Method for separating, screening and identifying earthworm gut culturable antibiotic resistant bacteria
A technology of antibiotic resistance, isolation and screening, applied in the field of soil biology, can solve the problems of colony screening, etc., and achieve the effect of easy control of the environment, simple operation and reliable operation method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
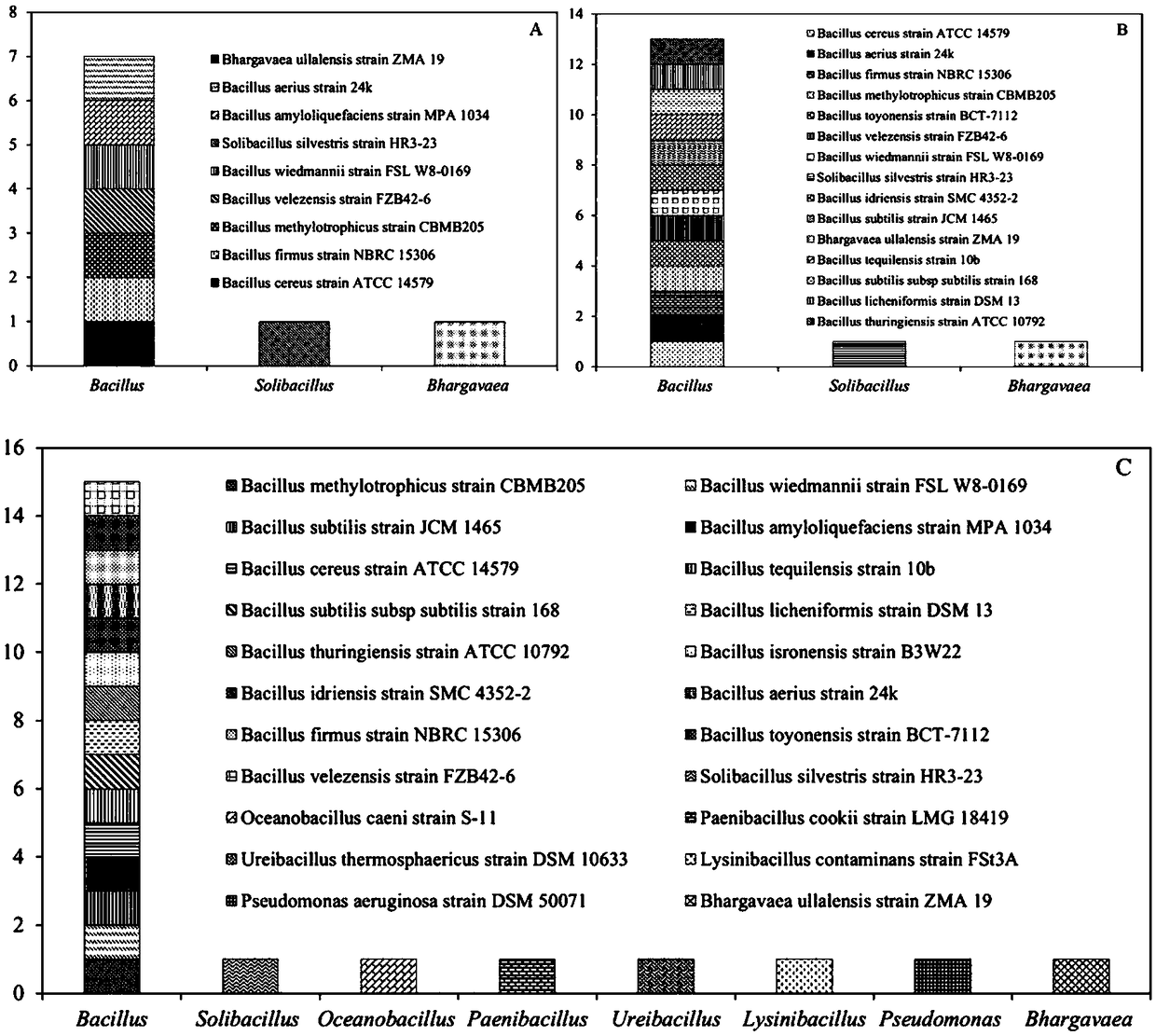
[0023] Example 1 Method for the isolation, screening and identification of a single tetracycline-resistant bacterium in the intestinal tract of Eisenia chinensis
[0024] Samples were collected in an earthworm farm in Huaian City, Jiangsu Province. The farm used pig manure, cow dung, a small amount of wheat bran and mushroom residue as raw materials to raise earthworms, and the temperature was kept at about 25 °C. Select the red Eisensis with a body weight in the range of 0.3-0.5g and obvious rings (Eisenia foetida) As experimental objects, they were placed on ice packs and quickly transported back to the laboratory. Immediately transfer the returned earthworms to a Petri dish on ice, and let them stand for about 15 minutes to stop defecating. Wash the surface of the earthworm with neutral PBS buffer solution 2-3 times to remove impurities such as soil on the surface of the earthworm, and then put it back into the petri dish on ice. A series of optimizations have been carri...
