Active targeted gene delivery nanoparticle, and preparation method and application thereof
A gene delivery and active targeting technology, applied in the field of nanobiotechnology gene therapy, can solve the problems of short circulation time in vivo, non-specific adhesion, cytotoxicity, etc., achieve active targeted transfection efficiency and improve safety and stability, broad clinical application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Preparation of cationic polymer / gene complex
[0034]The PAsp(DET) and sFlt-1 plasmids were dissolved in HEPES (10mM, pH7.4), respectively, the concentration of the sFlt-1 plasmid was 0.05μg / μl, and the concentration of the PAsp(DET) solution was adjusted according to different N / P ratio requirements. Mix the PAsp(DET) solution and 2 times the volume of sFlt-1 plasmid solution and vortex for 30 seconds to prepare a PAsp(DET) / pDNA complex solution with a final concentration of sFlt-1 plasmid of 33.3 μg / mL. Using the same method and procedure, PAsp(EDA), PAsp(TET) and PAsp(TEP) or their derivatives can be used to construct cationic polymer / pDNA complexes.
[0035] Also, according to the same steps and methods as above, PAsp(EDA), PAsp(DET), PAsp(TET) and PAsp(TEP) or their derivatives and mRNA, siRNA, oligonucleotides, etc. can be used to form cationic polymers / mRNA complexes, cationic polymer / siRNA complexes, cationic polymer / oligonucleotide complexes, etc. ...
Embodiment 2
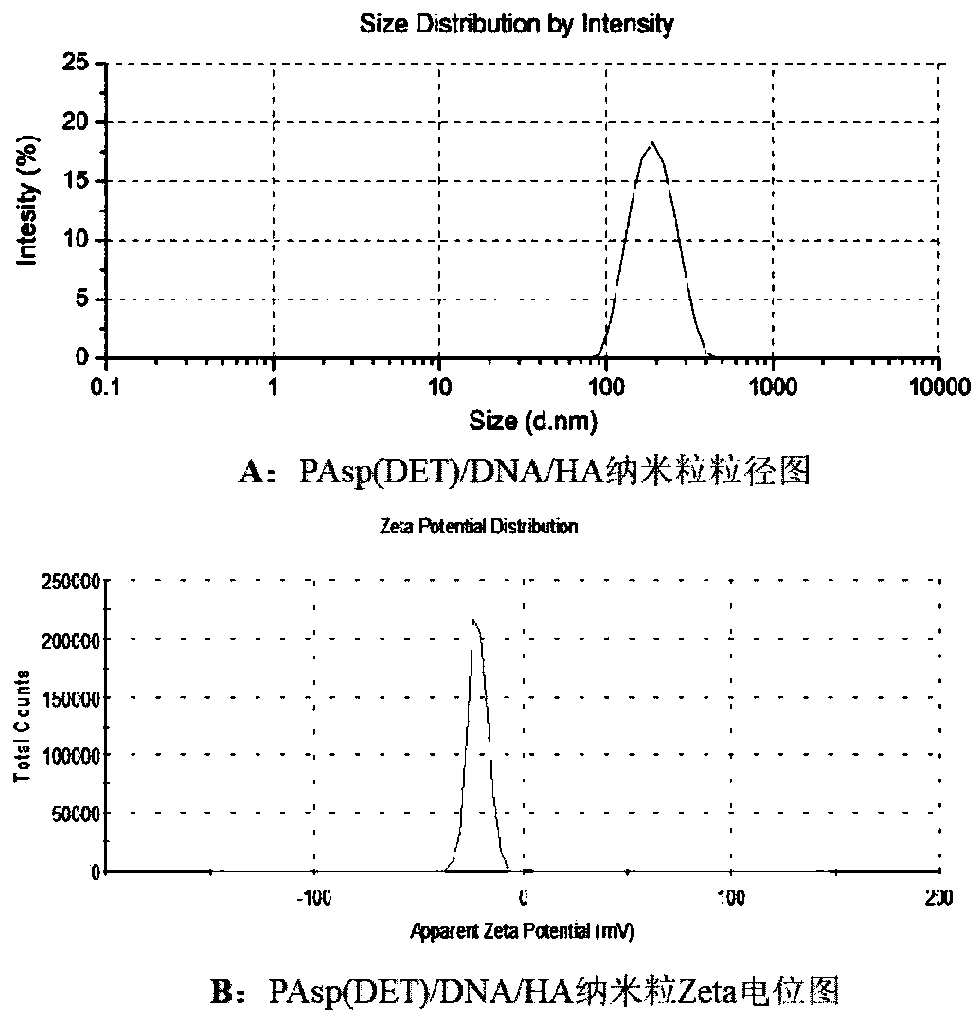
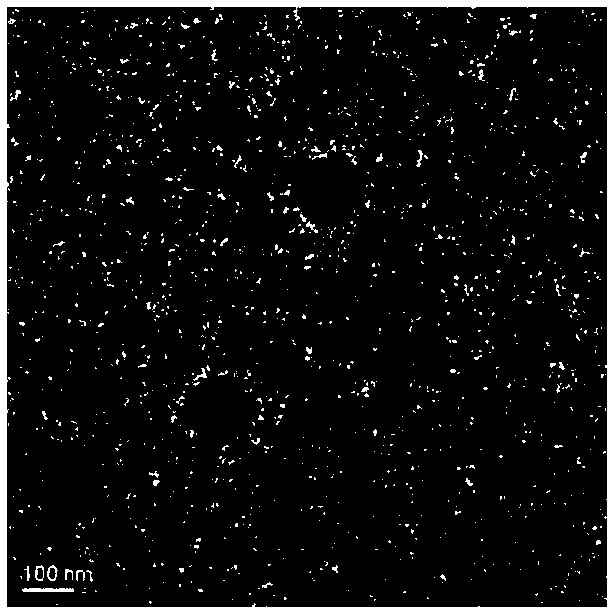
[0036] Embodiment 2: Preparation of PAsp(DET) / DNA / HA nanoparticles
[0037] In this example, PAsp(DET) is poly{N'-[N-(2-aminoethyl)-2-aminoethyl]aspartic acid}, HA is hyaluronic acid, and HA is made form a chemical bond with the core of the complex. EDC is 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide hydrochloride and NHS is N-hydroxysuccinimide.
