Fluid extraction of metal and/or metalloid
A metalloid, extraction technology, applied in solid solvent extraction, solvent extraction, preparation/processing of rare earth metal compounds, etc., can solve the problems of low solubility of metals and other non-organic substances, weak van der Waals force, and low metal ion efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment I
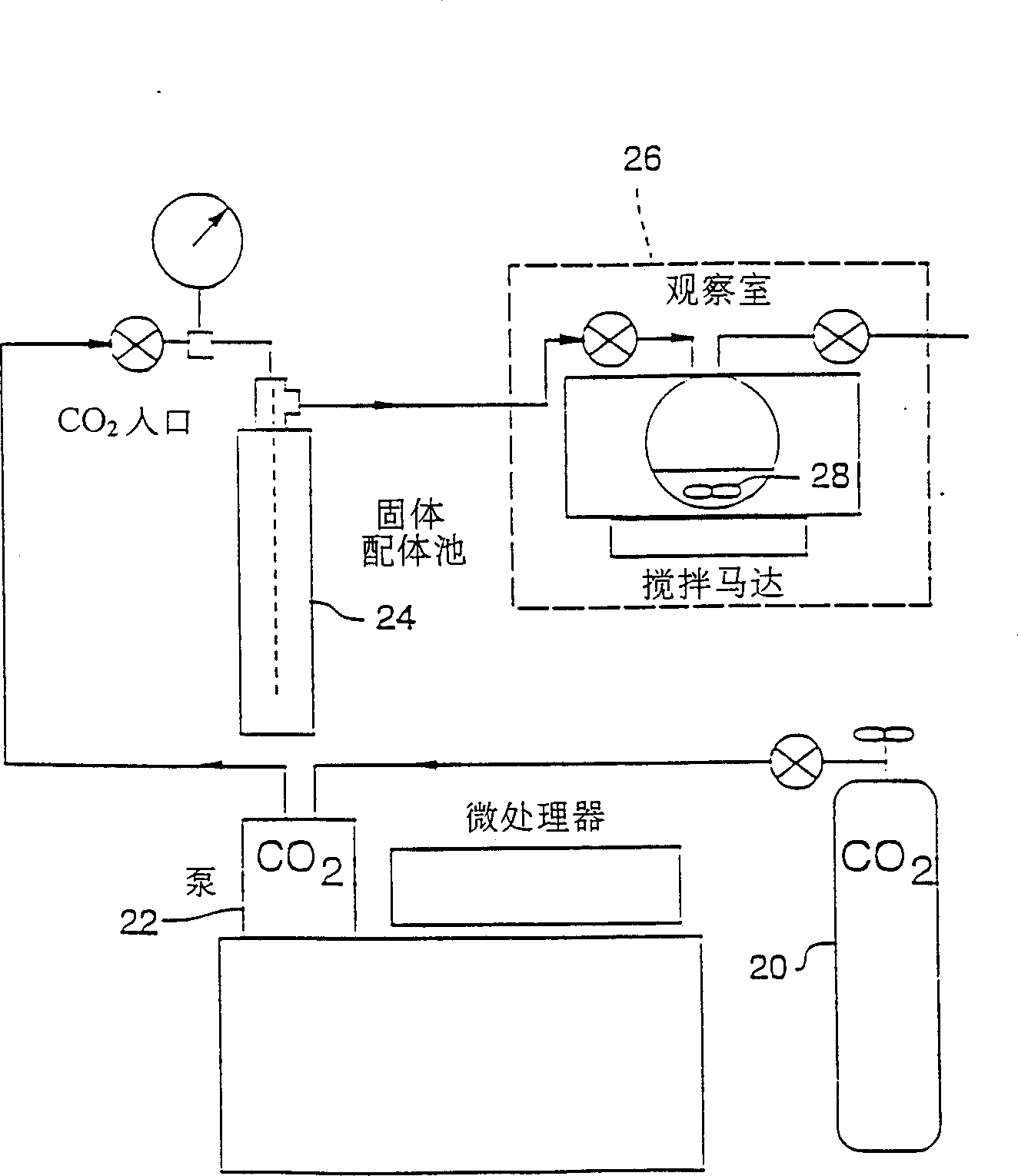
[0094] This embodiment illustrates the method for a large amount of and continuous SFE extraction, see figure 1 The extraction apparatus shown. figure 1 The larger extraction unit includes a feedstock source 20 of supercritical carbon dioxide, which directly extracts copper ions from an aqueous solution. Supercritical CO from the high-pressure syringe pump 22 2 Conveyed through solid sodium bis(trifluoroethyl)dithiocarbamate (FDDC), contained in a high pressure extractor 24 of stainless steel. Subsequently, supercritical CO containing dissolved FDDC 2 Introduced into a second extractor 26, which is equipped with a quartz window and contains less than SCF CO 2 Cu(NO 3 ) 2 Aqueous solution 28. Soluble in CO with the formation 2 The complex of Cu(FDDC) 2 , to monitor Cu extraction by UV-Vis spectroscopy, Cu(FDDC) 2 The structure is as follows.
