Chitosan superfine fiber systems
A technology of chitosan and chitosan salt, which is applied in fiber treatment, fiber chemical characteristics, melt spinning, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the functional ability of polymers to interact with cells, and achieve the effect of promoting hemorrhage control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
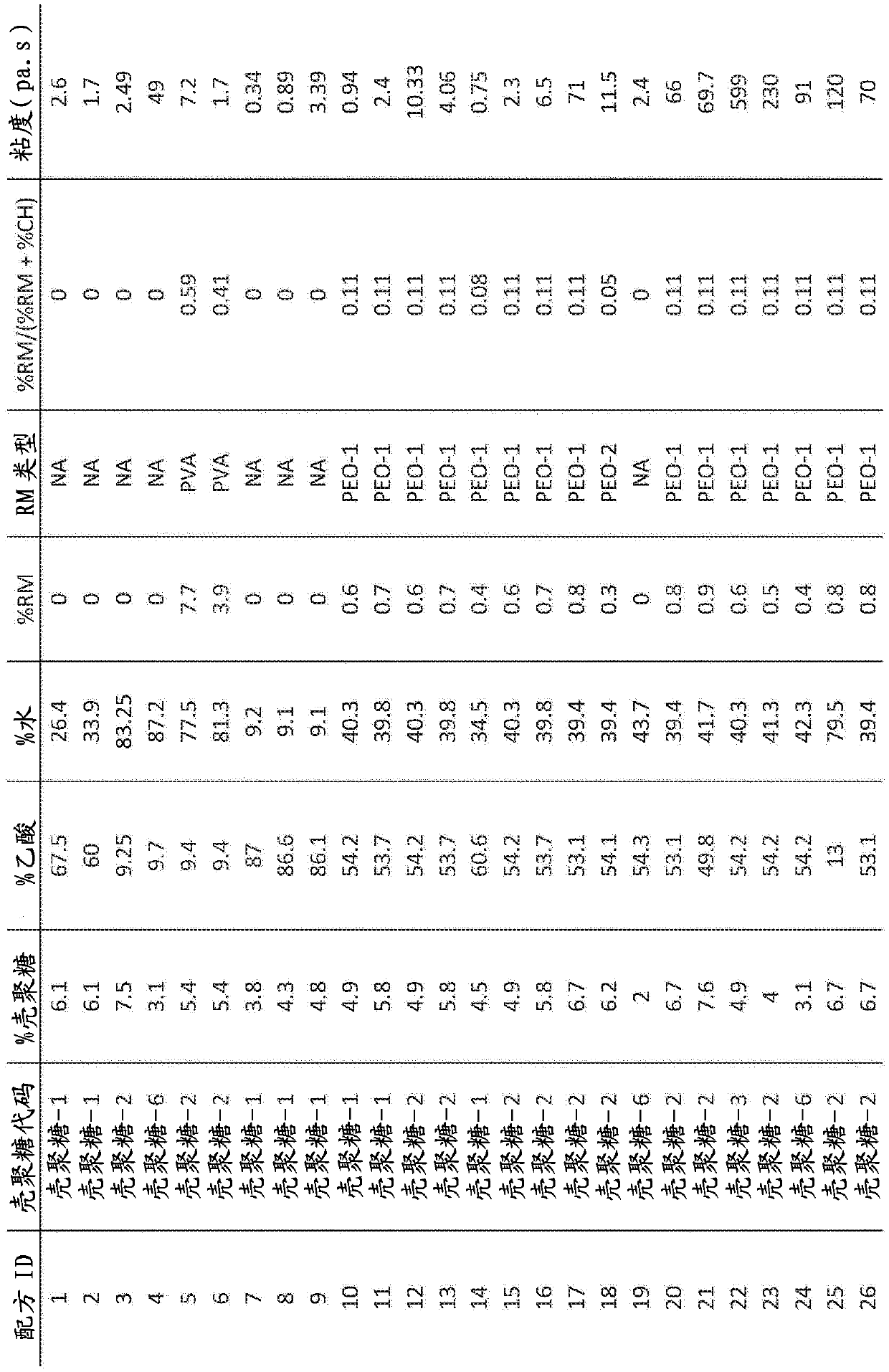
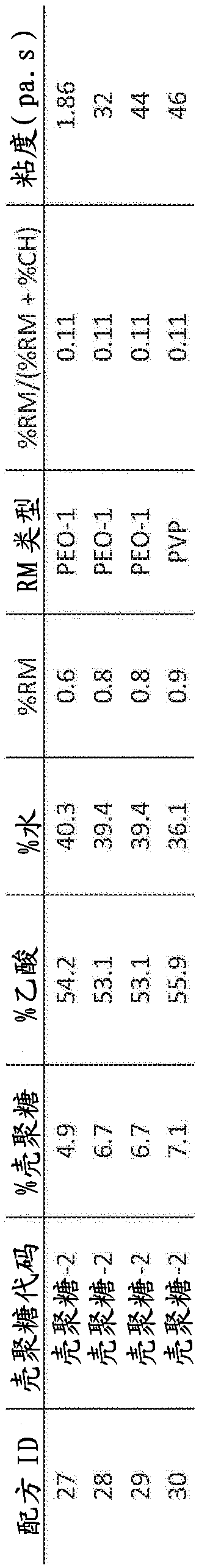
[0077] Example 1 details results from pilot scale experiments. Subsequent evaluations from Formulation 25 had a basis weight of 17.6 g / cm 2 Fiber samples of: a) tissue attachment and stability (see Example 2), and b) hemostatic efficacy in an anticoagulated porcine injury model of gastrointestinal bleeding (see Example 3).
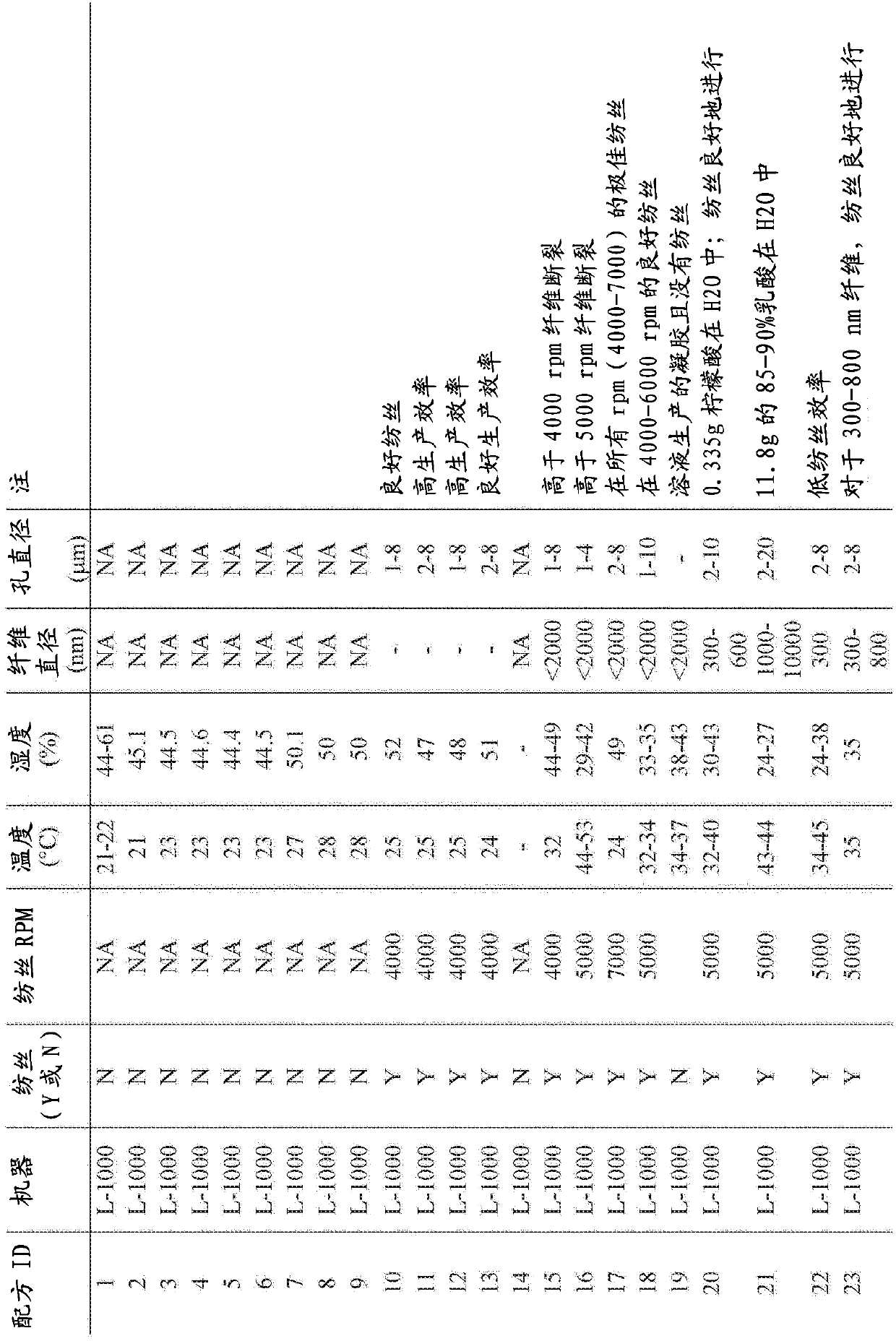
[0078] Example 1. Formulations 25-30, Example Fiber Tests: On Production Scale Spinning on FE 1.1 (FibeRio Technology Corporation)
[0079] Tables 1, 2 and 3 demonstrate that a chitosan-based solution (with a polymer content of 89% w / w chitosan and 11% w / w polyethylene oxide (400 kDa)) was tested on a pilot scale machine (FE1. 