Efficient induced pluripotent stem cell reprogramming method for blood cells
A technology for pluripotent stem cells and blood cells, applied in the field of high-efficiency induced pluripotent stem cell reprogramming, can solve the problems of abnormal karyotype, low reprogramming efficiency, low efficiency, etc., and achieve the effect of less accumulation of gene mutations and convenient source of samples
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
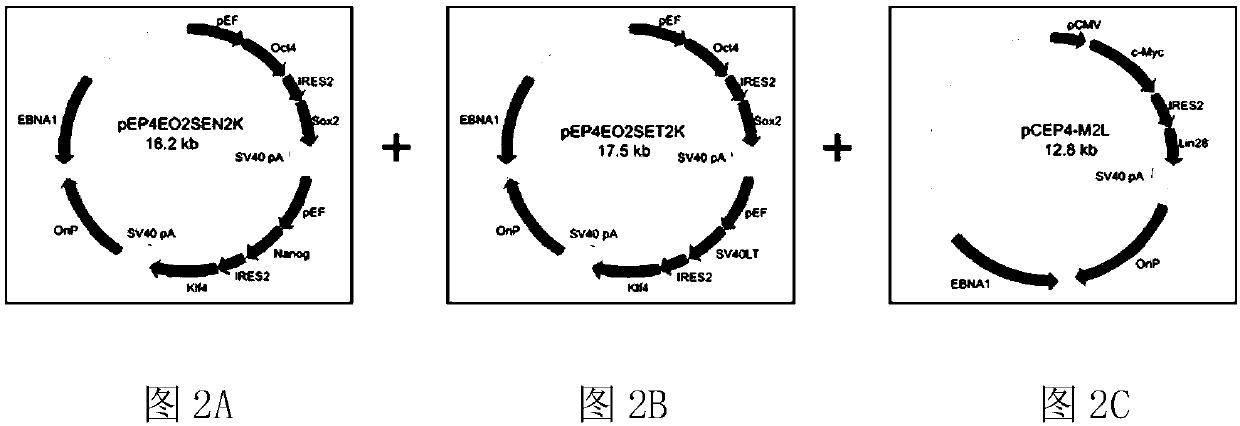
[0073] Episomal vector construction
[0074] As shown in Figure 2, three kinds of episomal vectors were constructed in this embodiment, all of which amplified the ORF sequence in the potency determinant gene by polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and inserted the ORF sequence into the vector containing OriP / The mammalian expression vector pCEP4 of EBNA1 was constructed as an episomal vector, and all three episomal vectors contained at least one internal ribosome entry size (IRES), among which the first episomal vector was pEP4-E -O2S-E-N2K, which sequentially contains the first promoter, POU5F1, IRES2, SOX2, the second promoter, NANOG, IRES2 and KLF4, and the second vector is pEP4-E-O2S-E-T2K, which sequentially contains The third promoter, POU5F1, IRES2, SOX2, the fourth promoter, SV40LT, IRES2 and KLF4, the third vector is pCEP4-M-2L, which contains the fifth promoter, MYC, IRES2 and LIN28A in sequence; the above-mentioned first The second, third and fourth promoters are all ...
