Extracellular vesicle and inclusion extraction method and device based on electrostatic adsorption
An extraction device and electrostatic adsorption technology, applied in the field of extracellular vesicle separation and extraction, can solve the problems of low yield, cumbersome operation, and low sample purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Example 1 Adsorption of anion exchange resin particles to extracellular vesicles
[0064] 1. Preparation of reagents and consumables
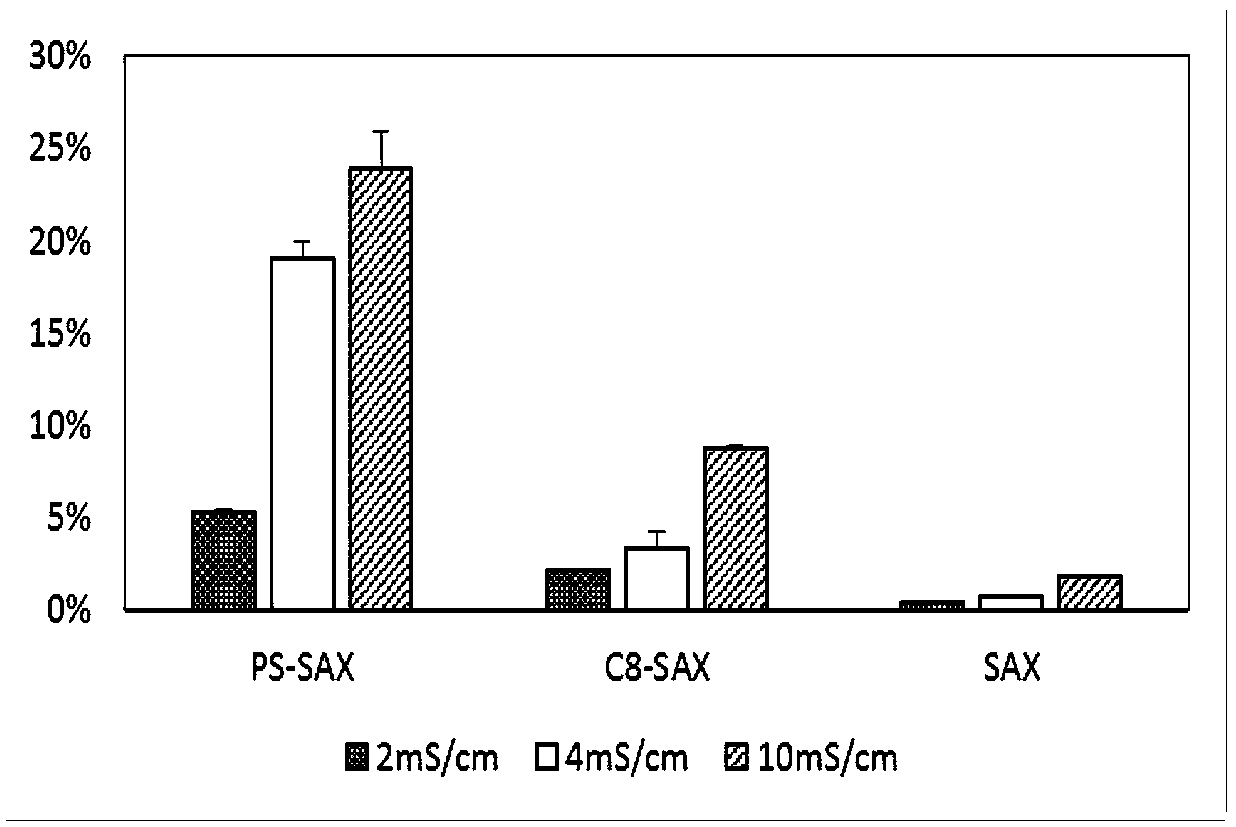
[0065] The anion exchange resin particles used include polystyrene particles with quaternary ammonium functional groups (PS-SAX), silica gel particles with C8 and quaternary ammonium functional groups (C8-SAX) and silica gel particles with quaternary ammonium functional groups (SAX), particle size Between 30-800μm. Cell membrane green fluorescent probe DIO. Commercial human serum. Dilute the PBS solution at pH 7.4 with DI water to prepare buffer solutions with conductivity of 2mS / cm, 4mS / cm and 10mS / cm respectively.
