Organic electroluminescent material and organic light-emitting device thereof
A technology of electroluminescent materials and organic light-emitting devices, which is applied in the direction of luminescent materials, electric solid devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of low luminous efficiency and low lifespan, and achieve high luminous efficiency, low driving voltage, and increased volume. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
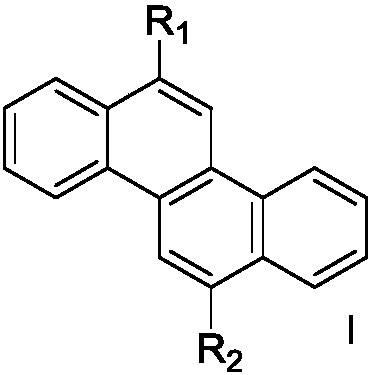
[0036] The preparation method of a kind of organic electroluminescent material described in the present invention, comprises that shown raw material generates a kind of organic electroluminescent material shown in formula I by following route reaction:
[0037]
[0038] 1,6-dibromo The target product is generated by suzuki or buchward reaction.
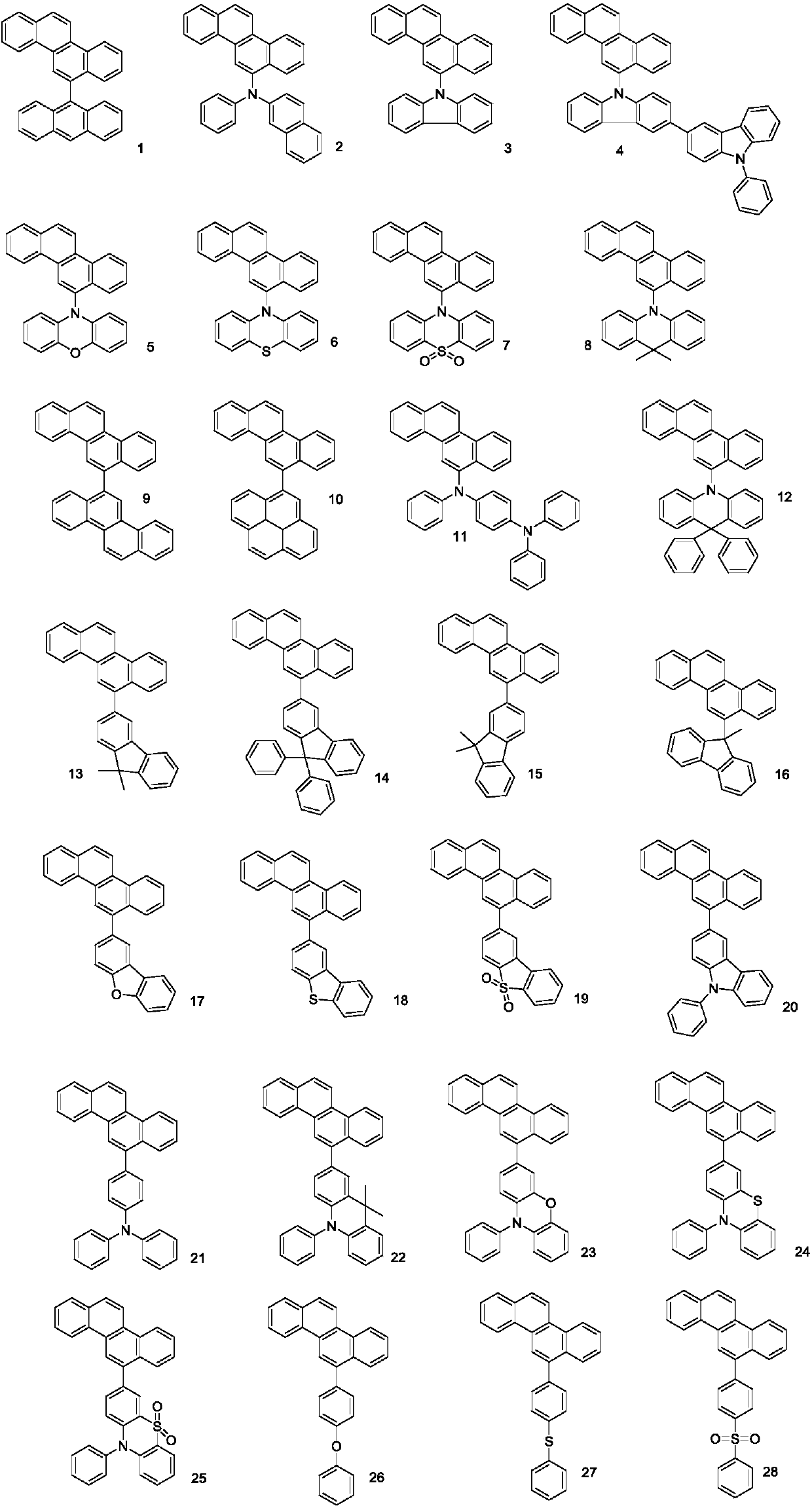
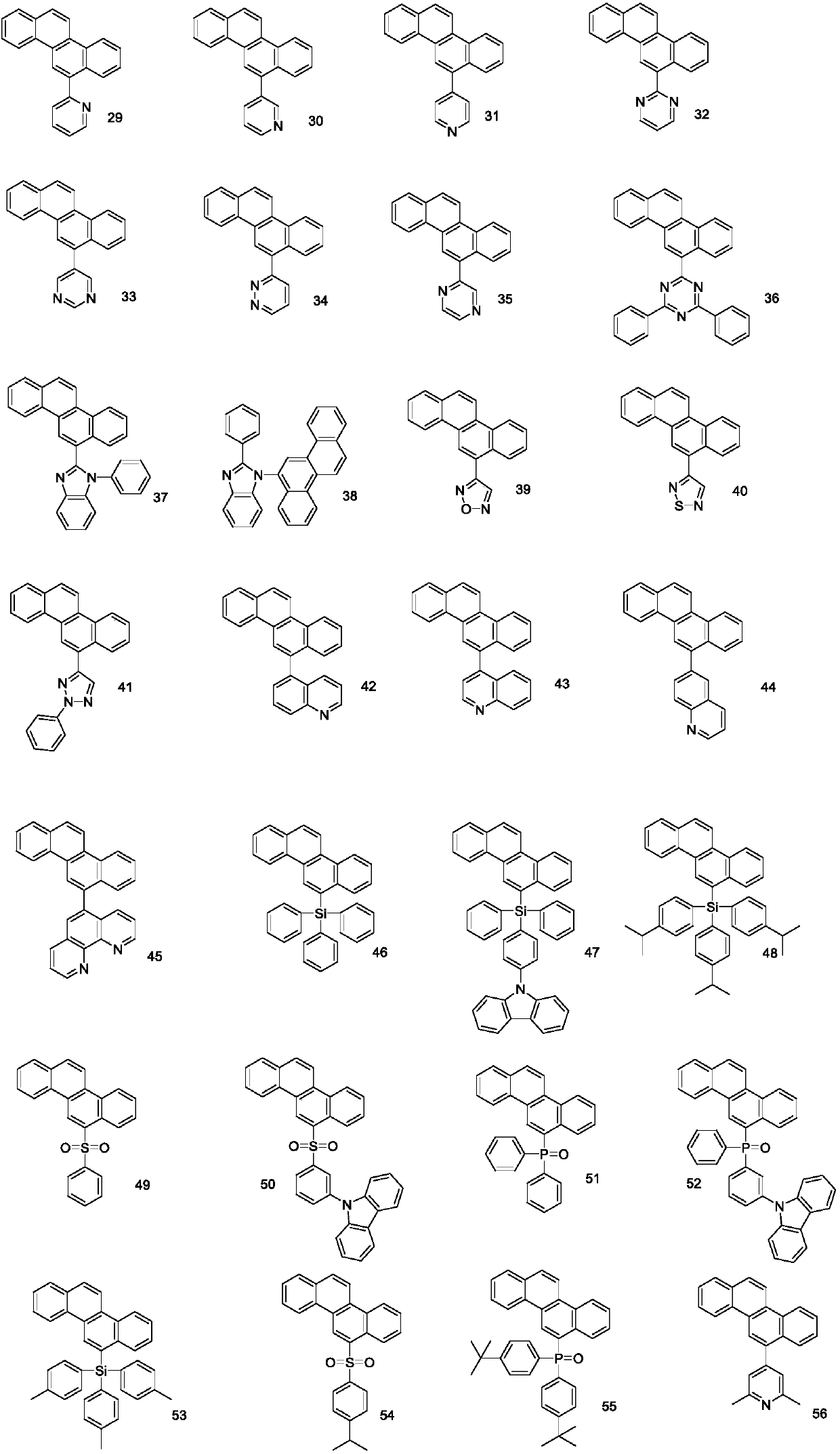
[0039] Among them, R 1 , R 2 independently selected from hydrogen, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 arylamine, substituted or unsubstituted C3-C30 heteroaryl, substituted or unsubstituted C18-C30 triphenyl One of silyl, substituted or unsubstituted C12-C30 diphenylphosphine, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 phenylsulfone, R 1 , R 2 Not simultaneously hydrogen.
