A cross-linked peptide enrichment method and its application in protein interaction research
A protein and enrichment technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, material analysis by electromagnetic means, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of inability to achieve selective enrichment of cross-linked peptides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] 1. Cross-linking reaction of protein samples
[0023] Dissolve 10 μg of bovine serum albumin sample (BSA) in 20 mM 4-hydroxyethylpiperazineethanesulfonic acid buffered saline solution (HEPES) at pH 7.4 to a final protein concentration of 1 mg / mL and use dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) Dissuccinimidyl tartrate (DST) was prepared at a concentration of 25 mM, the cross-linking agent was added to the BSA solution to make the final concentration 1 mM, and reacted at room temperature for 1 h.
[0024] 2. Removal of excess cross-linking agent
[0025] Ammonium bicarbonate solution (ABC) was added to the reaction solution in step 1 to make the final concentration 50 mM to terminate the cross-linking reaction.
[0026] 3. Dissolution, denaturation and reduction of protein samples
[0027] Add urea and DTT to the cross-linked BSA solution in step 2, so that the final concentration of urea in the solution is 8M, and the final concentration of DTT is 10mM, and react in a water bath at ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] 1. Cross-linking reaction of BSA protein samples; removal of excess cross-linking agent; dissolution, denaturation and reduction, alkylation, enzymatic hydrolysis, enrichment of cross-linked peptides, removal of non-specific adsorption peptides and peptide The release steps of the segments are the same as in Example 1.
