Method for controlling hydrogenation chrome molybdenum steel inclusions
A hydrogen-prone chromium-molybdenum and inclusion technology, applied in the field of hydrogen-prone chromium-molybdenum steel inclusion control, can solve the problems of reducing material plasticity, toughness and fatigue limit, anisotropy, cold and hot processing performance deterioration, etc., to achieve desulfurization Efficient and stable, reducing impurities and optimizing the casting process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
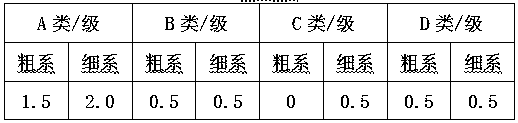
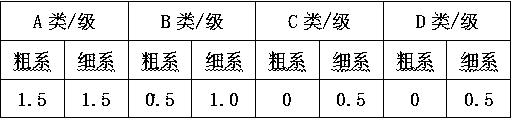
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] The method for controlling inclusions in hydrogen-prone chromium-molybdenum steel in this embodiment includes converter smelting, vacuum carbon deoxidation, LF refining, VD vacuum treatment, and continuous casting of slabs. The specific process steps are as follows:
[0020] (1) Converter smelting process: Smelting is carried out by the compound blowing method of stirring with top-blown oxygen and bottom-blown argon. During the process, lime is added to form slag, and the slag is melted throughout the process to control the alkalinity of the slag; at the end of blowing, the molten steel [C]: 0.07%, [P]: 0.006%, [S]: 0.023%, [O]: 700ppm, blowing end temperature is 1620℃;
[0021] (2) Vacuum carbon deoxidation process: Converter tapping does not add alloys and pre-deoxidizers, ladle temperature is 1570°C, directly enters the vacuum position, increases carbon to 0.11% according to the carbon content of molten steel, and then carries out vacuum carbon deoxidation treatment f...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The method for controlling inclusions in hydrogen-prone chromium-molybdenum steel in this embodiment includes converter smelting, vacuum carbon deoxidation, LF refining, VD vacuum treatment, and continuous casting of slabs. The specific process steps are as follows:
[0030] (1) Converter smelting process: Smelting is carried out by the compound blowing method of stirring with top-blown oxygen and bottom-blown argon. During the process, lime is added to form slag, and the slag is melted throughout the process to control the alkalinity of the slag; at the end of blowing, the molten steel [C]: 0.06%, [P]: 0.007%, [S]: 0.030%, [O]: 600ppm, blowing end temperature is 1630℃;
[0031] (2) Vacuum carbon deoxidation process: no alloy and pre-deoxidizer are added to the converter, the temperature of the ladle is 1580°C, and it directly enters the vacuum position, and the carburization is increased to 0.12% according to the carbon content of the molten steel, followed by vacuum ca...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The method for controlling inclusions in hydrogen-prone chromium-molybdenum steel in this embodiment includes converter smelting, vacuum carbon deoxidation, LF refining, VD vacuum treatment, and continuous casting of slabs. The specific process steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) Converter smelting process: Smelting is carried out by the compound blowing method of stirring with top-blown oxygen and bottom-blown argon. During the process, lime is added to form slag, and the slag is melted throughout the process to control the alkalinity of the slag; at the end of blowing, the molten steel [C]: 0.08%, [P]: 0.005%, [S]: 0.028%, [O]: 700ppm, blowing end temperature is 1600℃;
[0041] (2) Vacuum carbon deoxidation process: no alloy and pre-deoxidizer are added to the converter, the temperature of the ladle is 1575°C, and it directly enters the vacuum position, and the carburization is increased to 0.13% according to the carbon content of the molten steel, followed by vacuum ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com