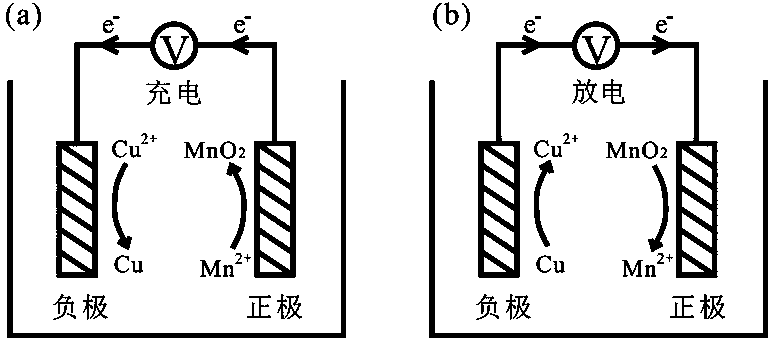
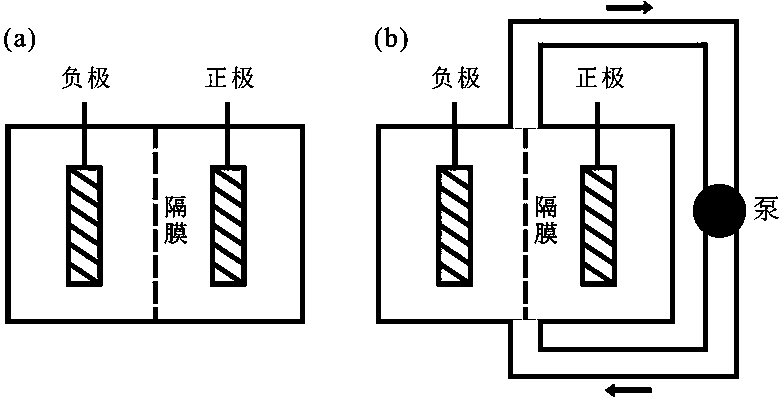
Copper-manganese aqueous secondary battery based on deposition/dissolution reaction on positive and negative poles
A secondary battery and two-pole technology, applied in secondary batteries, circuits, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of aggravating environmental pollution and increasing costs, and achieve high safety, high power energy density, and good charge and discharge performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: A copper-manganese secondary battery based on dual deposition / dissolution reactions of positive and negative electrodes, the negative current collector is copper foam, and the positive current collector is carbon paper.
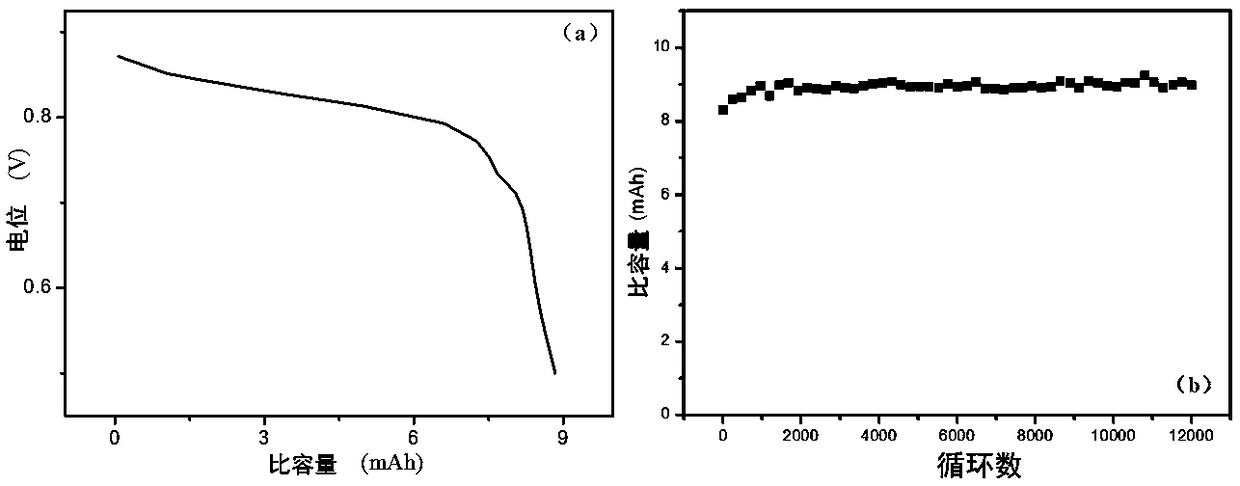
[0028] In this example, copper foam (3 cm*3 cm) is used as the negative current collector, carbon paper (3 cm*3 cm) is used as the positive current collector, and the electrolyte contains 1 mol / L copper sulfate, 1 mol / L manganese sulfate and 0.5 mol / L sulfuric acid (10 mL). The separator is a non-woven fabric, which only serves to prevent short-circuiting of the positive and negative electrodes. Constant voltage 1.2 V charging to 9 mAh (1 mAh / cm 2 ), 10 mA / cm 2 Discharged to 0.5V at a current density, the Coulombic efficiency reached 100% after 100 cycles. at 30 mA / cm 2 In the case of discharge, the Coulombic efficiency reaches 97%, and it can stably cycle 8000 times.
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2: A copper-manganese secondary battery based on dual deposition / dissolution reactions of positive and negative electrodes, the negative current collector is copper foam, and the positive current collector is carbon felt.
[0030] In this example, copper foam (3 cm*3 cm) is used as the negative current collector, carbon felt (3 cm*3 cm) is used as the positive current collector, and the electrolyte contains 1 mol / L copper sulfate, 1 mol / L manganese sulfate and 0.5 mol / L sulfuric acid (10 mL). The separator is a non-woven fabric, which only serves to prevent short-circuiting of the positive and negative electrodes. Constant voltage 1.2 V charging to 9 mAh (1 mAh / cm 2 ), 10 mA / cm 2 Discharged to 0.5V at a current density, the Coulombic efficiency reached 100% after 70 cycles. at 30 mA / cm 2 In the case of discharge, the Coulombic efficiency reaches 98%, and it can be stably cycled for 11,000 times.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3: A copper-manganese secondary battery based on dual deposition / dissolution reactions of positive and negative electrodes, the negative current collector is copper foam, and the positive current collector is graphite felt.
[0032] In this example, copper foam (3 cm*3 cm) is used as the negative current collector, graphite felt (3 cm*3 cm) is used as the positive current collector, and the electrolyte contains 1 mol / L copper sulfate, 1 mol / L manganese sulfate and 0.5 mol / L sulfuric acid (10 mL). The separator is a non-woven fabric, which only serves to prevent short-circuiting of the positive and negative electrodes. Constant voltage 1.2 V charging to 9 mAh (1 mAh / cm 2 ), 10 mA / cm 2 Discharged to 0.5V at a current density, the Coulombic efficiency reached 100% after 60 cycles. at 30 mA / cm 2 In the case of discharge, the Coulombic efficiency reaches 99%, and it can stably cycle 12,000 times.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com