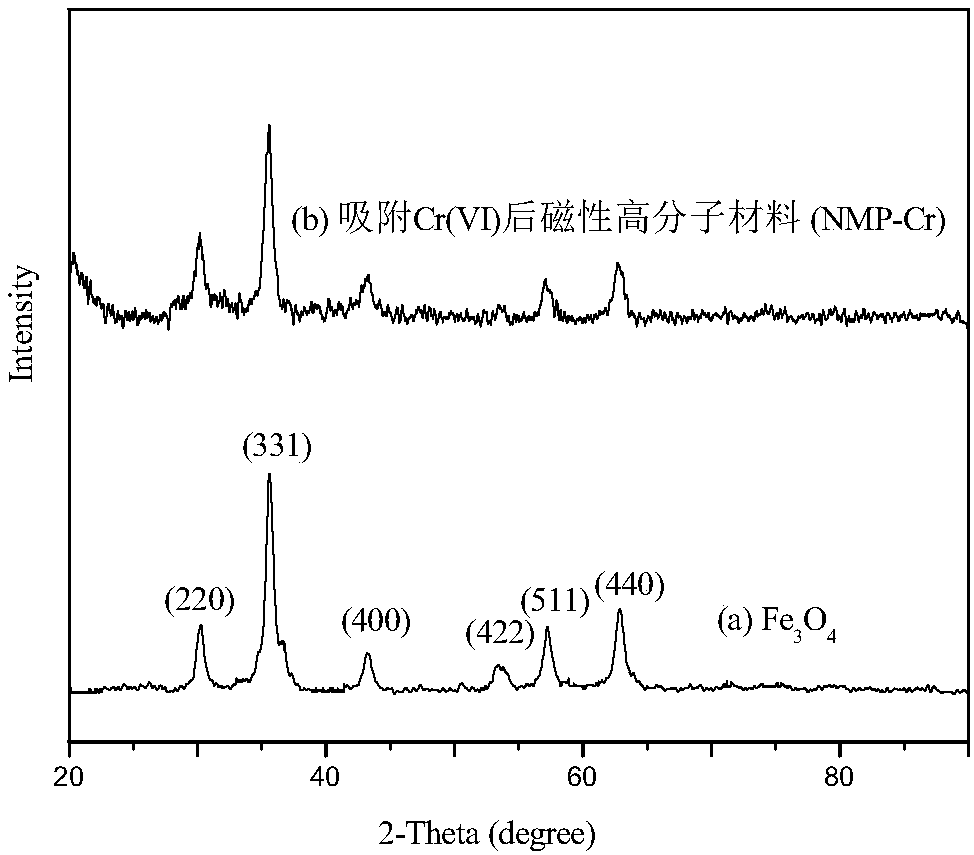
Comprehensive utilization method of Cr(VI) (hexavalent chromium)-adsorbed magnetic macromolecular material
A polymer material and magnetic technology, which is applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of magnetic polymer materials after adsorption of Cr(VI), can solve the problems such as the comprehensive utilization has not been effectively carried out, the waste composition is unknown, the structure is unknown, etc., and the process and cost are saved. , good dispersion, high recovery efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0029] Synthesis and characterization of amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymer composites (series 1-5, similar to series 6, change MMA to St) (Acta Chemical Sinica, 2009, 67(13), 1509-1514; J.Mater.Sci .2010,45,5291–5301; J.Hazard.Mater.2010,182,295–302; Ind.Eng.Chem.Res.2013, 52,12723-12732, etc.) There are records of the synthesis and characterization of some materials:
[0030] 1 nm Fe 3 o 4 Synthesis of particles
[0031] Synthesis of Nano Fe by Co-precipitation 3 o 4 Particles according to Fe 2+ :Fe 3+ = 1.5:2 (the ratio of the amount of substance) to prepare Fe 2+ and Fe 3+ After the solution of ions is fully dissolved, use ammonia water to provide alkalinity, adjust its pH value to 8-9, and stir at a speed of 500 r min- 1 , the reaction temperature is 353K, and the reaction time is 1h. The reaction principle is shown in reaction formula (1):
[0032] Fe2++2Fe3++8OH-→Fe3O4+4H2O (1)
[0033] After the reaction was completed, magnetically separated, w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com