Preparation method of aramid fiber 1313 modified fiber
A modified fiber and aramid fiber technology, which is applied in the field of spinning fiber preparation technology, can solve the problems of low fiber strength and achieve the effects of improving performance, improving defoaming efficiency, improving mechanical strength and heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
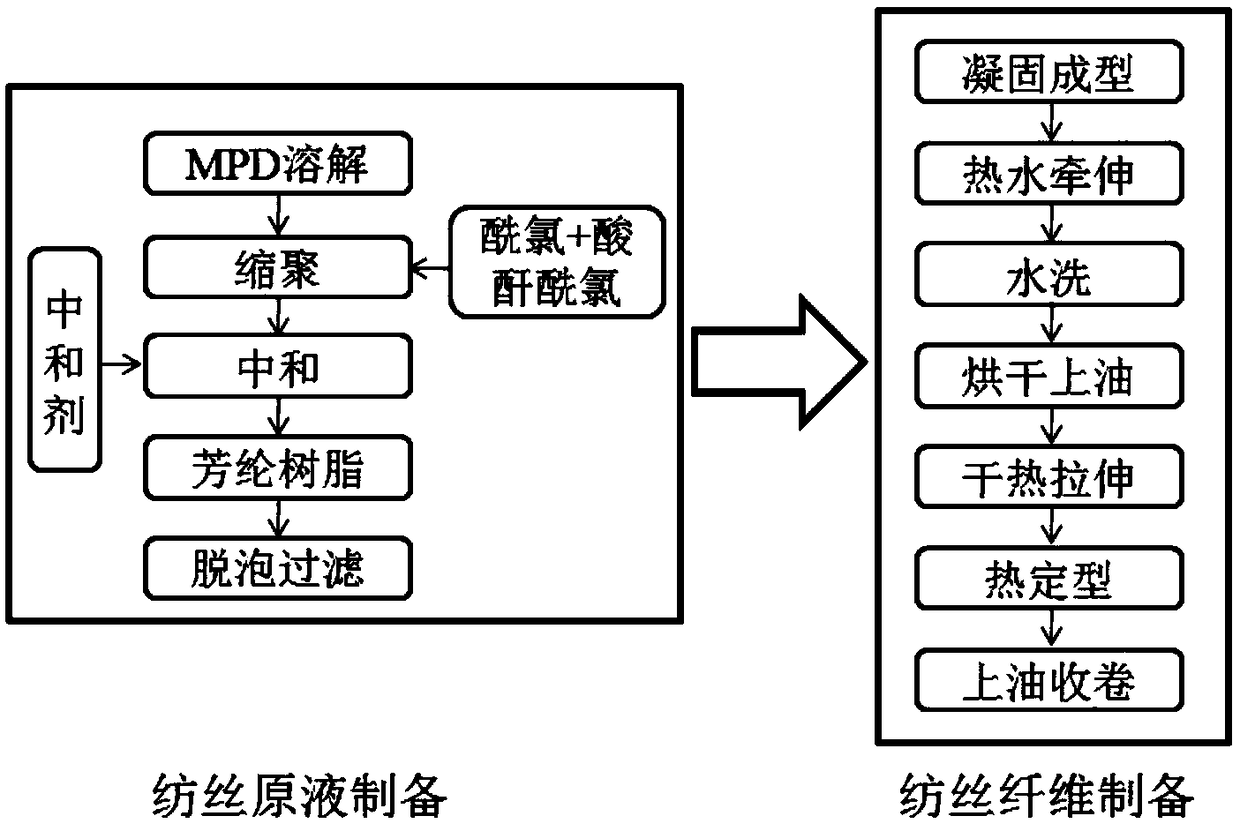
[0032] The preparation method of the aramid fiber 1313 modified fiber of a specific embodiment of the present invention, comprises the following steps:
[0033] (1) Dissolve m-phenylenediamine in a polar solvent, freeze and cool the solution and mix it with molten isophthaloyl chloride and anhydride acid chloride in a low temperature environment to obtain aramid 1313 modified solution containing hydrogen chloride .
[0034] The anhydride acid chloride used is where R is one or more of them. The polyamic acid produced during the polymerization process will be dehydrated and cyclized during the dry heat stretching process of the fiber to further improve the fiber performance.
[0035] The molar ratio of m-phenylenediamine to acid chloride (isophthaloyl chloride + anhydride acid chloride) is 1:1.001-1:1.08, preferably 1:1.01-1:1.05. The acid anhydride acid chloride is 1-14% of the molar weight of m-phenylenediamine, preferably 5-10%.
[0036] The polar solvent is an amid...
