Detection reagent of atherosclerosis and preparation method thereof
A technology for detection of atherosclerosis and reagents, applied in the fields of biotechnology and clinical diagnosis, can solve the problems of not reflecting plaque vulnerability well, increased metabolic activity, false positives and false negatives, etc. The effect of high inflammation and low inflammation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Example 1. Synthesis of Polypeptide Derivative-like Atherosclerosis Detection Reagents
[0053] Taking a specific detection reagent compound of the present invention as an example, its synthesis steps are as follows:
[0054] (1) The derivative polypeptide sequence (Fmoc-Pip-Lys(Boc)-Lys-(Boc)-Arg(Pbf)-Pro-Hyp) protected by Fmoc was synthesized on 2-chlorotrityl chloride resin by solid-phase synthesis method (tBu)-Gly-Cpg-Ser(tBu)-D-Tic-Cpg). The resin was treated with 20% piperidine / DMF to remove the Na-Fmoc protecting group. 4-(Bromomethyl)phenylacetic acid (3 equiv) was activated with N,N'-diisopropylcarbodiimide (3 equiv) in 5 mL of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone and then coupled to N- end. Subsequently, 1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4-bis(tert-butyl acetate) (3 equiv.) was alkylated by secondary amine in 5 mL of N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone Coupled to a polypeptide sequence. The polypeptide was cleaved from the resin with 95% TFA, and the synthesized polypeptide was purified by...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Embodiment two, stability analysis
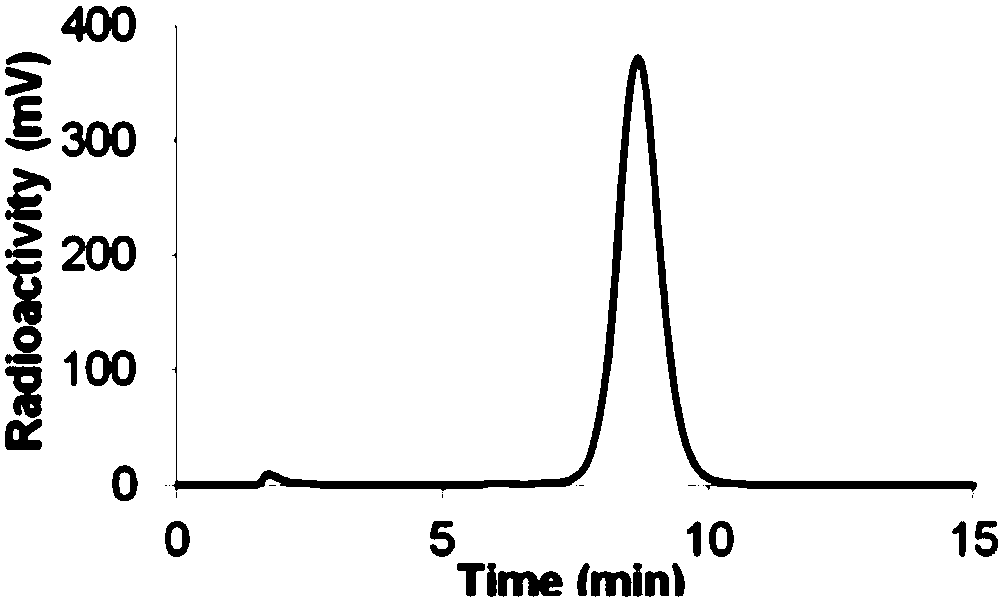
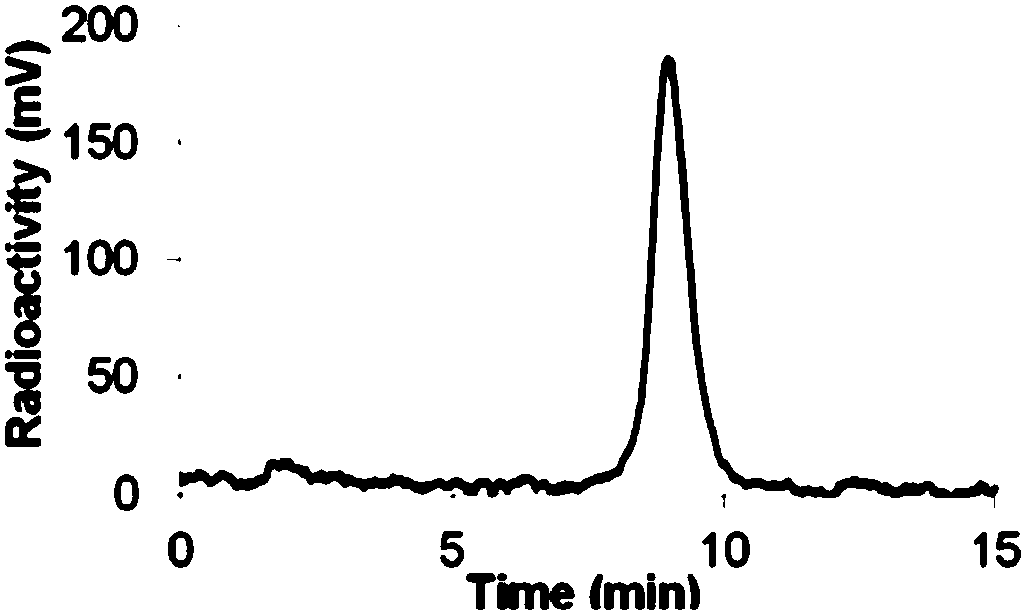
[0058] Stability is an important indicator of in vivo diagnostic reagents. The detection reagents prepared in Example 1 were incubated in phosphate buffer and mouse serum at 37°C for 5, 15, 30, 60, and 120 minutes, and quenched with 70% acetonitrile at the end. Inactivated and centrifuged for 20 minutes, the stability of the polypeptide was determined by radioactive HPLC. The stability of the polypeptide in phosphate buffer saline and mouse serum can maintain at least two half-lives, indicating that the polypeptide has good stability.
