Method for rapidly determining biomass in liquid fermentation liquor
A liquid fermentation and rapid determination technology, applied in the field of biomass determination, can solve the problems of cumbersome operation, high cost, and great difficulty, and achieve the effects of strong correlation, less reagent consumption, and strong operation convenience
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] Example 1 Monascus (Monascus) Determination of bacterial count
[0035] Insert Monascus spores into the centrifuged fermentation medium without precipitation, and after 3 days of fermentation, centrifuge the fermentation broth at 4500rpm for 10 minutes, discard the supernatant, and obtain the precipitation of Monascus pure bacteria; preparation of the fermentation medium without precipitation by centrifugation: monosodium glutamate 22.33 g, ammonium sulfate 9.72g, anhydrous glucose 42.50g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 9.00g, manganese sulfate monohydrate 0.21g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 2.1g, add water to 1000mL, autoclave at 121℃ for 20 minutes;
[0036] Insert Monascus spores into the fermentation medium with precipitation in centrifugation, centrifuge the fermentation broth at 4500rpm for 10min after 3 days of fermentation, discard the supernatant, and obtain the mixed precipitation of Monascus thallus and medium; prepare the fermentation medium with precipit...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2 Rhizopus oryzae (Rhizopus oryzae) Determination of bacterial count
[0047] The determination steps of the metal ion method are consistent with the operation steps of the amount of Monascus in Example 1. The standard curve between the absorbance value ΔA of Rhizopus oryzae and the mass of pure bacteria is shown in Table 3. The determination comparison between the metal ion method and the glucosamine method is shown in Table 4.
[0048] Table 3 Relevant data of the determination of the amount of Rhizopus oryzae
[0049]
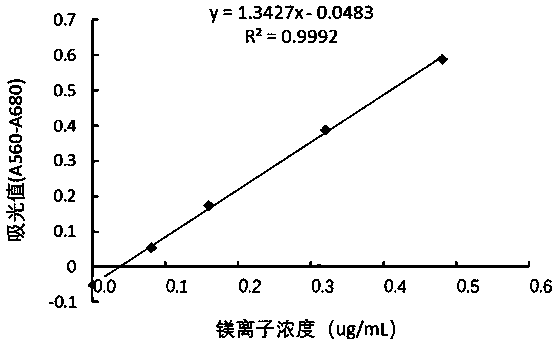
[0050] The standard curve between △A and the mass of pure bacteria is: y=3.7039x-0.0483, R 2 =0.9992.
[0051] Table 4 Comparison of different determination methods
[0052]
[0053] The correlation coefficient of the two determination methods is 0.9835, which means that there is 98.35% certainty that the two determination methods are related.
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Paecilomyces (Paecilomyces sp.) Determination of bacterial count
[0055] The determination steps of the metal ion method are consistent with the operation steps of the amount of Monascus in Example 1. The standard curve between the absorbance value ΔA of Paecilomyces and the mass of pure bacteria is shown in Table 5. The determination comparison between the metal ion method and the glucosamine method is shown in Table 6.
[0056] Table 5 Relevant data of Paecilomyces determination and standard curve drawing
[0057]
[0058] The standard curve between △A and the mass of pure bacteria is: y=0.1135x-0.0609, R 2 =0.9986.
[0059] Table 6 Comparison of different assay methods
[0060]
[0061] The correlation coefficient of the two determination methods is 0.9825, which means that there is 98.25% certainty that the two determination methods are related.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com