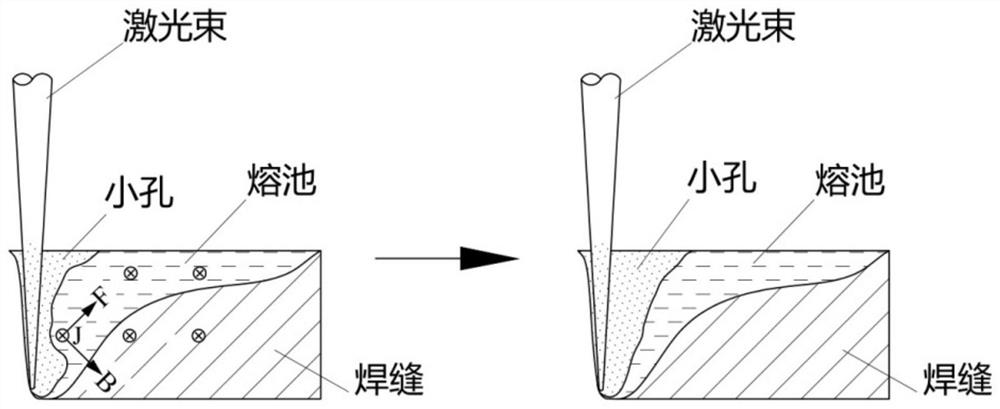
A method of controlling molten pool in laser welding based on Lorentz force
A laser welding and control method technology, applied in laser welding equipment, welding equipment, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of unstable welding process, easy to produce pores, humps and arc craters, etc., achieve good fluidity and increase penetration depth , the effect of enhancing the ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
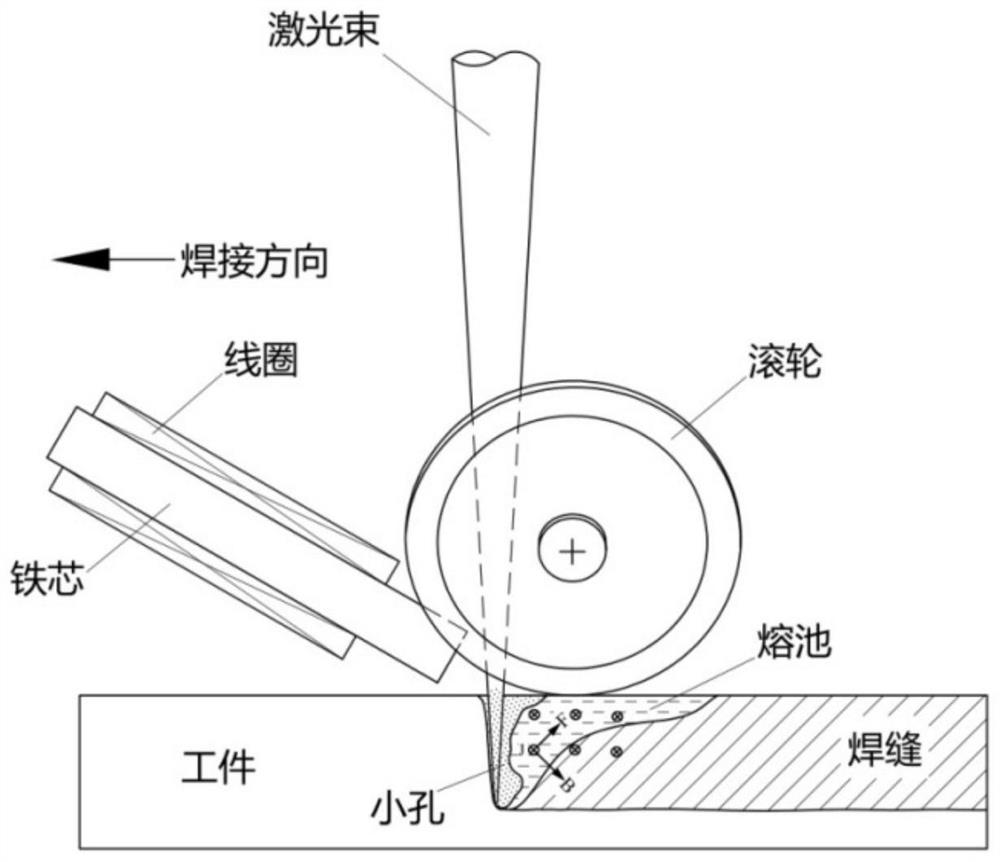
[0031] The specific implementation device of this embodiment is as figure 2 , image 3 shown. The welding material is 316L stainless steel, the thickness of the plate is 20mm, and the dirt is removed on the surface; the laser power is 18KW, the spot size is 0.45mm, and the welding speed is 1m / min; Material: chrome-zirconium copper, electrode form: a pair of rollers, the angle between the two electrodes is 60°, the distance between the electrodes (the distance between the electrode and the contact point on the workpiece surface) is 12mm, the current is 100A DC, the distance between the electrode and the laser beam (the electrode contact point) The distance between the connection line and the central axis of the beam) is 2mm; the strip-shaped NdFeB permanent magnet is arranged obliquely in front of the molten pool to form an angle of 30° with the surface of the workpiece, the size of the magnet is 50×9×4mm, and the magnetic field strength in the welding area is 0.1T.