Embodiment 2
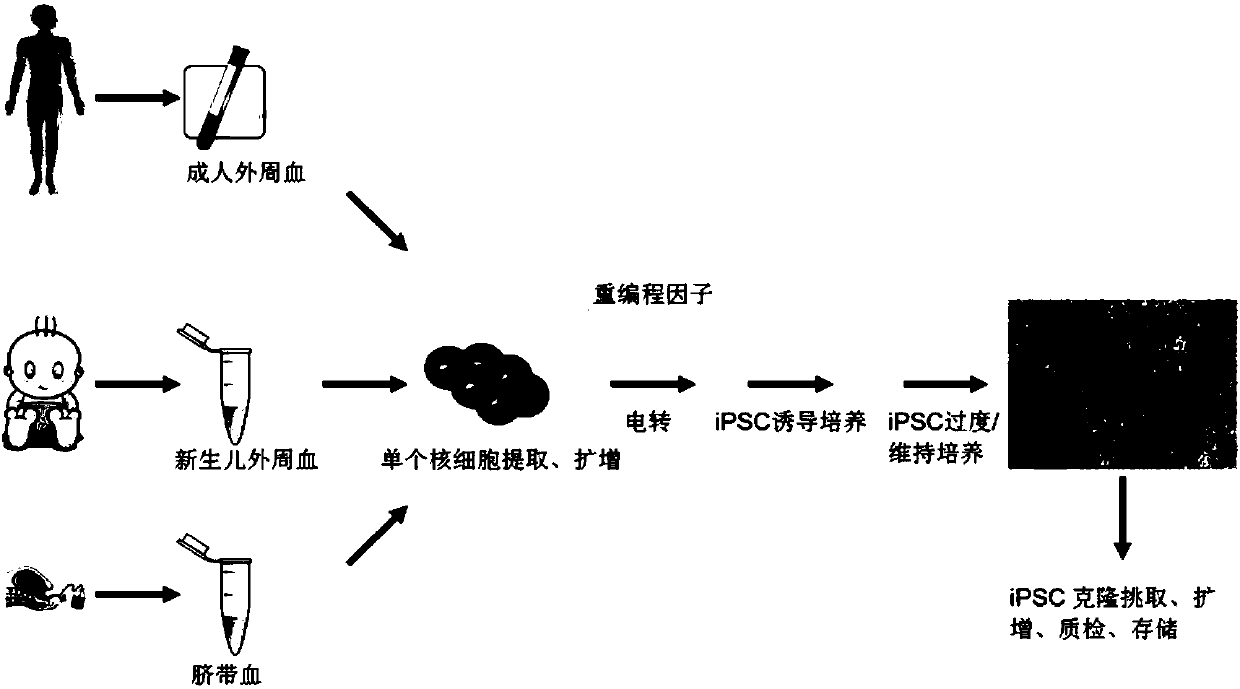
[0076] 1. Acquisition of red blood cell progenitor cells
[0077] Collect a blood sample of at least 10 μl, transfer it to a lymphocyte separation tube, centrifuge, take the mononuclear cell layer, wash it twice with DPBS centrifugation, take a sample and count it, and take 0.5×10 cells according to the counting result. 6 Cells / ml seeded in 96, 48, 24, 12 or 6-well plate, add erythrocyte progenitor cell expansion medium, place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator. The same volume of fresh expansion medium as the initial medium was added to each well on the 4th and 8th day of expansion respectively.
[0078] The specific formulation of the expansion medium in this example is: each liter of expansion medium contains 10ml of ITS additive, 10ml of GlutaMAX, 1ml of Lipid Concentrate, 250 μmol of L-ascorbic acid 2-phosphorylated hemimagnesium salt hydrate, 3 μmol of ferrous sulfate, Ferric nitrate 0.2 μmol, lipoic acid 1 μmol, hydrocortisone 1 μmol, stem cell factor 100 μg, e...
Embodiment 3
[0082] episomal vector-induced reprogramming
[0083] a, recovery, after the erythrocyte progenitor cells in Example 2 are overgrown, get 0.5~4×10 erythrocyte progenitor cells 6 , using the pEP4-E-O2S-E-N2K, pEP4-E-O2S-E-T2K and pCEP4-M-2L episomal vectors constructed in Example 1 to electrotransfect the above erythroid progenitor cells, and then inoculate them on induced pluripotent stem cells Culture medium and Matrigel or vitronectin or other cell matrix-coated six-well plate, the transfection content of each plasmid DNA is pEP4-E-O2S-E-N2K: pEP4-E-O2S-E-T2K : pCEP4-M-2L=1:1:1.
[0084] b. After 48 hours, half of the medium was replaced with fresh pluripotent stem cell induction medium, and the culture was continued until 10 days, and the medium was changed every other day, that is, reprogramming was carried out on the feeder-free system.
[0085] The pluripotent stem cell induction medium of this example has the following components: adding one or more of the following s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com