[0095] right figure 1 For a large extraction system, the mixing of the water phase and the supercritical fluid phase can be...
Embodiment II
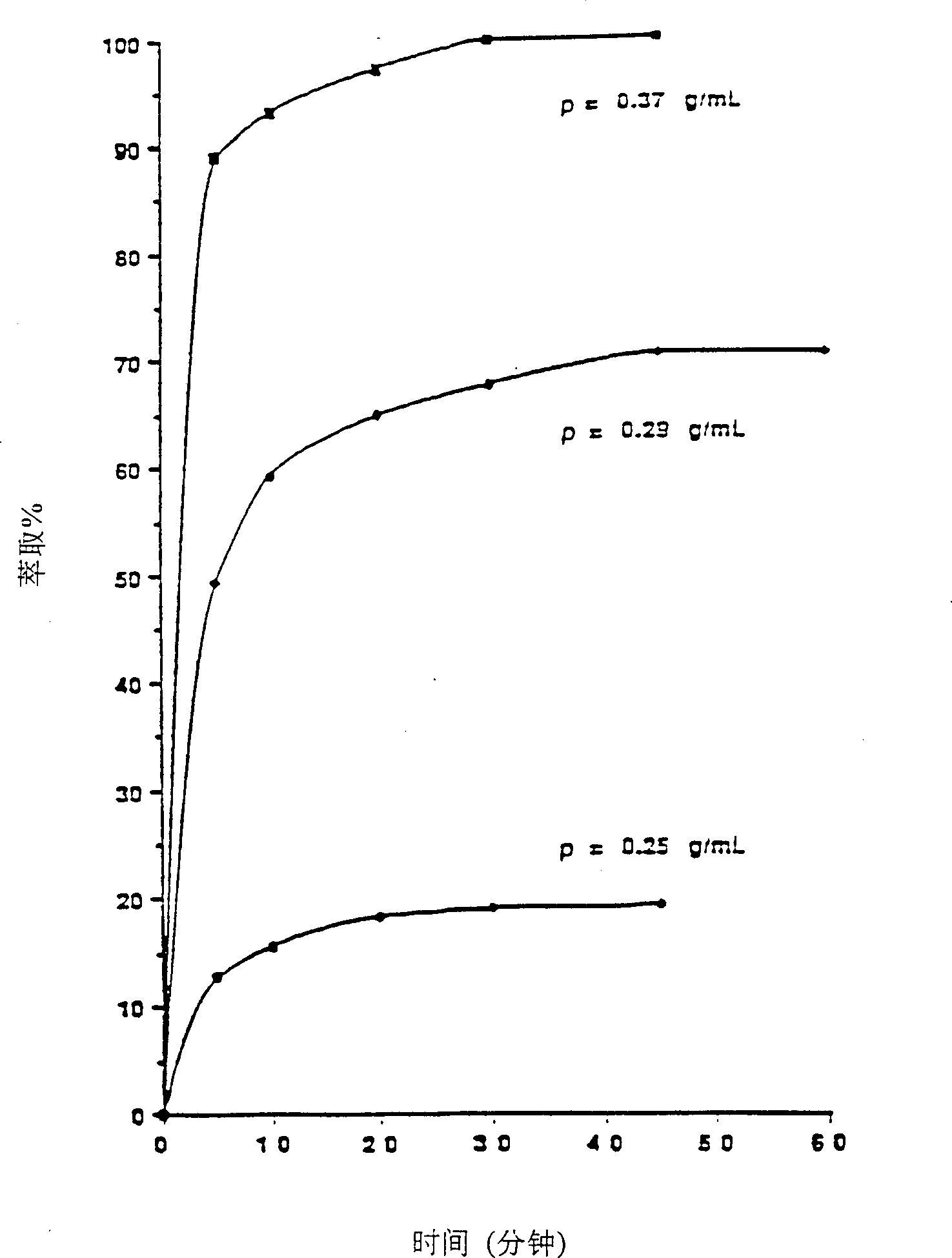
[0099] This example illustrates a method for the extraction of metals and / or metalloids from solid matrices. The same equipment used in Example 1 was used to extract the copper ions adsorbed on the solid substrate. At this point, it will be adsorbed on silica (SiO 2 ) on solid Cu(NO 3 ) 2 Place in a second extractor. Then, supercritical carbon dioxide containing dissolved ligand FDDC was added thereto. Cu(FDDC) dissolved in supercritical carbon dioxide 2 to monitor the extraction rate. The initial extraction rate is still very fast. After about 20 minutes, the carbon dioxide phase was saturated with dissolved metal complexes. At this time, about 80% of the copper ions can be dissolved in the final fluid density of 0.55g / cm 3 is extracted.
[0100] In Examples I and II, the metal chelate is completely obtained by precipitation from supercritical carbon dioxide by reducing the pressure of the system. It can also be seen that the present invention can be used to recover...