[0066] 2. Preparation of green fluorescently labeled extracellular vesicles (fEVs)
[0067] Thawed commercial human plasma was centrifuged at 1300g for 15 minutes to remove cytoplasmic debris. Then transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 3000g for 15 minutes, mix the supernatant with PBS at a v...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2 Adsorption effect of different device forms on fEVs
[0072] 1. Preparation of reagents and consumables
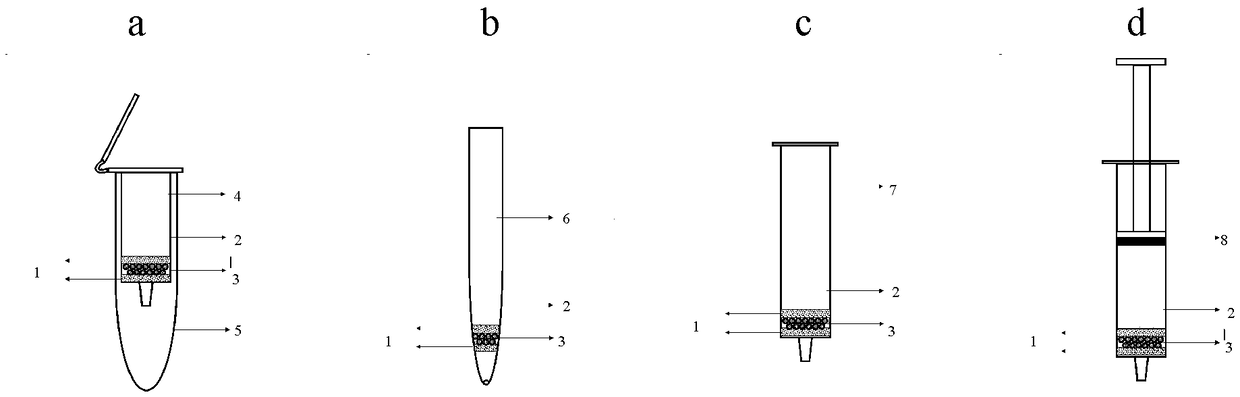
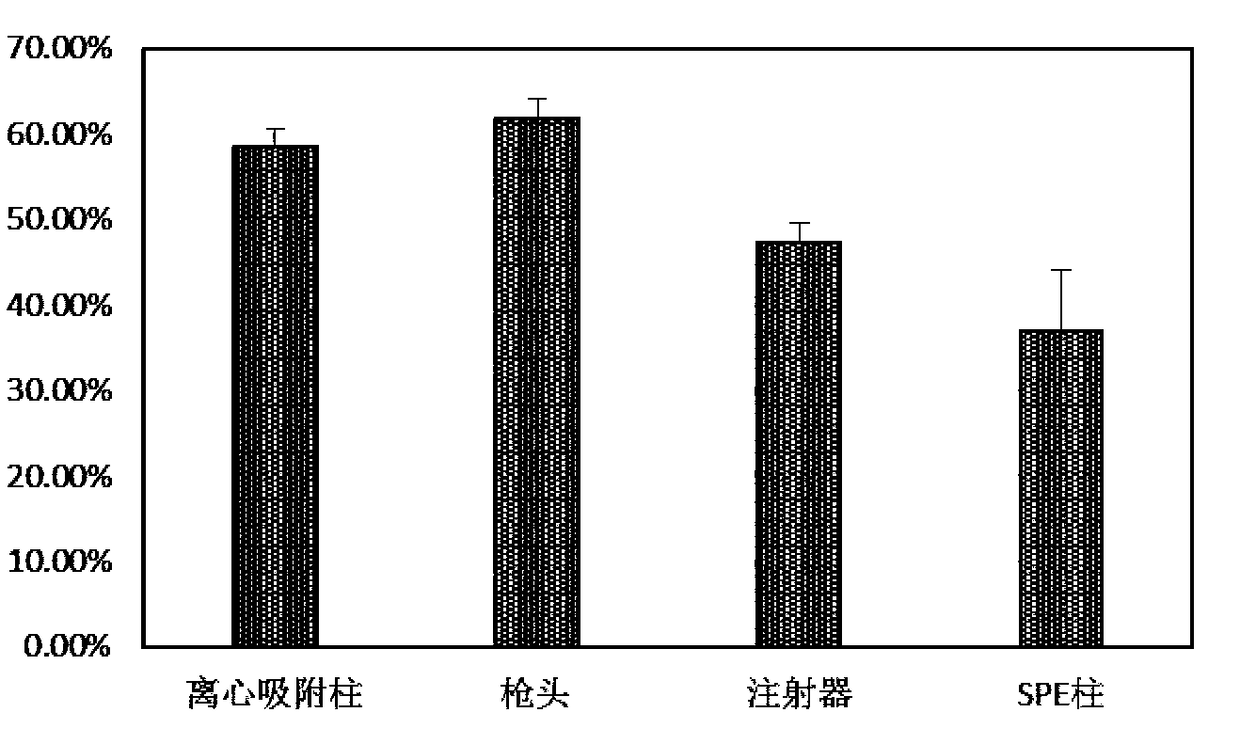
[0073] The anion exchange resin particles used are silica gel particles (SAX) with quaternary ammonium functional groups, and the particle size is between 30-800 μm. Green fluorescently labeled extracellular vesicles (fEVs) were prepared in the same way as in Experimental Example 1. The centrifugal adsorption column used is a centrifugal empty column with an outer tube volume of 15 mL. Use a pipette with a standard 1mL tip. The syringe used is a 1mL disposable syringe. The solid phase extraction column (SPE column) used was an empty SPE column (12 mL) with an inner diameter of 13 mm. Unless otherwise specified, the sieves used are all hydrophobic sieves with a pore size of 10 μm. The specific assembly method is as figure 1 shown.
[0074] 2. Adsorption of fEVs by anion exchange resin particles with different assembly forms
[0075]Add fEVs to PBS b...
Embodiment 3
[0076] The influence of embodiment 3 conductivity on EVs trapping effect
[0077] 1. Preparation of reagents and consumables
[0078] The centrifugal adsorption column used is a centrifugal empty column with an outer tube volume of 15 mL, and the selected sieve plate is a hydrophobic sieve plate with a pore size of 10 μm. The used anion exchange resin particles are silica gel particles (SAX) with quaternary ammonium functional groups, and the particle diameter is 30-800 μm. The biological sample used is the supernatant of 22rv1 cells cultured in exosome-free fetal bovine serum medium, which is filtered through a 0.45 μm filter membrane before use. Use DI water and NaCl to adjust the conductivity of the cell supernatant between 4-80mS / cm. The kit used for EVs nucleic acid extraction was miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen). The obtained RNA was analyzed with Agilent RNA 6000 Pico Kit.
[0079] 2. Capture EVs in cell supernatant and extract RNA
[0080] Such as figure 1 Assemble the...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com