Method of selective electrolytic leaching recycling gold and copper from waste memory strips
A memory stick, selective technology, applied to the improvement of process efficiency, photographic technology, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of inability to deal with waste memory sticks, lead and tin are not recycled, can not be recycled, and achieve good economic benefits The effects of social benefits, consumption saving, and short leaching cycle time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 Utilizes the selective recovery of sodium sulfite and sodium chloride
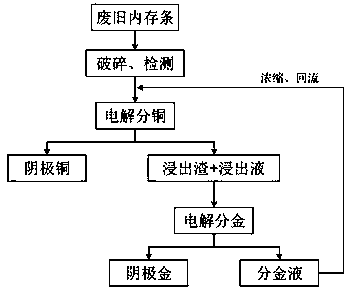
[0029] (1) Take the memory stick and put it into the RETSCH SM300 coarse crusher made in Germany for crushing, and crush it to a particle size of 3~5mm, shake it well, take three sets of parallel samples for digestion, and then get Table 1 through ICP detection.
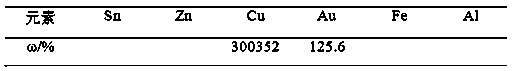
[0030] Table 1 Element content of waste gold fingers (ω, Au, Cu unit g / t)
[0031]
[0032] (2) Copper separation: Take 5g of the broken golden finger, add 50ml of 5mol / L hydrochloric acid, configure a reaction system with a liquid-solid volume-to-mass ratio of 10:1mL / g, stir at 700 rpm, and at a temperature of 25°C, add Sodium sulfite 1.4g, using a φ1cm carbon rod as the cathode and anode, the pole distance is 3cm, the contact length with the reaction system is 2.5cm, the DC voltage is 3V, and the constant temperature leaching time is 3h. After testing, about 1.48g of copper was leached, the leaching rate of copper was 98...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Embodiment 2 Utilizes the selective recovery of ferrous sulfate and potassium iodide
[0036] (1) Take samples, put them into RETSCH SM300 coarse crusher made in Germany for crushing, and crush until the particle size is 3~5mm, shake well, take three sets of parallel samples for digestion, and get Table 2 through ICP detection.
[0037] Table 2 Element content of waste gold fingers (ω, Au, Cu unit g / t)
[0038]
[0039] (2) Copper separation: take 130 grams of broken golden fingers, add 1300 ml of 7mol / L hydrobromic acid, configure a reaction system with a liquid-solid volume mass ratio of 10:1mL / g, set the stirring speed at 700rpm, and the temperature at 25°C , add 92.64 grams of ferrous sulfate, use a graphite plate with a thickness of 0.5cm as the cathode and anode, the pole distance is 6cm, the contact depth with the reaction system is 3.5cm, the voltage is 5V, and the constant temperature leaching time is 3h. Tested. About 38.65g of copper was leached, the lea...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Embodiment 3 Selective recovery using sodium sulfite and sodium chloride plus AC / DC superimposed power supply
[0043] (1) Take a sample, put it into a RETSCH SM300 coarse crusher made in Germany for crushing, and crush it to a particle size of 3-5 mm, shake it well, take three sets of parallel samples for digestion, and obtain Table 3 through ICP detection.
[0044] Table 3 Element content of waste gold fingers (ω, Au, Cu unit g / t)
[0045]
[0046] (2) Copper separation: Take 400 grams of broken golden fingers, add 4000 ml of 6mol / L hydrochloric acid, configure a reaction system with a liquid-solid volume mass ratio of 10:1mL / g, set the stirring speed at 700rpm, and the temperature at 25°C, add 64 grams of sodium sulfite, using a graphite plate with a thickness of 0.8cm as the cathode and anode, the distance between the poles is 10cm, the contact depth with the reaction system is 3.5cm, an external AC and DC superimposed power supply, the AC frequency is 800Hz, the a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com