1) Spinnability under centrifugal spinning. One polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) formulation (#30) was not successfully spun. The typical flow rate of the chitosan solution from FE1.1 during spinning is about 5.0 g / min, the fastest flow rate is about 8.0 g / min from the spinneret. Since the highest expected flow rate specified for FE1...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Example 2. In vitro tests of ultrafine chitosan fibers for tissue adhesion, foldability and dissolution resistance in harsh biological environments such as the stomach
[0089] INTRODUCTION: Tissue adhesion, foldability, and resistance to dissolution in harsh biological environments such as the stomach are highly desirable features of ultrafine chitosan fiber nonwoven matrices intended for medical applications, which Includes external wound care, internal implantation, drug delivery, hemostatic applications, and delivery through endoscopes or catheters for minimally invasive wound care and hemostasis.
[0090] a) The dissolution resistance to synthetic gastric juice at 37°C was studied as follows. Synthetic gastric juice was prepared according to a formulation of pepsin (1.6 g), NaCl (1 g), water (500 ml), all added to a Nalgene LDPE 1000 ml bottle and mixed. The acidity was adjusted to pH 3-4 using Millipore pH 0-14 Universal Indicator Strips and 3.0M HCl was added dr...
Embodiment 3
[0098] Example 3. Porcine injury model of hemostasis, manual application in gastric injury to evaluate the efficacy of chitosan-based ultrafine nonwoven fibers: a) 15 minutes after application; and b) closed and evaluated by gastroscopy at 180 minutes Evaluation of hemostasis in the stomach
[0099] Foreword: Application of observations and successful bleeding control of arterial bleeding in the anticoagulated bleeding model described in this example not only demonstrates the application of the tissue-attached ultrafine chitosan fibers of the present invention in targeted wound care, bleeding and general wound care It has broad applicability for fluid loss and has also demonstrated particular suitability for fluid loss in addressable wound care, bleeding, and minimally invasive procedures, such as control of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
[0100] Methods: All experiments were performed in accordance with the 2011 National Research Council "Guide for the Care and Use of Labo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com