Composition, preparation and application of magnetic liposome vesicles
A magnetic liposome and liposome technology, applied in transportation and packaging, chemical instruments and methods, dissolution, etc., can solve problems such as poor biocompatibility, poor emulsification performance, and instability of magnetic oleic acid vesicles , to achieve the effects of easy control, easy access to raw materials, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment one: Fe 3 o 4 Preparation of nanoparticles
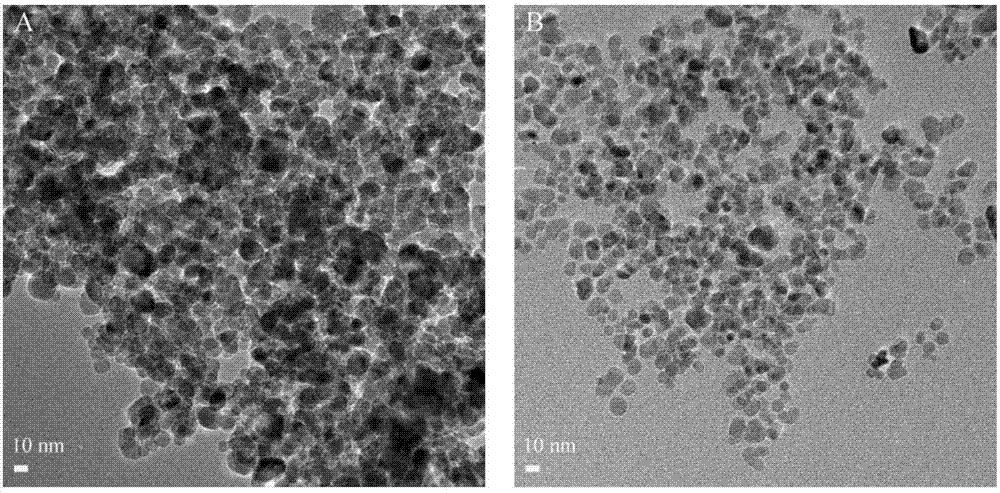
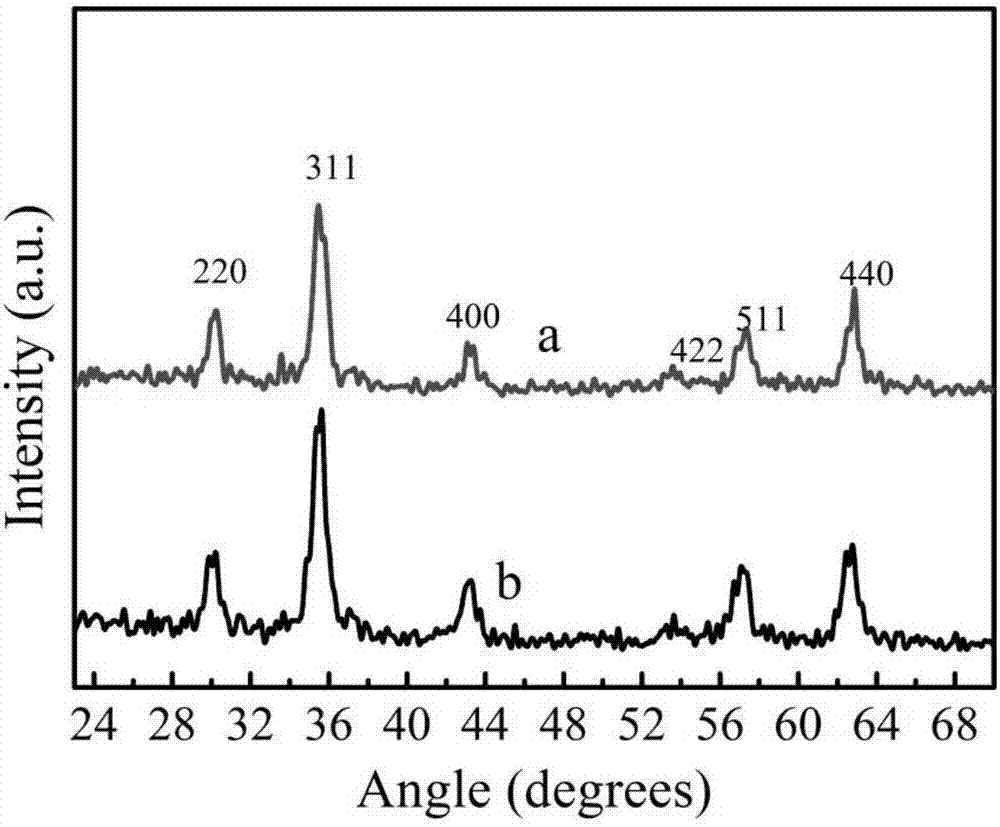
[0033] 0.12mol of FeCl 3 ·6H 2 O and 0.06mol FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O was dissolved in a four-necked flask with 1000 mL of ultrapure water. Stir vigorously under a nitrogen atmosphere, quickly add 100mL of 25% concentrated ammonia water at 70°C, stir for 20min, take out the precipitated solid particles, cool to room temperature, and wash with water until neutral to obtain Fe 3 o 4 Nanoparticles. Disperse 1wt% nanoparticles in 10 times the volume of pH 10 buffer solution (borax-sodium hydroxide), drop it on the copper grid, absorb the excess solution with filter paper, and characterize it with TEM (200kV) after natural drying. See attached figure 1 (A)Fe 3 o 4 RT-TEM images.
