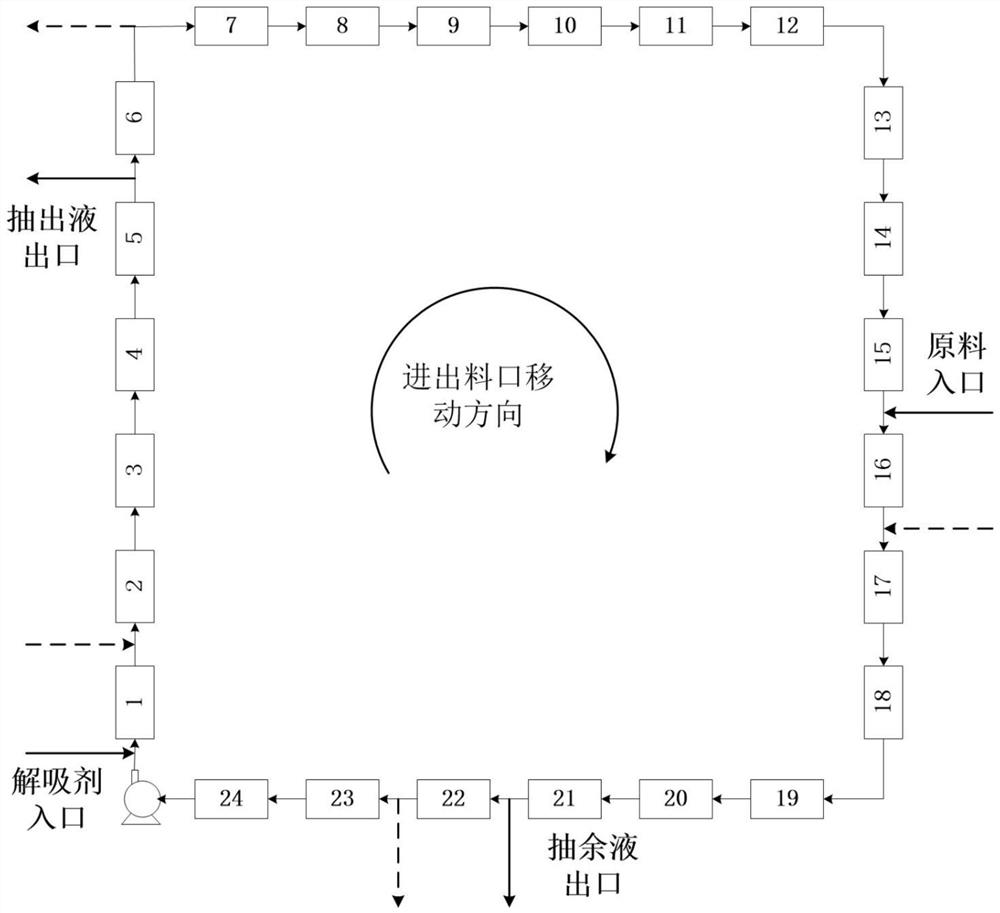
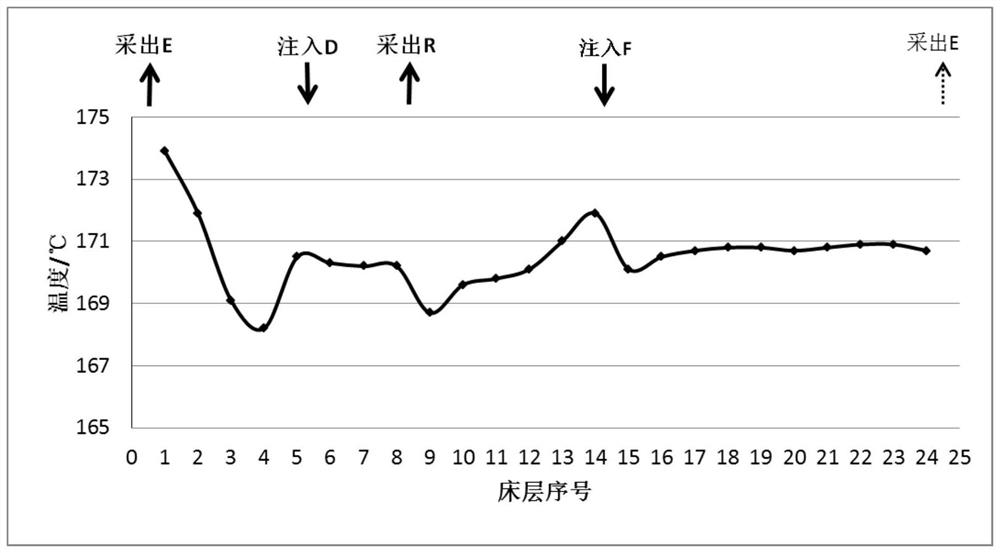
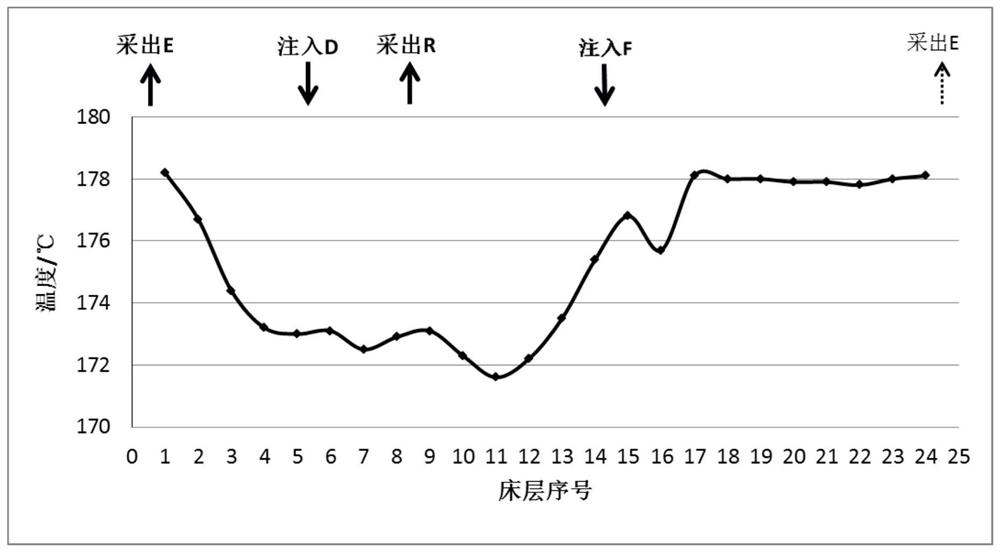
Method for Simulated Moving Bed Adsorption and Separation of Paraxylene in C8 Aromatics
A technology for simulating moving bed and C8 aromatics, which is applied in the field of isomers and can solve problems such as poor separation effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0022] The preparation method of the above-mentioned adsorbent is as follows: mixing NaX zeolite with a binder, rolling into balls, and roasting to obtain matrix pellets. Then use barium and / or potassium compound solution to carry out ion exchange, and after exchange, the solid is dried and activated to obtain the adsorbent. The compound containing potassium and barium is preferably nitrate or chloride of potassium or barium. When preparing an adsorbent with BaKX zeolite as an active component, the matrix pellets can be contacted with a barium-containing compound solution for Ba ion exchange, and then contacted with a potassium-containing compound solution for K ion exchange, and then dried and activated. The calcination temperature is preferably 480-560°C, and the drying temperature is preferably 90-130°C.
[0023] The desorbent used in the adsorption and separation process of the method of the present invention is p-diethylbenzene, whose boiling point is higher than that of...
example 1
[0032] Prepare the adsorbent used in liquid phase adsorption separation.
