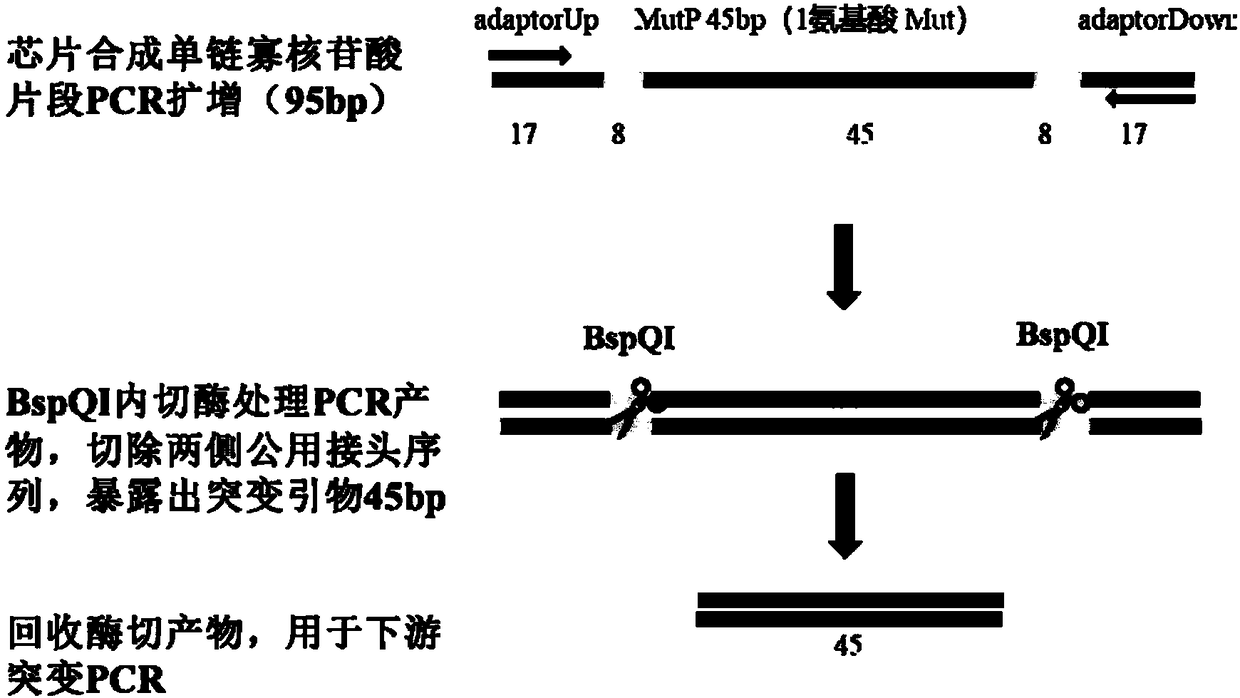
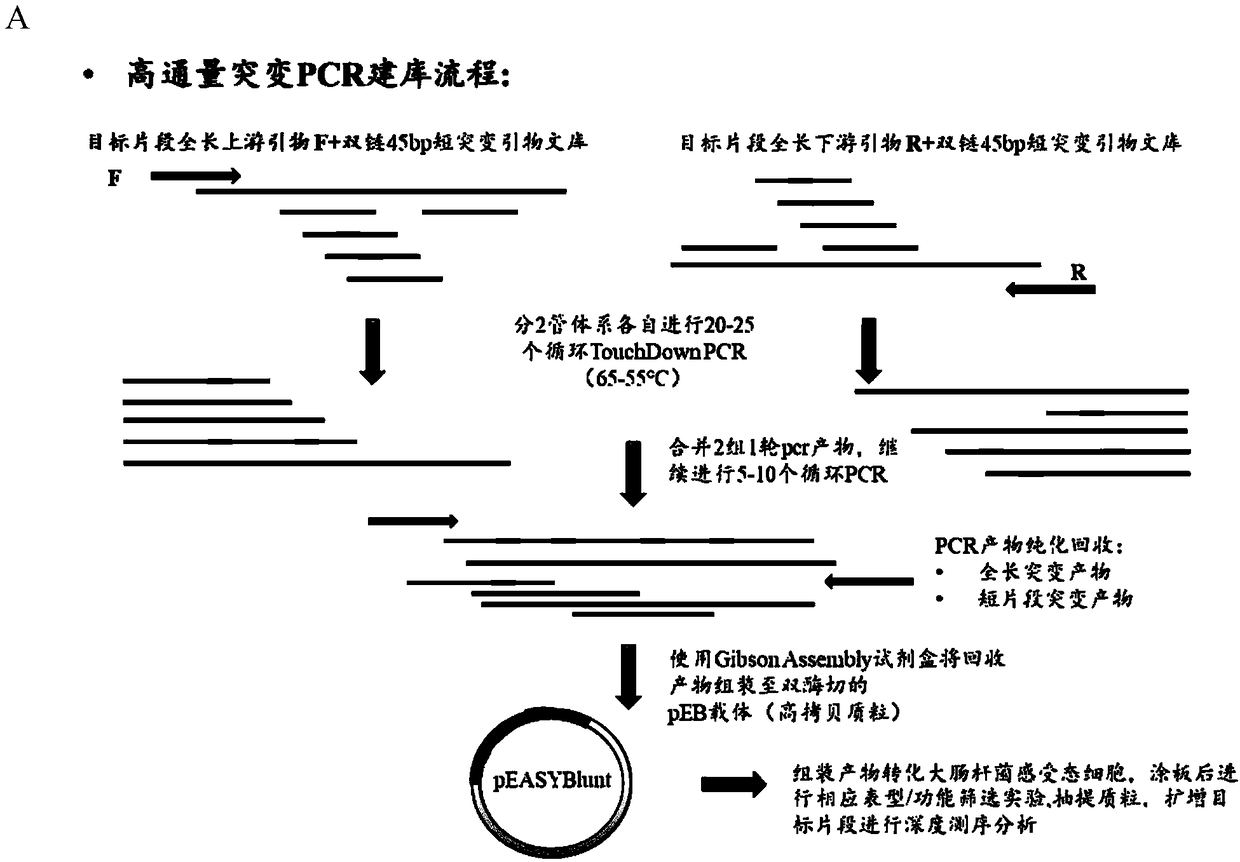
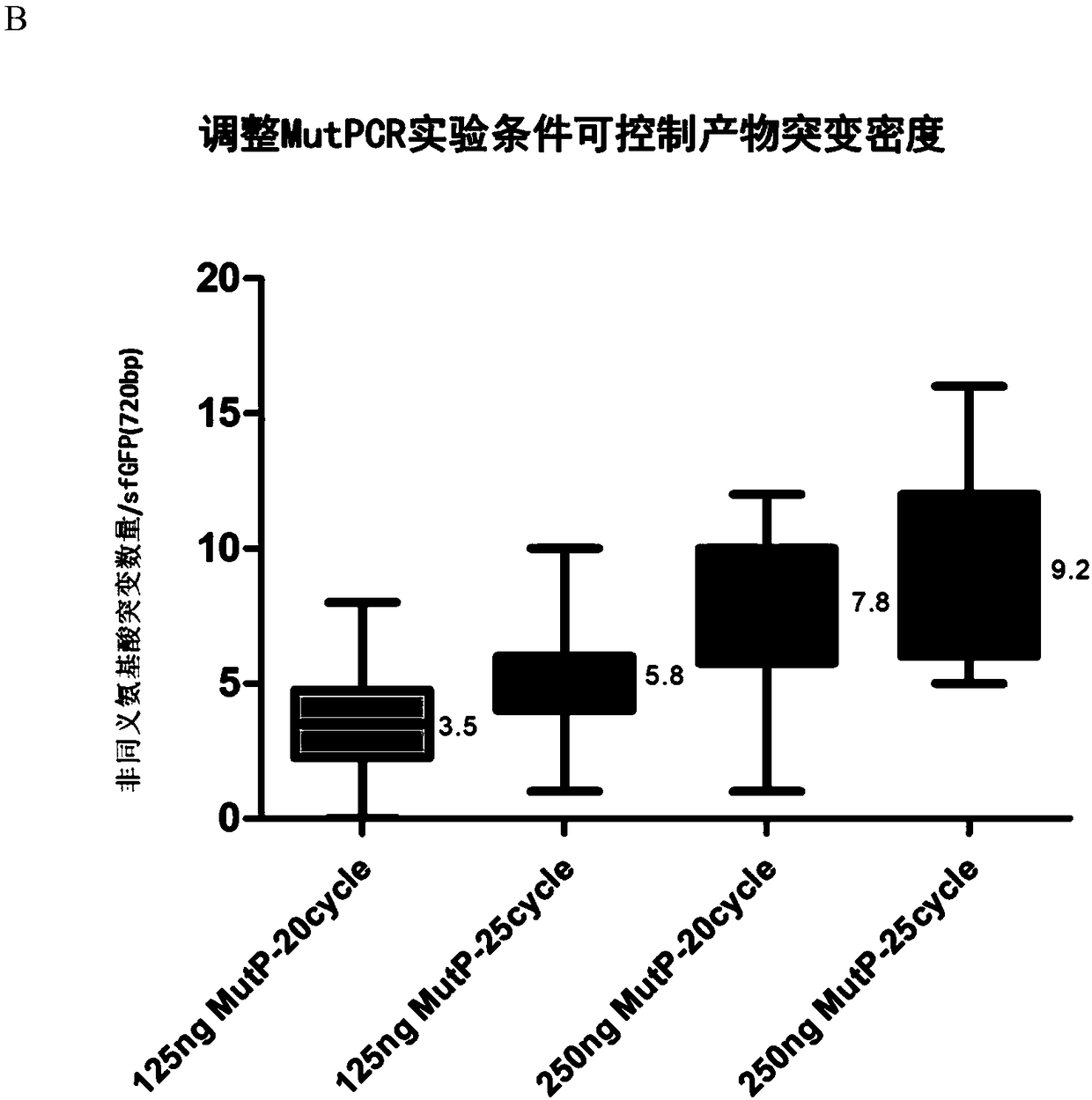
High throughput DNA multi-site precise base mutation method
A high-throughput, multi-site technology, applied in the field of gene manipulation, which can solve the problems of difficult screening experiments, large number of degenerate primers, and low PCR amplification efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1, Construction of GFP Full Amino Acid Saturation Mutant Library
[0055] In this example, the effectiveness of the mutation method described in the present invention was verified by constructing a full amino acid saturation mutant library of GFP.
[0056] 1. Selection of target gene sequence, primers for full amino acid site saturation mutation, and corresponding oligonucleotide chip synthesis sequence design.
[0057] (1) The gene template sequence to be mutated is selected as sfGFP (238aa, its gene sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1), and there are 13 amino acid substitutions (S2R, S30R, Y39N) compared with the amino acid sequence of GFP (Aequorea Victoria (Jellyfish)) , F64L, S65T, S72A, F99S, N105T, Y145F, M153T, V163A, I171V, A206V), without changing the spectrum, the fluorescence intensity and protein stability of GFP were improved.
[0058] (2) Select the target mutation site as the 2-238 amino acids except the first ATG start codon (a total of 237 amino ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com