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Preparation of magnetically conjugated linoleic acid vesicles CLA@Fe 3 o 4
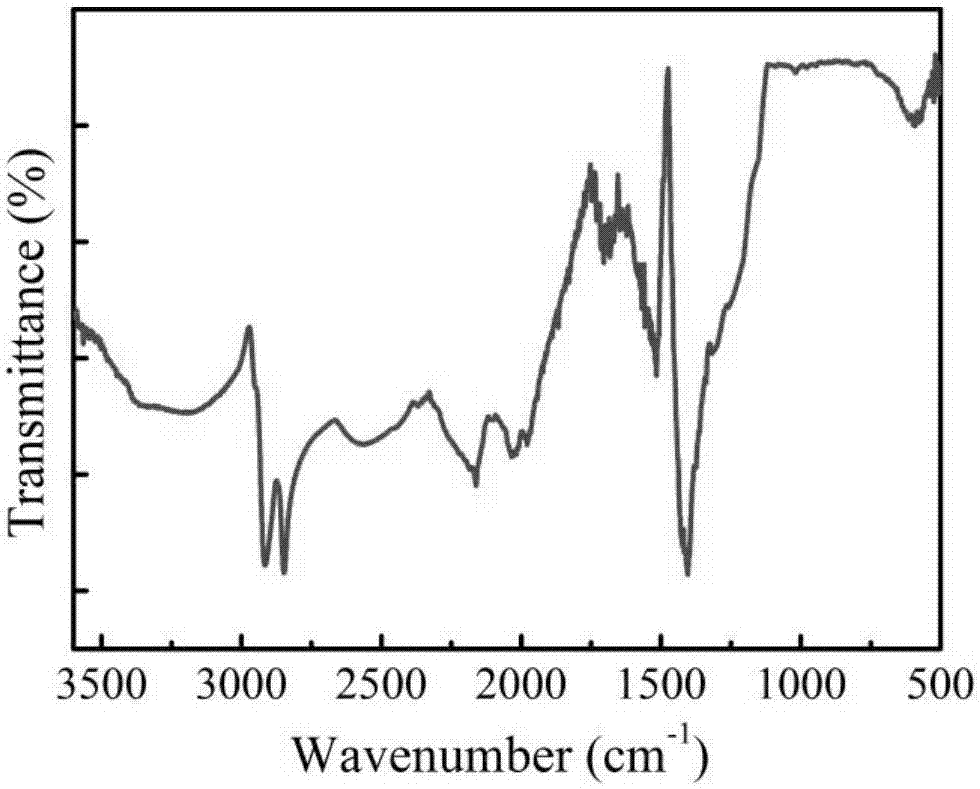
[0035] In a water bath at 80°C, 1.2 g of Fe 3 o 4 Add the nanoparticles into a flask containing 100mL of ultrapure water, ultrasonically disperse the solution, adjust the pH of the solution to pH7 with 0.1mol / L hydrochloric acid aqueous solution, and slowly add 10mL of 17% sodium conjugated linoleate dropwise into the flask while stirring with nitrogen aqueous solution. After 1 hour, remove the flask from the water bath and cool it to room temperature, adjust the pH to about 5, place a magnet on the bottom of the flask to absorb the magnetic vesicles, remove the upper liquid by magnetic decantation, and wash the magnetic vesicles with ultrapure water for several times. The obtained magnetic vesicles were dried in a vacuum oven at 45°C to obtain magnetically conjugated linoleic acid particles (CLA@Fe 3 o 4 ).
[0036] Magnetic Conjugated Linoleic Acid Vesicular Particles CLA@Fe...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Magnetic self-crosslinking conjugated linoleic acid vesicles SCLA@Fe 3 o 4 preparation of
[0041] The obtained 0.1g CLA@Fe in embodiment two 3 o 4 The vesicles were dispersed in 10mL of 0.015M phosphate buffer at pH 10, and added to a 25mL three-neck flask, and 7% APS aqueous solution of the monomer mass was added into the flask, and reacted in a water bath at 80°C for 7h under stirring with nitrogen to obtain SCLA@Fe 3 o 4 Vesicle solution. The absorbance A234 of the solution at 234 nm before and after self-crosslinking was measured with a UV-visible spectrophotometer, and the self-crosslinking was judged by comparing their changes. See attached Figure 5 (A)CLA@Fe 3 o 4 UV spectra before and after self-crosslinking, (B) SCLA@Fe 3 o 4 RT-TEM images.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com