[0033] Mix NaX zeolite with a silica / alumina molar ratio of 2.4 and kaolin at a mass ratio of 92:8, roll into a ball, and bake at 520°C for 6 hours to take spherical particles with a particle size of 0.5 to 1.0 mm, and use barium nitrate solution Carry out ion exchange, the liquid / solid volume ratio of solution and adsorbent is 10, the concentration of barium nitrate solution is 0.3mol / L, and the exchange degree calculated according to the residual sodium content after exchange is 95 mol%. After the exchange, the solid was dried at 100° C. for 3 hours and activated at 220° C. for 2 hours to obtain an adsorbent A, wherein the content of BaX was 93.41% by mass and the content of kaolin was 6.59% by mass.
example 2
[0035] Mix NaX zeolite with a silica / alumina molar ratio of 2.4 and kaolin at a mass ratio of 92:8, roll into a ball, and bake at 520°C for 6 hours to take spherical particles with a particle size of 0.5 to 1.0 mm, and use barium nitrate solution For ion exchange, the liquid / solid volume ratio of the solution to the adsorbent is 10, and the concentration of the barium nitrate solution is 0.3 mol / L. Get the solid after Ba ion exchange and carry out ion exchange with the solution of Potassium Chloride, the concentration of Potassium Chloride is 0.5mol / L, and the liquid / solid volume ratio of solution and adsorbent is 2, calculates by the residual sodium content after exchange The degree of exchange was 95 mol%. After the exchange, the solid was dried at 100°C for 3 hours and activated at 220°C for 2 hours to obtain Adsorbent B, wherein the content of BaKX was 93.1% by mass, the content of kaolin was 6.9% by mass, and the molar ratio of K to Ba in the BaKX zeolite was 0.12.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com