[0042] 2. Fractionation of enriched cross-linked peptides and determination of cross-linked sites
[0043] The cross-linked peptides released in step (1) were desalted, lyophilized, fractionated by cation exchange separation, desalted, lyophilized and redissolved in 0.1% formic acid solution for mass spectrometry analysis.
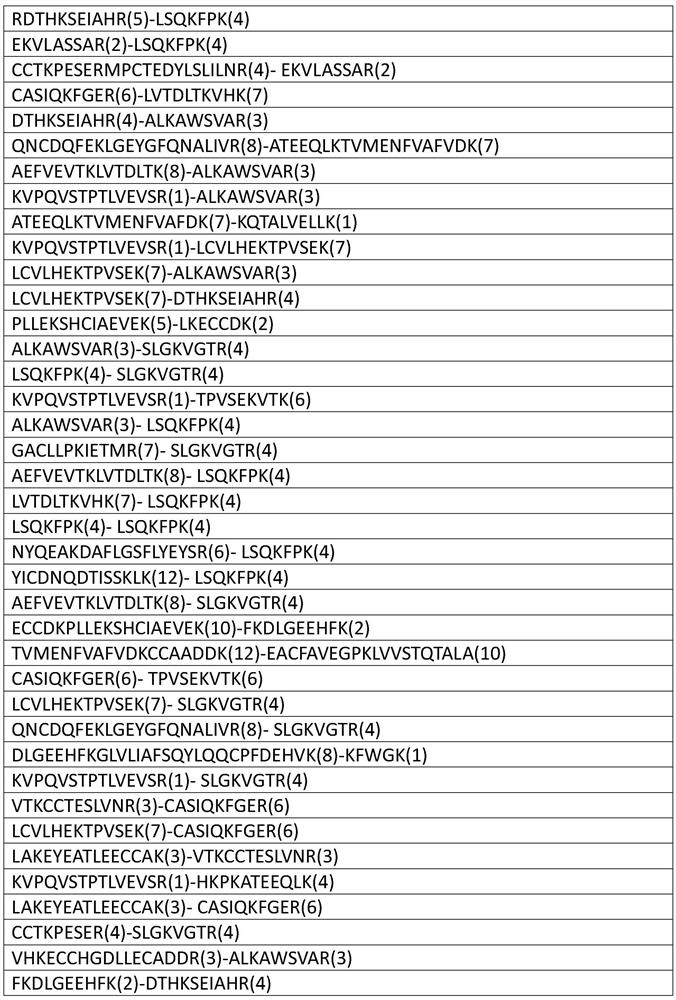
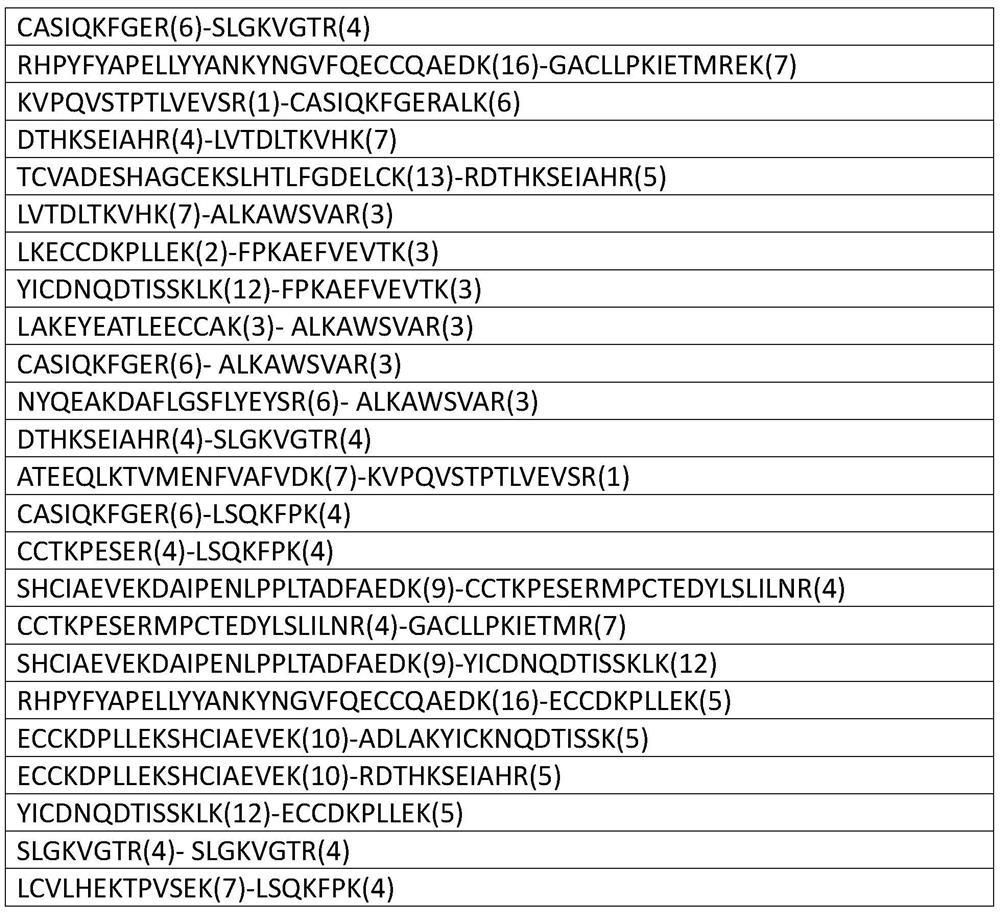
[0044] Identification result
[0045]
[0046]
[0047]
Embodiment 3
[0049] 1. Cross-linking reaction of protein samples
[0050] Dissolve 10 μg of rabbit creatine kinase protein sample (CK) in 50 mM phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) with a pH of 7.4, the final protein concentration is 1 mg / mL, and prepare DST with a concentration of 25 mM in dimethylformamide (DMF). The cross-linking agent was added to the CK solution so that the final concentration was 1 mM, and reacted at room temperature for 1 h.
[0051] 2. Removal of excess cross-linking agent
[0052] Tris buffer solution (Tris) was added to the reaction solution in step 1 to make the final concentration 50 mM to terminate the cross-linking reaction.
[0053] 3. Dissolution, denaturation and reduction of protein samples
[0054] Add urea and DTT to the cross-linked CK solution in step 2, so that the final concentration of urea in the solution is 8M, and the final concentration of DTT is 10mM, and react in a water bath at 37°C for 30min.
[0055] 4. Alkylation and enzymatic hydrolysis of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com