Embodiment III
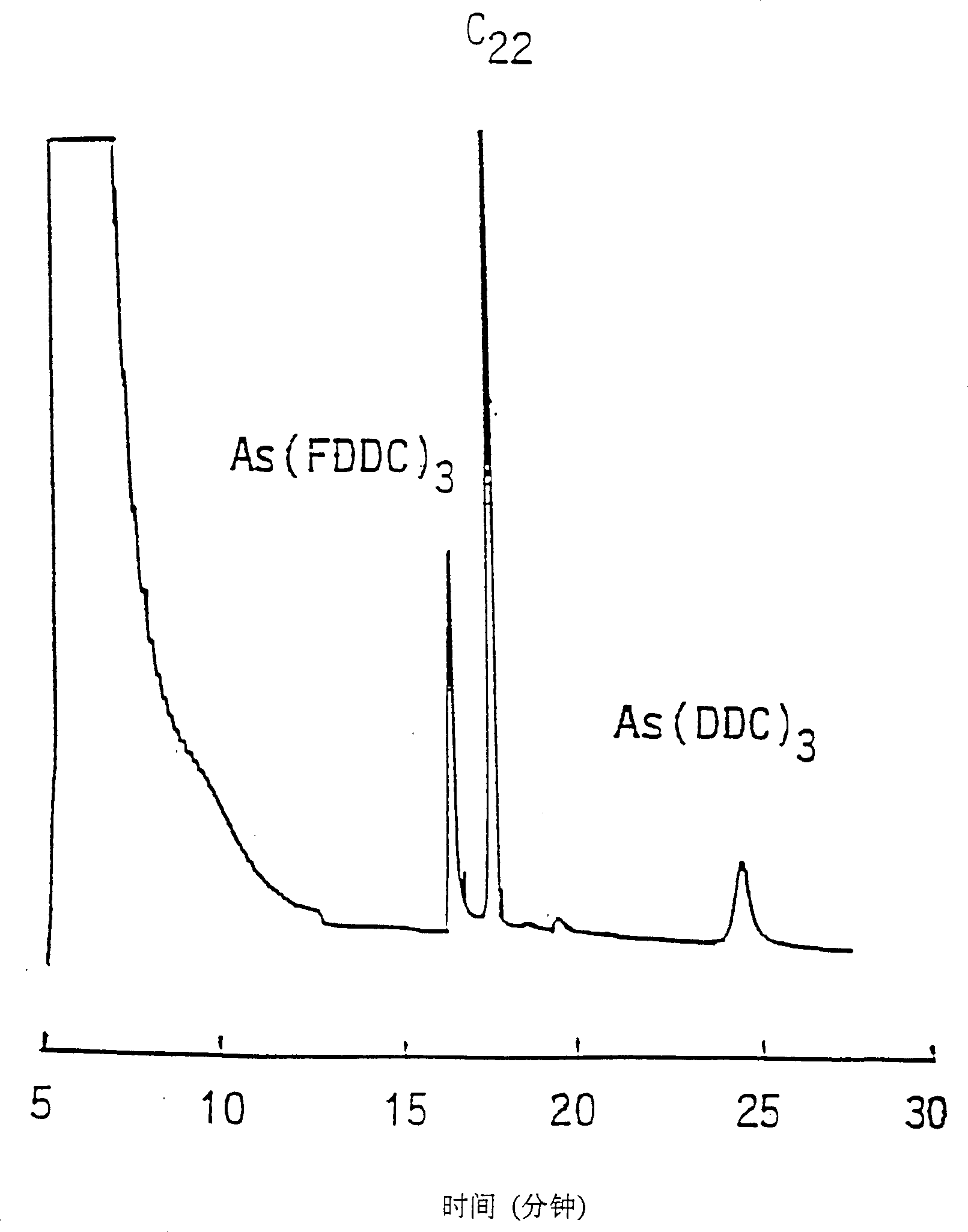
[0103] This example describes the use of fluorinated chelating agents for SFE according to the present invention. When implementing the above-mentioned extraction method, it is found that the solubility of the metal chelate in supercritical carbon dioxide will be enhanced after the fluorination of the chelating agent is combined. It has been found that fluorination of sodium diethyldithiocarbamate (DDC) to form sodium bis(trifluoroethyl)dithiocarbamate or lithium (FDDC) increases the concentration of metal diethyldithiocarbamate. The solubility is at least 3 orders of magnitude. For example, Cu(DDC) 2 The solubility in supercritical carbon dioxide measured by UV-visible light is (1.1±0.2)×10 -6 mol / L. After fluorinating the terminal methyl group of DDC, Cu(FDDC) 2 The solubility in supercritical carbon dioxide is (9.1±0.3)×10 -4 mol / L. Another example of increased solubility in supercritical carbon dioxide is obtained with acetylacetonate (ACAC) of the β-diketone. Cu(AC...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com