Embodiment 2
[0032] Example 2 The method of isolation, screening and identification of sulfamethoxazole-resistant bacteria in Daping No. 2 intestinal tract
[0033] Samples were collected in an earthworm farm in Huaian City, Jiangsu Province. The farm used pig manure, cow dung, a small amount of wheat bran and mushroom residue as raw materials to raise earthworms, and the temperature was kept at about 25 °C. The Daping No. 2 with a weight in the range of 0.3-0.5g and an obvious ring was selected as the experimental object, and it was placed on an ice pack and quickly transported back to the laboratory. Immediately transfer the returned earthworms to a Petri dish on ice, and let them stand for about 15 minutes to stop defecation. Wash the surface of the earthworm with neutral PBS buffer solution 2-3 times to remove impurities such as soil on the surface of the earthworm, and then put it back into the petri dish on ice. Afterwards, 3 earthworms were placed in 50wt.% absolute ethanol. During...
Embodiment 3
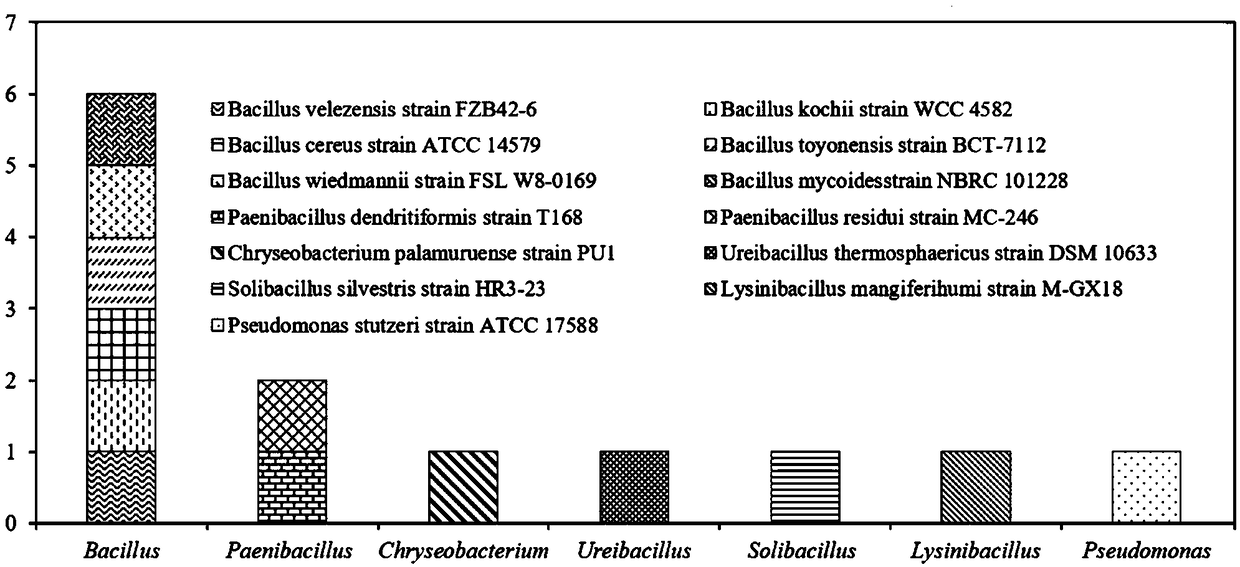
[0035] Example 3 Method for Isolation, Screening and Identification of Tetracycline-Sulfadiazine Resistant Bacteria in the Intestines of the William Ringworm
[0036] Samples were collected in an earthworm farm in Huaian City, Jiangsu Province. The farm used pig manure, cow dung, a small amount of wheat bran and mushroom residue as raw materials to raise earthworms, and the temperature was kept at about 25 °C. Select a William's ringworm with a body weight in the range of 3-5g and obvious rings (Pheretima guillelmi) As experimental objects, they were placed on ice packs and quickly transported back to the laboratory. Immediately transfer the returned earthworms to a Petri dish on ice, and let them stand for about 15 minutes to stop defecation. Wash the surface of the earthworm with neutral PBS buffer solution 2-3 times to remove impurities such as soil on the surface of the earthworm, and then put it back into the petri dish on ice. Afterwards, three earthworms were placed ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com