Method for recovering nickel and molybdenum from waste nickel-molybdenum catalyst
A waste catalyst and catalyst technology, applied in the recovery of rare metals, recovery of nickel and molybdenum from waste nickel-molybdenum catalysts, can solve the problems of large amount of sodium carbonate, high energy consumption, strong corrosiveness of roasting equipment, etc. The effect of large, simple operation and easy continuous production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
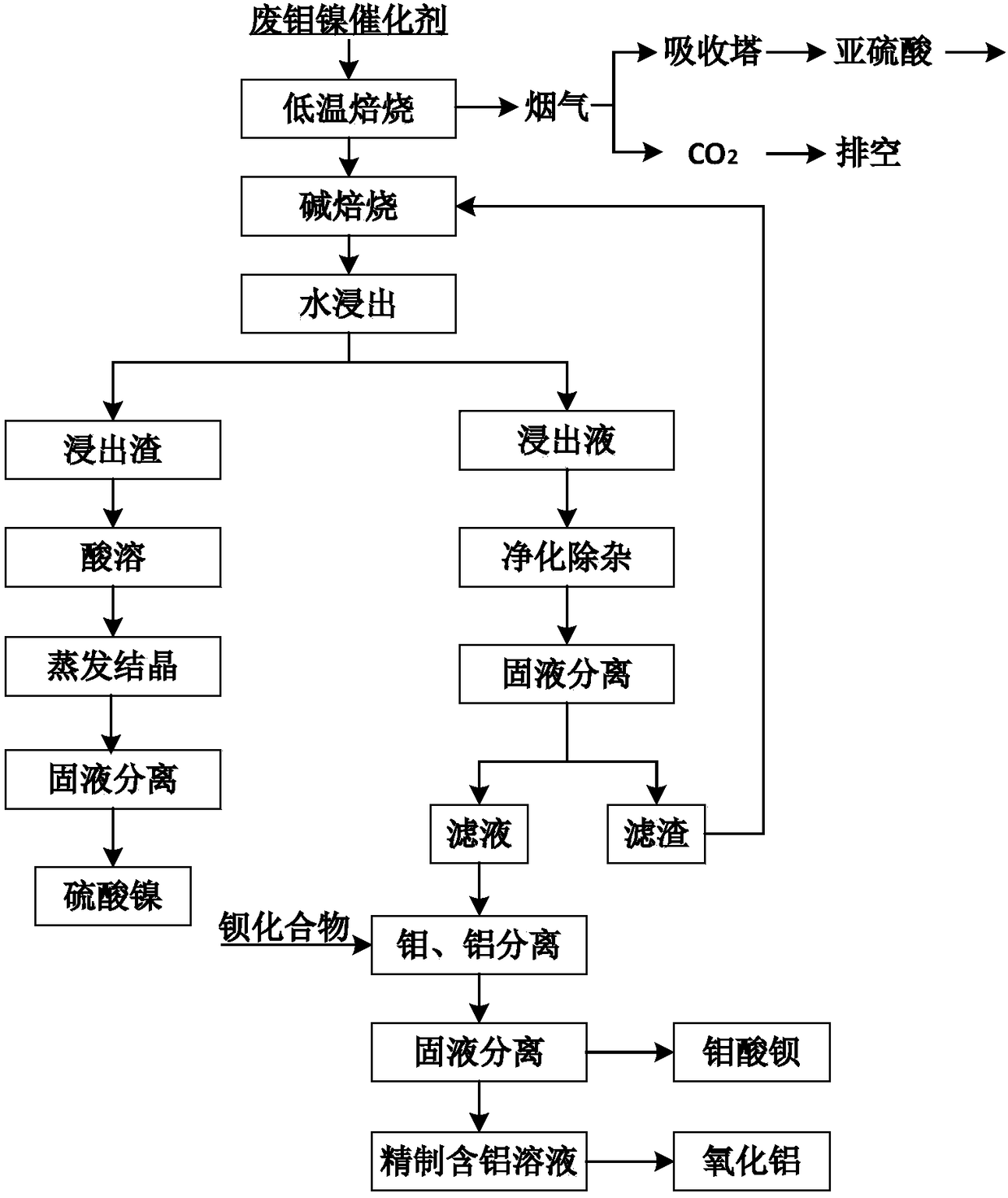
[0048] according tofigure 1 Shown process flow chart reclaims above-mentioned spent nickel-molybdenum catalyst, carries out according to the following steps:
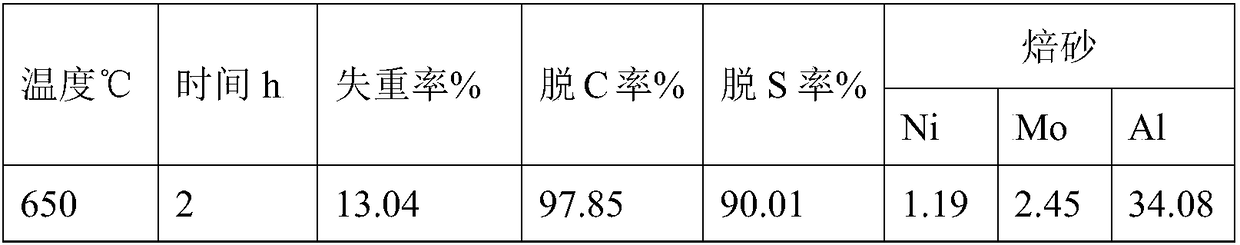
[0049] (1) Put the waste nickel-molybdenum catalyst to be treated into an electric heating type roaster for a period of low-temperature oxidation roasting. The roasting temperature is 650°C, the heating rate is 15-20°C / min, and the roasting time is 2h. At the same time, the valuable metal sulfide in the spent catalyst is converted into a valuable metal oxide; the flue gas is introduced into the spray alkali scrubber through the fan to remove SO 2 smoke.
