Method for degrading polyethylene terephthalate
A technology of construction method and inoculum amount, applied in the field of environmental science, which can solve problems such as poisoning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1: a kind of host bacterium
[0030] Construction of PETase and MHETase plasmids: PETase (GAP38373.1) and MHETase (A0A0K8P8E7.1) genes synthesized by the company and pHP13-43 expression vector were digested with BamHI and EcoRI, purified by agarose gel electrophoresis, and linearized PETase and MHETase after pHP13-43 expression vector and endonuclease digestion. The digested fragment and the vector were ligated with T4 DNA ligase, transformed into Escherichia coli, and after successful verification by colony PCR, enzyme digestion and sequencing, the plasmid was extracted as the vector plasmid for Bacillus subtilis expression.
[0031] Bacillus subtilis transformation method:
[0032] 1) Take glycerol to freeze Bacillus subtilis, streak on LB plate, and culture at 37°C. On the next day, take fresh single bacteria and inoculate them into 4ml GM1 medium test tubes, and culture overnight at 37°C and 200rpm.
[0033] 2) Transfer 400 μl of bacterial liquid into ...
Embodiment 2
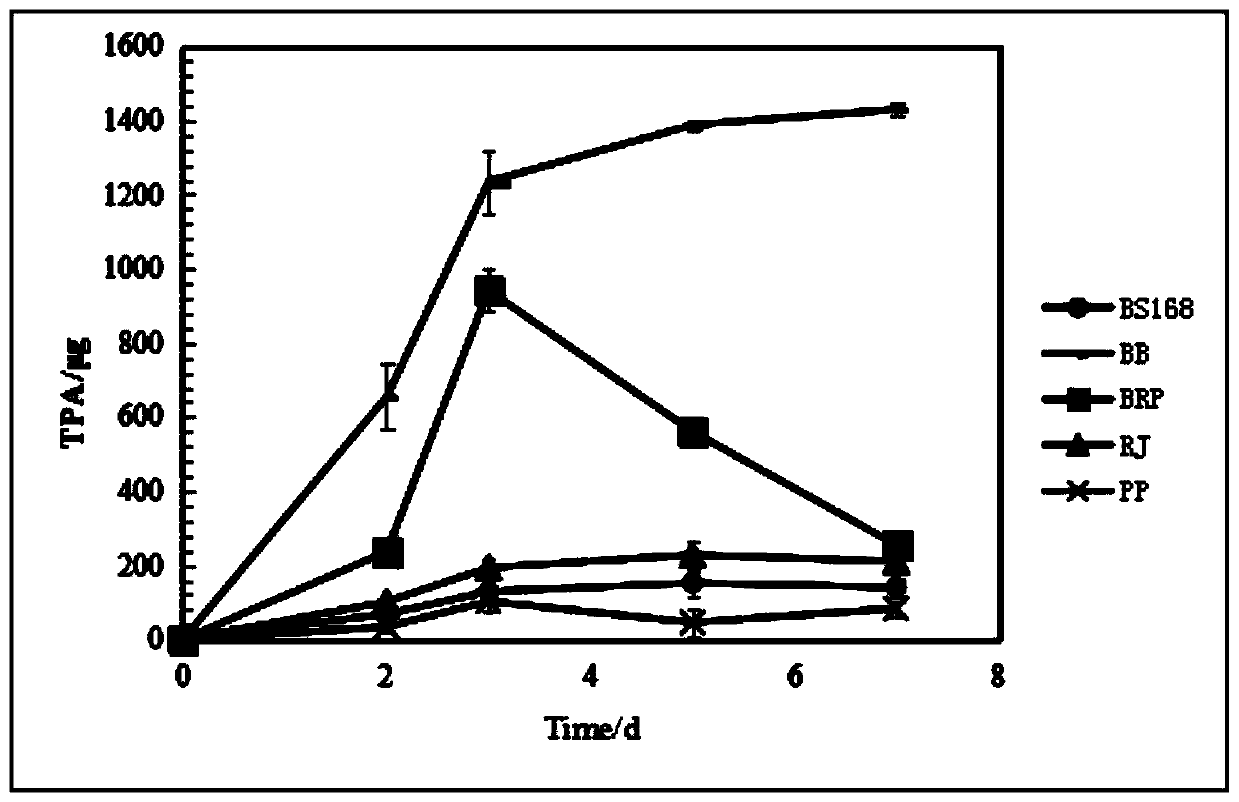
[0037] Embodiment 2, mixed bacteria system degrades PET
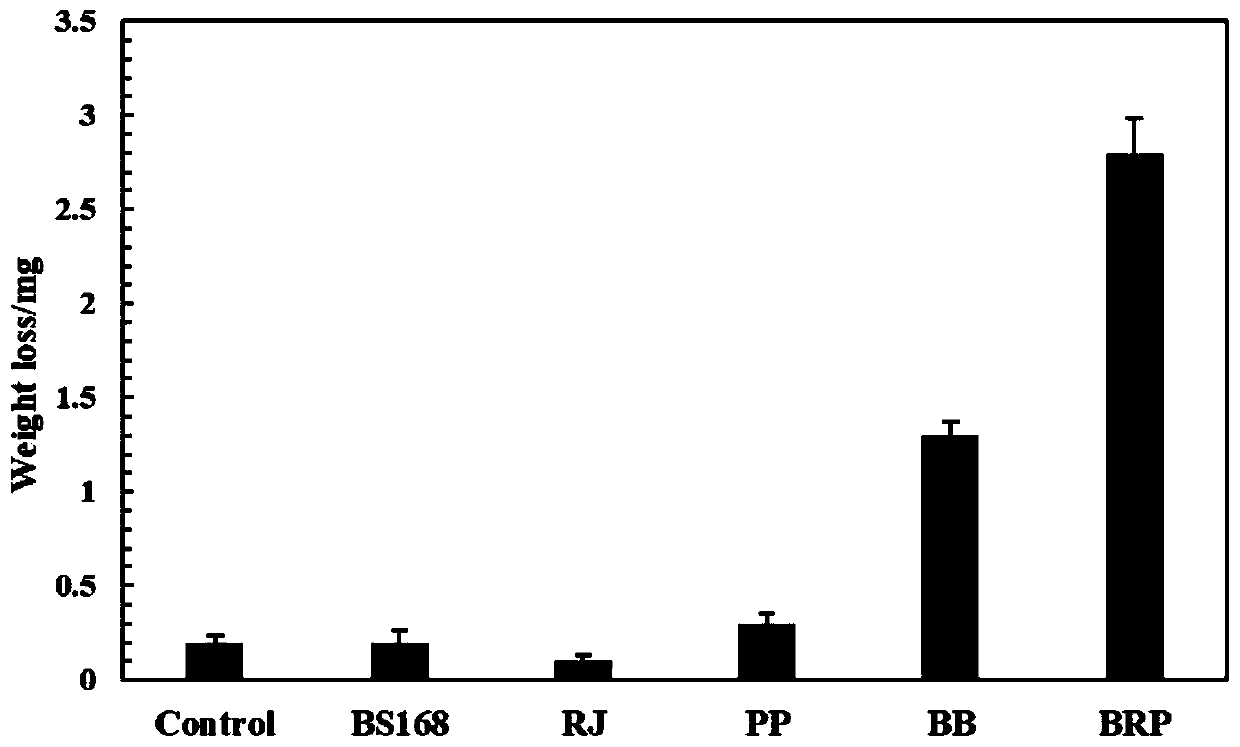
[0038] Before inoculation, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas putida and Rhodococcus were cultured overnight in LB medium earlier, and 5 milliliters of medium were collected by centrifugation at 4000rmp to collect the thalline, and the thalline was washed with W medium, and then the The OD600 of the bacteria was diluted to 1. The inoculum volume of single bacteria is 100 microliters, and the inoculation volume ratio of mixed bacteria (Bacillus subtilis (BB), Pseudomonas putida and Rhodococcus is 1:10) -5 :10) Inoculate a total volume of 100 microliters into W medium. from figure 1It can be seen that wild-type Bacillus subtilis (BS168), Rhodococcus (RJ) and Pseudomonas putida (PP) cannot degrade PET. Only Bacillus subtilis (BB) carrying PETase and MHETase plasmids could hydrolyze PET, and the quality of PET film decreased by 1.3 mg after seven days of reaction. However, compared with the single bacteria system, the degra...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3, change the impact of the inoculum size of Pseudomonas putida on PET degradation:
