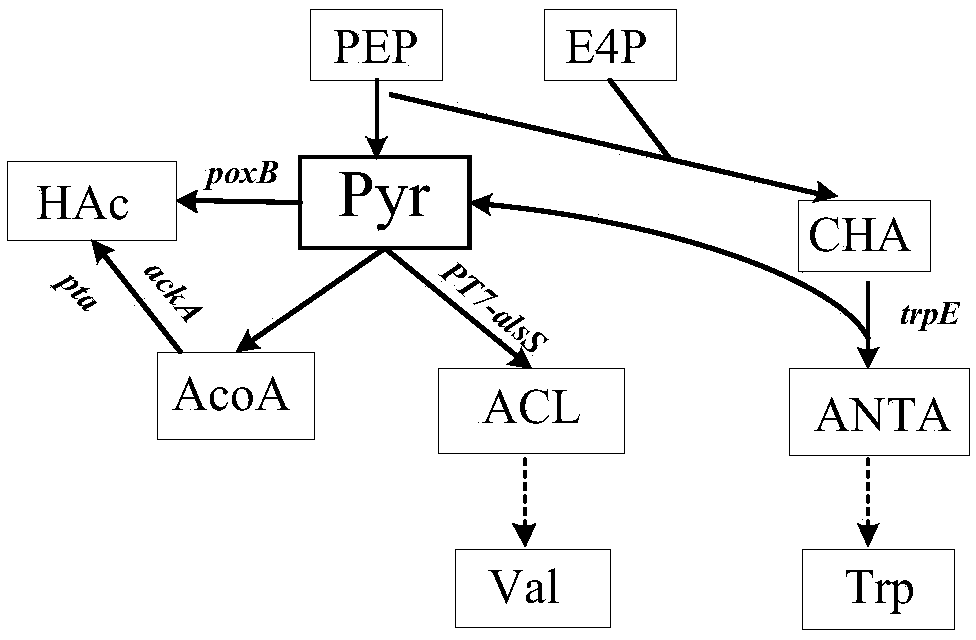
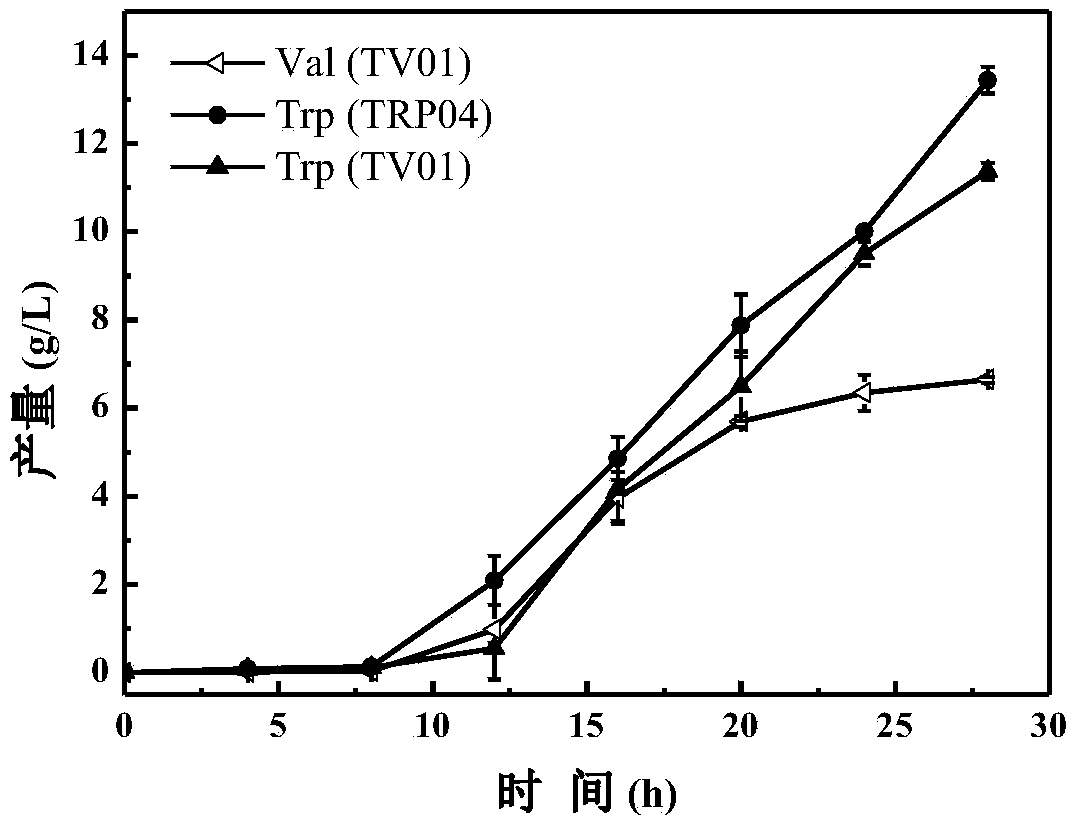
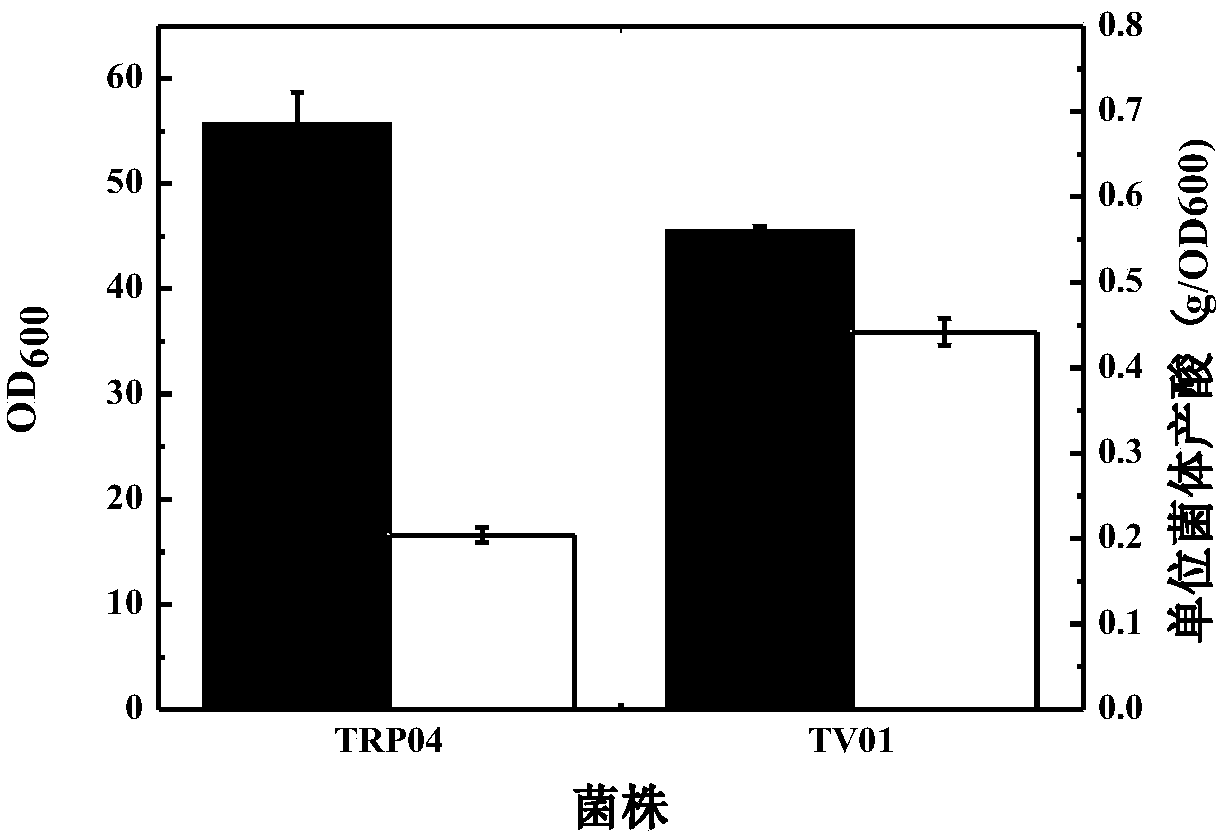
Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium and application of escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterium to synchronous production of L-tryptophan and L-valine through fermentation
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and Escherichia coli, applied in the field of microbial metabolism regulation and genetic engineering, can solve the problems of weakening, affecting the accumulation of target products in cells, insufficient supply of oxaloacetic acid, etc. The effect of trait improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Construction of Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria TV01 for synchronous fermentation of L-tryptophan and L-valine
[0045] 1. Methods of gene editing
[0046] The gene editing method used in the present invention is carried out with reference to the literature (Li Y, Lin Z, Huang C, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using CRISPR–Cas9 edited genome editing. Metabolic engineering, 2015, 31:13-21.), the method used The two plasmids are pREDCas9 and pGRB, in which pREDCas9 carries the elimination system of gRNA expression plasmid pGRB, the Red recombination system of lambda phage and the Cas9 protein expression system, spectinomycin resistance (working concentration: 100mg / L), cultured at 32°C ;pGRB uses pUC18 as the backbone, including promoter J23100, gRNA-Cas9 binding region sequence and terminator sequence, ampicillin resistance (working concentration: 100mg / L), and cultured at 37°C.
[0047] The concrete steps of this method are...
Embodiment 2
[0121] Embodiment 2: Synchronous production of L-tryptophan and L-valine by Escherichia coli genetic engineering bacteria TV01 shake flask fermentation
[0122] The specific operation of using Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria to carry out shake flask fermentation to produce L-tryptophan and L-valine synchronously is as follows:
[0123] Slant culture: Streak inoculation of -80°C preserved strains on the activated slant, culture at 37°C for 12 hours, and passage once;
[0124] Shake flask seed culture: use the inoculation loop to scrape the second-ring slant seeds and inoculate them into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 30mL of seed medium, seal with nine layers of gauze, and culture at 37°C and 200rpm for 8-10h;
[0125] Shake flask fermentation culture: Inoculate 10-15% inoculum into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask with fermentation medium (final volume is 30mL), seal with nine layers of gauze, 37°C, 200r / min shaking culture, during the fermentation process by sup...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com