Resource recycling method for N-methylmorpholine oxide in lyocell fiber production process
A technology of methylmorpholine and production process, which is applied in the field of recovery of N-methylmorpholine oxide in the production process of lyocell fiber, which can solve the problems of short resin life, heavy pollution in the recovery process, unstable production process, etc. , to achieve the effect of reducing recycling cost, short service life and cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
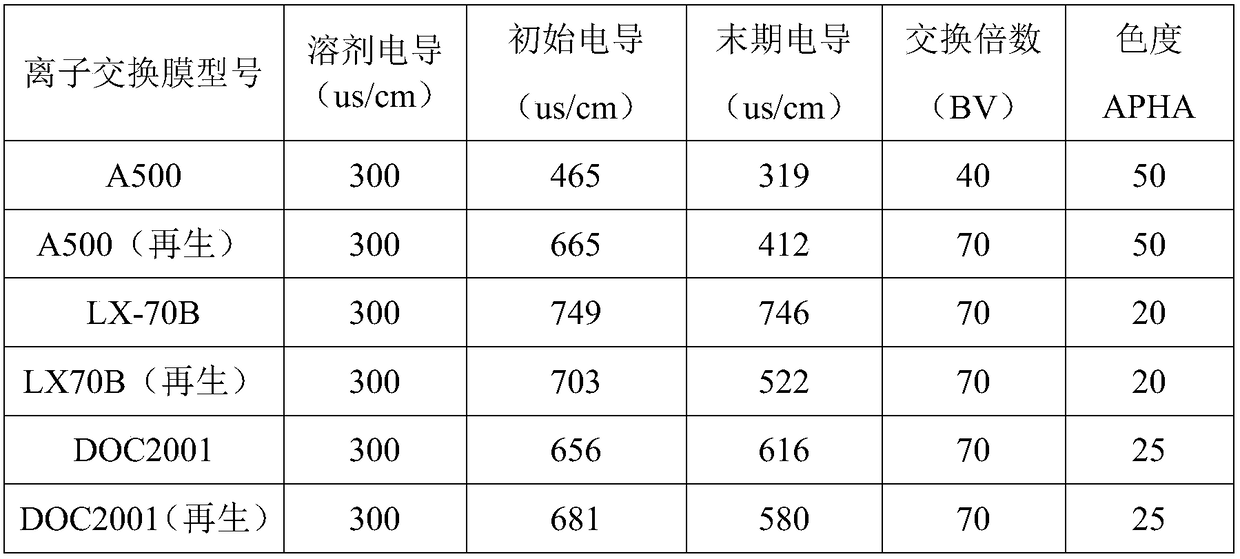
[0049] A method for resourceful regeneration of ion exchange resins in the production process of lyocell fibers, comprising the steps of:
[0050] Step 1, the first resource regeneration:
[0051] 1) First drain the NMMO solution in the ion exchanger, and then continuously inject fresh water to clean the ion exchanger. The cleaning solution generated by cleaning is divided into three stages for recovery, and the cleaning solution in the first stage is recovered and mixed with The previously discharged NMMO solution is used together as the NMMO solution to be recovered; the cleaning solutions of the second stage and the third stage are recovered and stored separately, and used as primary reuse water and secondary reuse water for the next cleaning of the ion exchanger;
[0052] 2) Regenerate the cation exchange membrane in the ion exchanger after step 1) cleaning: continuously feed the acid regeneration solution to clean the cation exchange membrane, the acid regeneration soluti...
Embodiment 2
[0071] A kind of recycling regeneration method of ion exchange resin in the lyocell fiber production process, with embodiment 1, difference is:
[0072] In step 1), end the recovery of the first stage when the NMMO in the cleaning solution is 1%, and enter the recovery of the second stage; end the recovery of the second stage when the NMMO in the cleaning solution is 0.05%, and enter the recovery of the third stage .
[0073] In step 2), the alkali that constitutes the alkali regeneration solution is potassium hydroxide; the saturated brine that constitutes the alkali regeneration solution is a saturated potassium chloride solution; in the alkali regeneration solution, the mass concentration of the alkali is 3%, and the salt The concentration of the lye is 5%; the alkali lye after the cleaning is diluted 80 times with pure water and is discharged when the Hazen color is less than 100 with a 50ml colorimetric tube, and the recovery of the second stage is entered; the lye after ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] A kind of recycling regeneration method of ion exchange resin in the lyocell fiber production process, with embodiment 1, difference is:
[0077] In step 1), end the recovery of the first stage when the NMMO in the cleaning solution is 3%, and enter the recovery of the second stage; end the recovery of the second stage when the NMMO in the cleaning solution is 1%, and enter the recovery of the third stage .
[0078] In step 2), the alkali that constitutes the alkali regeneration solution is potassium hydroxide; the saturated brine that constitutes the alkali regeneration solution is a saturated potassium chloride solution; in the alkali regeneration solution, the mass concentration of the alkali is 5%, and the salt The concentration of the lye is 20%; the lye after the cleaning is diluted 80 times with pure water and used as a 50ml colorimetric tube to complete the discharge when the Hazen color is less than 1000, and the recovery of the second stage is entered; the lye...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com