[0050] Table 3 The results of the first-stage roasting test of waste nickel-molybdenum catalyst
[0051]
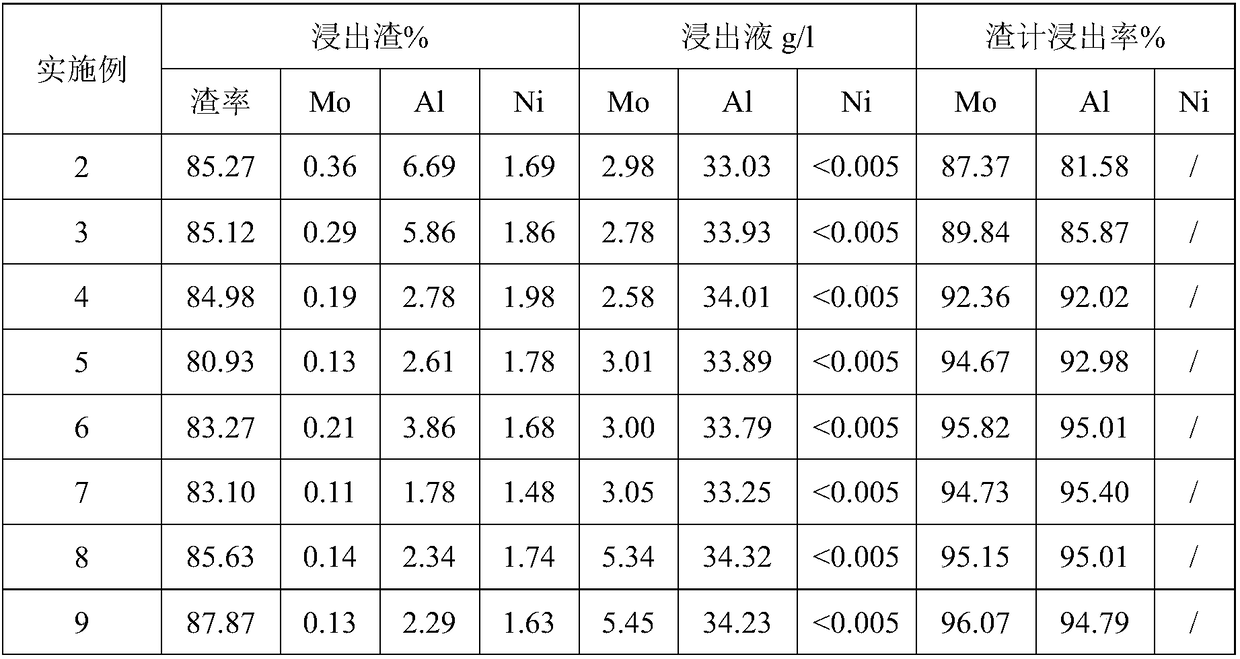
[0052] (2) After mixing the first-stage roasted material obtained in step (1) with sodium carbonate uniformly according to the molar ratio of 1:1.1, carry out the second-stage alkali roasting at high temperature, the roasting temperature is 1000°C, and the hea...
Embodiment 2
[0074] according to figure 1 The shown process flow chart reclaims the above-mentioned waste nickel-molybdenum catalyst, and the specific steps are the same as in Example 1, and the different reaction conditions are: a calcination temperature of 600° C., a calcination time of 2 h in the first stage; a calcination temperature of 950° C. in the second stage, and The roasting time is 70min, the ratio of alkali to material is 1.2:1; the temperature in the water leaching stage is 85°C, the time is 1.5h, and the liquid-solid ratio is 6:1; , the liquid-solid ratio is 7:1, and the time is 110 minutes; the molar ratio of barium hydroxide and molybdenum in the molybdenum precipitation stage is 2.5:1, the temperature is 80°C, and the time is 45min; the concentration of sodium bicarbonate in the neutralization and precipitation aluminum stage is 35g / L, and the temperature is 35°C , shaking time 8min.
Embodiment 3
[0076] according to figure 1 The shown process flow chart reclaims the above-mentioned waste nickel-molybdenum catalyst, and the specific steps are the same as in Example 1, and the different reaction conditions are: a calcination temperature of 580° C., a calcination time of 3 h in the first stage; a calcination temperature of 950° C. in the second stage, and The roasting time is 80 minutes, the ratio of alkali to material is 1.2:1; the temperature in the water leaching stage is 95°C, the time is 1h, and the liquid-solid ratio is 7:1; The liquid-solid ratio is 8:1, and the time is 120 minutes; the molar ratio between the precipitation molybdenum stage and molybdenum is 3:1, the temperature is 80°C, and the time is 50 minutes; the concentration of sodium bicarbonate in the neutralization and precipitation aluminum stage is 40g / L, the temperature is 35°C, and the shaking time is 10 minutes .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com