Embodiment 1
[0055] Dissolve m-phenylenediamine in N,N-dimethylacetamide and lower the temperature to -15°C. m-Phenylenediamine mixed with isophthaloyl chloride and trimellitic anhydride acid chloride at a molar ratio of 1:1.02 at 20°C, wherein the molar weight of trimellitic anhydride acid chloride is 5% of the molar weight of m-phenylenediamine to prepare aramid 1313 modified resin The content is 18.5%, and the logarithmic viscosity is 2.05. Hydrogen chloride produced during the polymerization process with Ca(OH) 2 Neutralize, and remove the impurities produced during the neutralization process to obtain spinning dope.
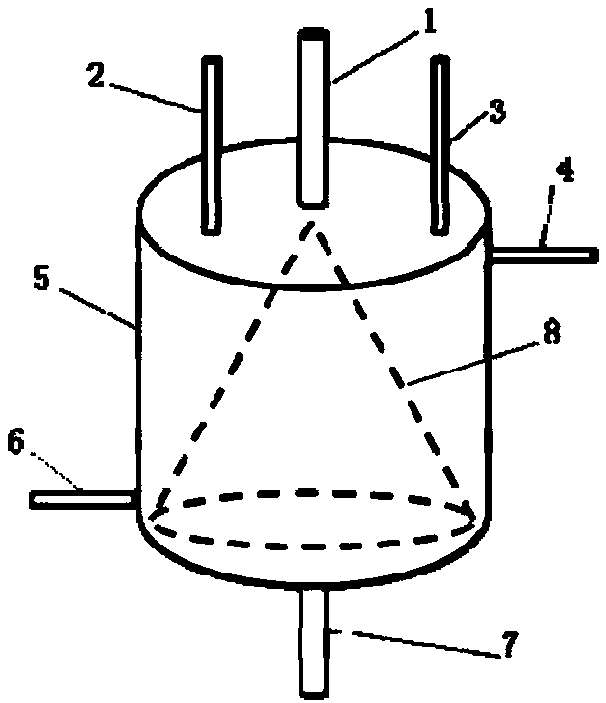
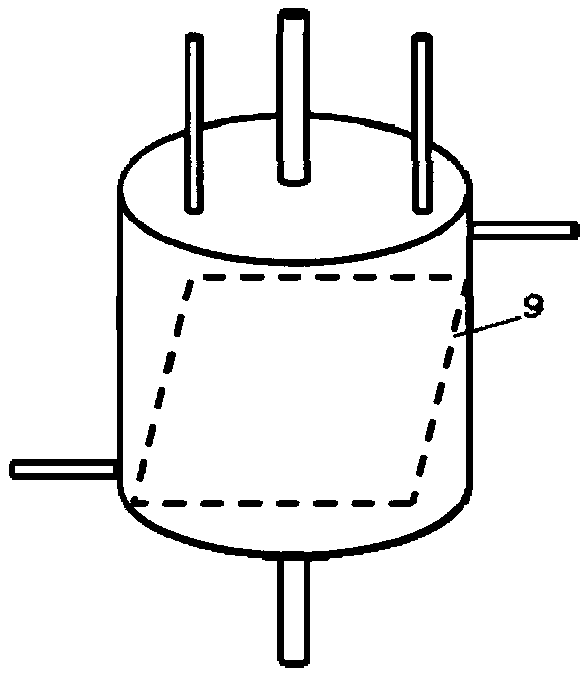
[0056] After being defoamed by an umbrella-shaped vacuum membrane, the stock solution is filtered through a filter, and enters a coagulation bath through a 200-hole spinneret with a pore size of 0.08 mm. The content of water in the primary coagulation bath is 35%, the content of N, N-dimethylacetamide is 65%, and the drawing ratio is -60%; the content of water in the s...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Dissolve m-phenylenediamine in N,N-dimethylacetamide and lower the temperature to -18°C. m-Phenylenediamine mixed with isophthaloyl chloride and trimellitic anhydride acid chloride at a molar ratio of 1:1.04 at 18°C, wherein the molar weight of trimellitic anhydride acid chloride is 8% of the molar weight of m-phenylenediamine to prepare aramid 1313 modified resin The content is 21%, and the logarithmic viscosity is 2.15. The hydrogen chloride produced in the polymerization process is neutralized with ammonia gas, and the impurities produced in the neutralization process are removed to obtain the spinning dope.
[0059] After the stock solution is degassed by a conical vacuum membrane, it is filtered through a filter, and enters a coagulation bath through a 100-hole spinneret with a pore size of 0.08mm. The content of water in the primary coagulation bath is 35%, the content of N, N-dimethylacetamide is 65%, and the drawing ratio is -60%; the content of water in the se...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Decomposition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fineness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com