Method for identifying oolong tea
A technology of oolong tea and catechins, which is applied in tea treatment before extraction, material analysis by observing the influence on chemical indicators, measuring devices, etc. Differences between oolong tea years and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1: the preparation of oolong tea extract
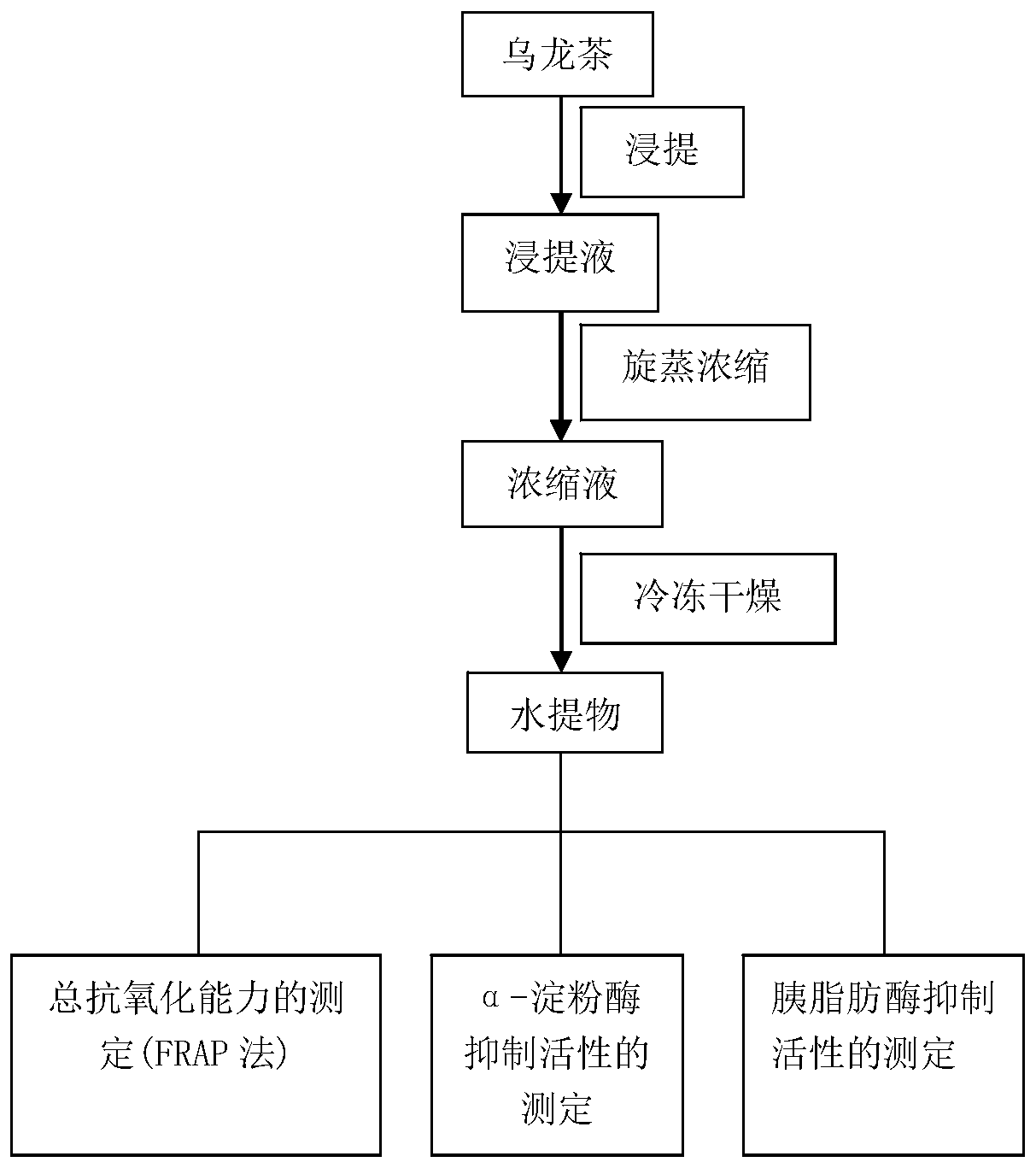
[0039] The preparation flow chart is attached figure 1 , including the following steps:
[0040] S1 Extraction: The raw material oolong tea is extracted 3-5 times with hot water, the water temperature is 80-90°C, and the extraction time is 0.5-1h.
[0041] S2 Filtration while hot: quickly filter the extracted tea soup with filter paper or cotton.
[0042] S3 Concentration by Rotary Evaporation: Concentrate the obtained extract by rotary evaporation between 40-60°C.
[0043] S4 freeze-drying: import the concentrate obtained from step S3 into a suitable container, store at -80°C for 6-10 hours, and then put it into a freeze dryer for freeze-drying.
[0044] S5 storage: put the freeze-dried powder into a ziplock bag, put it in a desiccator and store it at room temperature until use.
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: detection and experimental method:
[0046] 1. Content detection of main biochemical components of tea samples
[0047] Moisture determination: 103°C constant weight method; water extract determination: GB / T8305-2002; tea polyphenol content: ferrous tartrate method GB / T8313-2002; amino acid content: ninhydrin colorimetric method GB / T8314-2002 ; Soluble sugar content: anthrone-sulfuric acid colorimetric method;
[0048] 2. HPLC method to detect the content of catechin monomers in tea soup
[0049] Chromatographic column: Agilent ZORBAX Eclipse XDB-C18 column, 150mm×4.6mm; detection wavelength 280nm, detection temperature 28°C; mobile phase A: aqueous solution containing 0.5% acetic acid, 1% acetonitrile and 2% methanol, mobile phase B: containing 0.5 Aqueous solution of % acetic acid, 10% acetonitrile and 20% methanol; elution steps: within 30min, phase A from 72.5% to 20%, phase B from 27.5% to 80%, after 30min within 5min, phase A from 20% Recovery to ...
Embodiment 6
[0059] Embodiment 6: experimental result
[0060] 1. Table 1 Biochemical component content of aged oolong tea in different years / %
[0061]
[0062] Note: * p** p<0.01, with 2016 oolong tea as the control.
[0063] It can be seen from Table 1 that the contents of tea polyphenols and soluble sugars in the three kinds of oolong teas of different years do not have a universally applicable rule, but the contents of amino acids in the three kinds of oolong teas have a general rule. The content is generally lower than that of oolong tea in 2016. There are large differences in the content of flavonoids. In Huang Jinrong and Daye Qilan, the content of flavonoids in 1990 oolong tea is significantly lower than that of 2016 oolong tea. In Lingtou Dancong, the flavonoid content of 1990 oolong tea was higher than that of 2016 oolong tea. Therefore, according to the results, it can be seen that except for amino acids, other indicators are not universal indicators, and cannot be speci...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| control rate | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com