Method and device for recycling high-magnesium wastewater from power plants
A magnesium power plant, resource utilization technology, applied in the field of resource utilization of waste water from high-magnesium power plants, can solve the problems of unutilized magnesium resources and high dosing costs, and achieve the effects of reduced dosing costs, reduced energy consumption, and high-efficiency separation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] The composition of high-magnesium wastewater from a certain power plant is shown in Table 1. It is the wastewater after preliminary coagulation and sedimentation treatment. The coagulation and sedimentation process is a conventional process in this field, and will not be repeated here. where Ca 2+ The concentration is 580mg / L, Mg 2+ The concentration is 4650 mg / L, SO 4 2- : Mg 2+ The molar ratio is 0.73:1.
[0043] Table 1 Water quality characteristics of high magnesium wastewater from a power plant
[0044] project
quantity
Ca 2+ (mg / L)
580
Mg 2+ (mg / L)
4650
Cl - (mg / L)
6731
SO 4 2- (mg / L)
13580
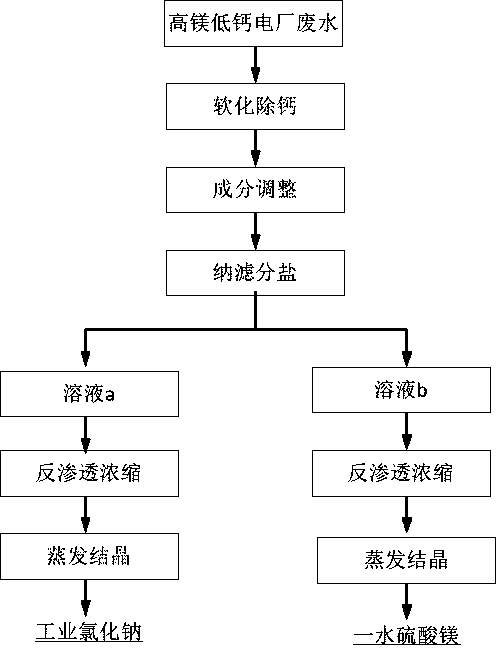
[0045] as attached figure 1 As shown, the steps of resource utilization of waste water from this high-magnesium power plant are:
[0046] (1) Softening and decalcification: add oxalic acid to the wastewater, the amount of oxalic acid added is 1.56kg / m 3 , so that the molar ratio of oxalate ions to...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The composition of high-magnesium wastewater from a certain power plant is shown in Table 2. It is the wastewater after preliminary coagulation and sedimentation treatment. The coagulation and sedimentation process is a conventional process in the field, and will not be repeated here. where Ca 2+ The concentration is 880mg / L, Mg 2+ The concentration is 10980mg / L, SO 4 2- : Mg 2+ The molar ratio is 0.47:1.
[0059] Table 2 Water quality characteristics of high magnesium wastewater from a power plant
[0060] project
quantity
Ca 2+ (mg / L)
880
Mg 2+ (mg / L)
10980
Cl - (mg / L)
18731
SO 4 2- (mg / L)
20580
[0061] as attached figure 1 As shown, the steps of resource utilization of waste water from the high-magnesium and low-calcium power plant are:
[0062] (1) Softening and decalcification: adding sodium oxalate to the wastewater, the amount of sodium oxalate added is 4.23kg / m 3 At this time, the pH...
Embodiment 3
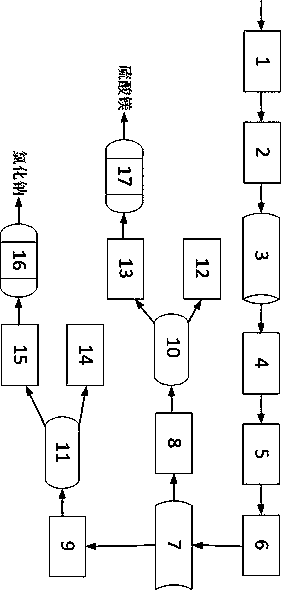
[0071] A high-magnesium power plant wastewater resource utilization device includes a softening pretreatment system, a tubular membrane ultrafiltration system, a component adjustment system, a nanofiltration salt separation system, a reverse osmosis concentration system, and an evaporation crystallization system connected in sequence.
[0072] Such as figure 2 As shown, the softening pretreatment system includes a reaction tank 1 and a first buffer tank 2, wherein an automatic dosing unit is provided above the reaction tank 1, and the automatic dosing unit includes a decalcifier adder and a Ph regulator adder for adding Calcium remover and pH regulator are added in the reaction tank 1. The reaction pool 1 is provided with a first agitator, and the water in the reaction pool 1 enters the first buffer pool 2 through the overflow port, and the water in the first buffer pool 2 enters the tubular membrane ultrafiltration system through a pump.
[0073] The tubular membrane ultraf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com