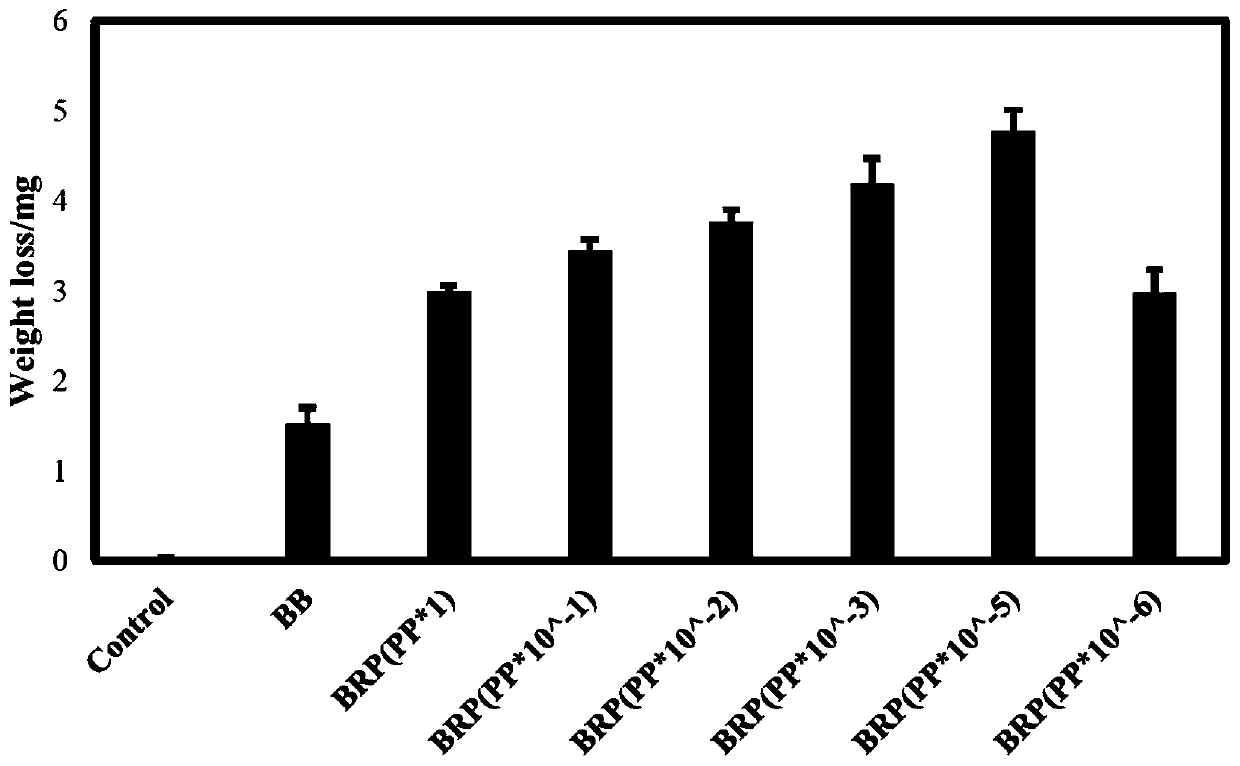
[0041] Before inoculation, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas putida and Rhodococcus were cultured overnight in LB medium earlier, and 5 milliliters of medium were collected by centrifugation at 4000rmp to collect the thalline, and the thalline was washed with W medium, and then the The OD600 of the bacteria was diluted to 1. Pseudomonas putida was diluted 1, 10, 100, 1000, 100000, 10000000 times and inoculated into 100 μL. The initial inoculation volume of Rhodococcus was 100 μL, and the inoculum volume of Bacillus subtilis was 100 μL, and inoculated into 20 ml of W medium. After adding the PET film and degrading it at 37°C for 7 days, wash the PET film with 10% SDS, absolute ethanol and water respectively, and weigh the quality change of the PET film after drying. The results are as follows: image 3 .
[0042] Depend on image 3 The results showed that when the inoculum of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com