Wet treatment method for recycling copper and zinc in bismuth middlings
A wet treatment and purpose technology, which is applied in the wet treatment of zinc and the recovery of copper in bismuth ore, can solve the problems of difficult separation and purification of leachate, large content of ferrous ions, etc., and achieve strong raw material adaptability and automation High, low load effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
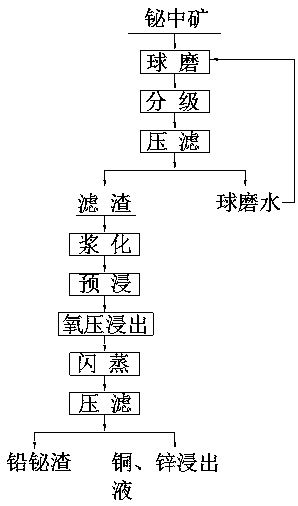
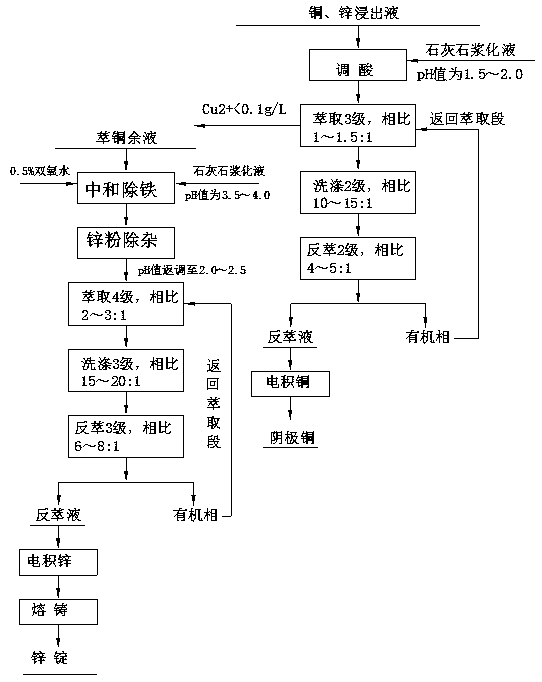
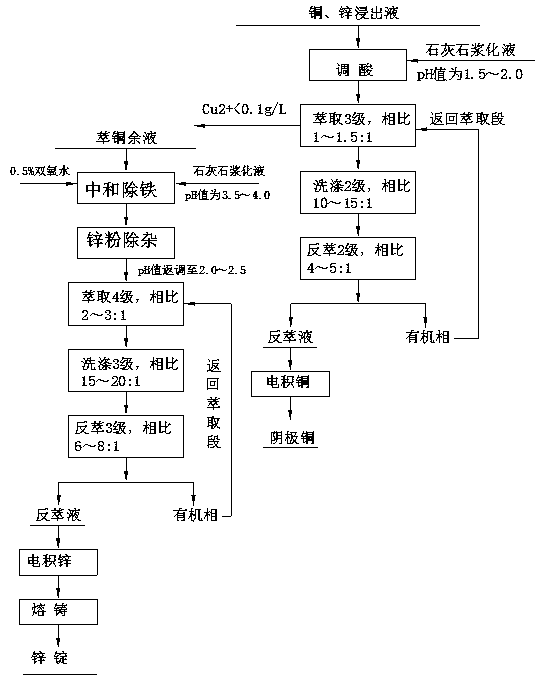
[0028] Example 1: Press Figure 1-2 The process shown is carried out.
[0029] It is realized through the following 4 steps and technical process: (1) Ball milling; (2) Oxygen pressure acid leaching of copper and zinc; (3) N902 extraction - stripping copper deposition; (4) P204 extraction - stripping electrowinning zinc.
[0030] 100t of bismuth middlings containing 18.63% bismuth, 7.59% copper, 7.72% lead, and 17.64% zinc were ball-milled by a wet ball mill, classified by a classifier, and filtered by a ceramic filter to obtain -160 mesh accounting for 98% bismuth middling powder.
[0031] Oxygen pressure leaching of copper and zinc: after electrolysis with diluted zinc (H 2 SO 4 180~200g / L, Zn 2+ 50~60g / L) and ball-milled bismuth ore powder for slurrying and pre-impregnation, and the pre-impregnated slurry is pumped into the 100m 3 In a horizontal reactor, react for 4 hours at a reaction temperature of 170-180°C, a total pressure of 1.4-1.6Mpa, and a slurry flow rate of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com