[0038] PAsp(DET) and EGFP plasmids were prepared into solutions with concentrations of 2.0 μg / μl and 0.05 μg / μl with Tris-HCl (10 mM, pH 7.4), respectively. A mixed solution of HA, EDC and NHS was prepared with water, and the concentrations of HA, EDC and NHS were 1.0 µg / µl, 0.15 µg / µl and 0.25 µg / µl, respectively. Use Tris-HCl to adjust the PAsp(DET) and EGFP plasmid solution to the desired concentration, mix the PAsp(DET) and EGFP plasmid solution in an appropriate ratio and vortex for 30 seconds to prepare the PAsp(DET) / DNA complex substance solution. After the complex solution is left at room temperature for 30 minutes, add t...
Embodiment 3
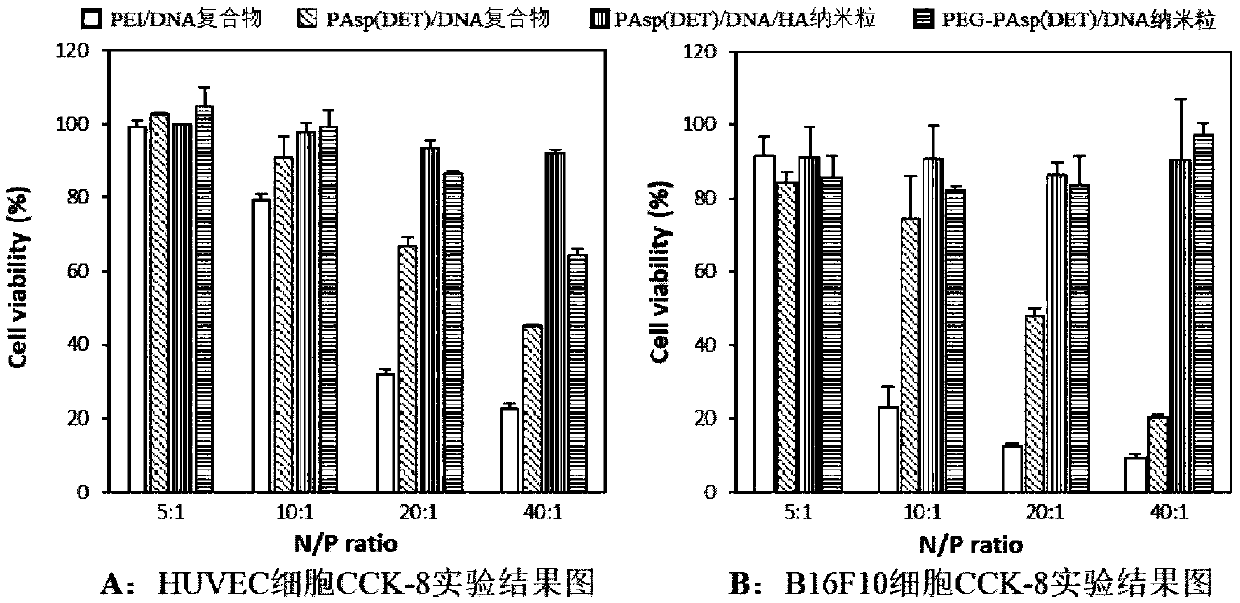
[0042] Example 3: Comparison of Cytotoxicity
[0043] Using the above preparation method, prepare PAsp(DET) / DNA / HA nanoparticles, and use CCK-8 experiment to investigate different N / P / COO - The ratio of cytotoxicity of the gene-delivered nanoparticles. After HUVEC / B16F10 cells in the logarithmic growth phase were digested with trypsin, 5×10 3 Cells / well were seeded in 96-well plate, 50 μl cell suspension per well, at 37°C, 5% CO 2 After culturing in the incubator for 24 hours, add the sample solution adjusted to 50 μl with the medium, and prepare four kinds of each sample solution with N / P ratio of 5:1, 10:1, 20:1 and 40:1. For solutions with different N / P ratios, the sample solution added to each well contained 1.0 μg of EGFP plasmid, and PEG-PAsp (DET) with low toxicity and 25K PEI with high toxicity were used as controls. After culturing for 24 hours, add 10 μl of CCK-8 solution to each well, continue culturing for 2 hours, and measure the absorbance value (A) at 450 nm ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com