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3. Specific identification of easily exfoliated plaques of atherosclerosis
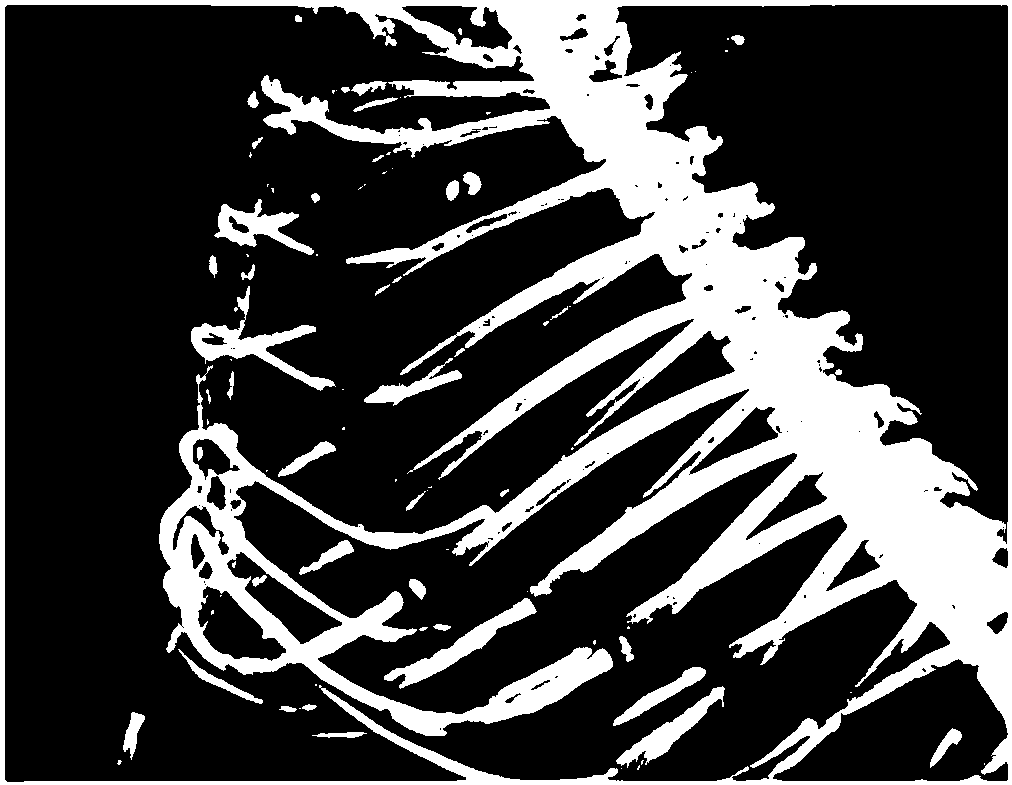
[0060] Feeding ApoE knockout mice with high-fat diet is a common way to construct atherosclerosis model. After ApoE- / - mice were fed high-fat diet for 40 weeks, routine methods were used to identify high-risk atherosclerosis (easy shedding, low calcification) individuals and low-risk atherosclerosis (hard shedding, high calcification) individuals. 7.4 MBq of the detection reagent prepared in Example 1 was injected through the tail vein, and PET / CT imaging was performed 20 minutes later. image 3 The CT and PET / CT imaging results are given, showing that the polypeptide has high radioactive signal at the easily exfoliated plaque, but almost no radioactive signal at the calcified plaque visible on CT, realizing the anti-exfoliative plaque of atherosclerosis specific identification.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com