Embodiment 2
[0033] In the present embodiment, the electrode of the implementation device is changed from the roller of embodiment 1 to a round rod, the electrode diameter is 5mm, the electrode material is chromium-zirconium copper, the electrode spacing (the distance between the electrode and the surface contact point of the workpiece) is 8mm, and 50A is applied between the two electrodes. Constant current; the distance between the electrode and the beam (the distance between the electrode contact line and the central axis of the beam) is 1mm, the welding material is 6061 aluminum alloy, the plate thickness is 4mm, and the surface removes dirt and oxide film; the laser power is 4.5KW, and the spot size is 0.45mm , welding speed 2m / min; front shielding gas: Ar gas, flow rate 15L / min, back 10L / min Ar gas shield; strip-shaped NdFeB permanent magnets are placed in front of the molten pool obliquely at an angle of 30° with the surface of the workpiece, the size of the magnet It is 50×9×4mm, and...
Embodiment 3
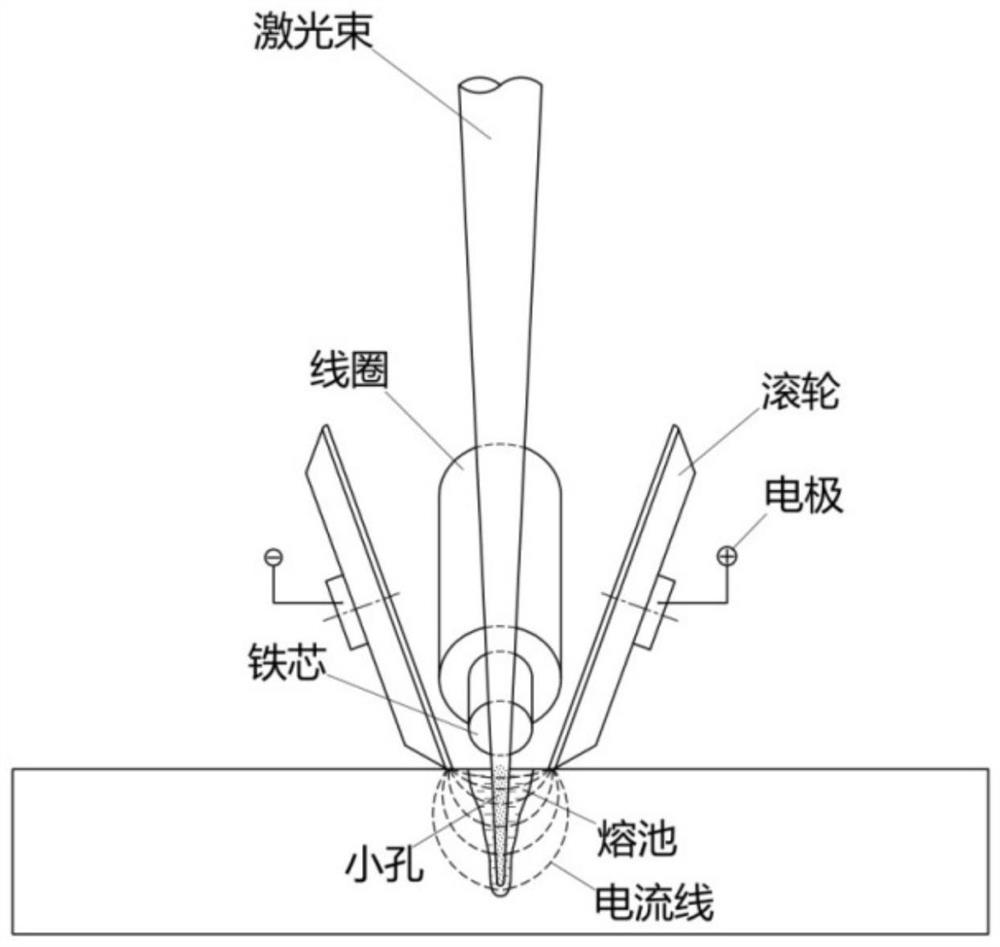
[0035] The specific implementation device of this embodiment is as Figure 4shown. The magnetic field is provided by an electromagnet coaxial with the laser, the magnetic field is a sinusoidal alternating magnetic field, the frequency is 50Hz, and the maximum magnetic field strength in the welding area is 0.2T. Welding material 2024 aluminum alloy, plate thickness 6mm, remove dirt and oxide film on the surface; laser power 5KW, spot size 0.45mm, welding speed 1.5m / min; front shielding gas: Ar gas, flow rate 15L / min, back 10L / minAr Gas protection; electrode material: chrome-zirconium copper, electrode form: a pair of rollers, the angle between the two electrodes is 60°, the electrode spacing (the distance between the electrode and the contact point on the workpiece surface) is 12mm, the current is DC 100A, the electrode and the laser beam The distance (the distance between the electrode contact line and the central axis of the beam) is 2mm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com