[0040] The present invention also provides an organic light emitting device, and the organic light emitting device may be an organic light emitting device well known to those skilled in the art. The organic light-emitti...
Embodiment 1
[0041] Embodiment 1: the preparation of compound 1
[0042]
[0043] 6-bromo Add 100mmol to a mixed solvent of toluene, ethanol, and water, add 1 equivalent of 9-anthraceneboronic acid, 3 equivalents of sodium carbonate, and 0.01 equivalent of tetrakistriphenylphosphine palladium under nitrogen protection, and react for 5 hours at reflux temperature. After the reaction is completed Pass through a silica gel column to obtain product 185mmol.
Embodiment 2
[0044] Embodiment 2: the preparation of compound 4
[0045]
[0046] In the reaction vessel, add 4-1 100mmol; 6-bromo 100mmol, potassium tert-butoxide 300mmol, Pd 2 (dba) 3 1mmol, ultrasonically deoxygenated xylene, stirred and dissolved, replaced the air three times, added 4% (4mmol, 50% m / V) of the ligand tri-tert-butylphosphine, replaced the air three times again, and refluxed for 6h. Cool to room temperature, add enough dichloromethane to completely dissolve the product, pass through a small amount of silica gel funnel, and remove catalyst and salt. The filtrate was concentrated to a viscous state and subjected to column chromatography to obtain 80 mmol of product 4.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com