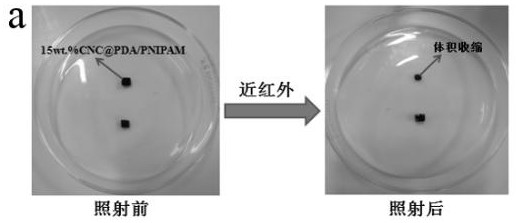
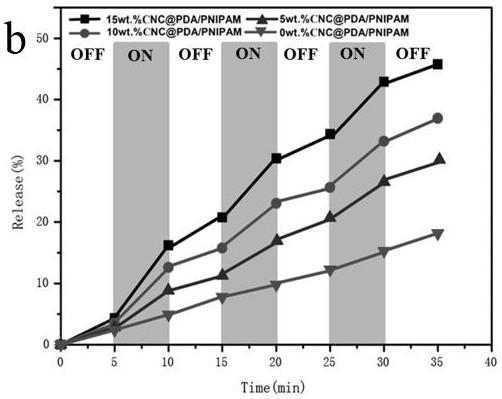
A kind of cellulose/n-isopropylacrylamide drug controlled release hydrogel and preparation method thereof
An isopropylacrylamide and hydrogel technology, which is applied in the directions of pharmaceutical formulations, photosplitting of drugs in vivo, and medical preparations with non-active ingredients, etc., to achieve simple and easy modification operation, improve mechanical properties and performance excellent effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) According to the mass ratio of cellulose raw material to sulfuric acid of 1:50, the cotton fiber raw material was added to a 50 wt% sulfuric acid solution, and the nanocellulose was obtained by ultrasonicating for 3 hours at a temperature of 60 °C, and the obtained nanocellulose was dialyzed. Then the nanocellulose solution is obtained;
[0028] (2) Dissolve 2.0 g of dopamine hydrochloride in 20 g of the nanocellulose suspension with a mass fraction of 10.0% obtained in step (1), adjust pH=8.5 with hydrochloric acid, and react at room temperature for 24 h. After that, an appropriate amount of deionized water was added to the nanocellulose to prepare a nanocellulose solution with a mass fraction of 8.0%.
[0029] (3) Take 0.4g of N-isopropylacrylamide and add it to 0.12g of the cellulose aqueous solution obtained in step (2), then add 0.004g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide cross-linking agent, magnetic force After stirring for 30-40min, the near-infrared responsive cel...
Embodiment 2
[0033] (1) According to the mass ratio of cellulose raw material to sulfuric acid of 1:50, the straw pulp fiber raw material was added to a 50 wt % sulfuric acid solution, and the nanocellulose was obtained by ultrasonicating for 3 hours at a temperature of 60 °C. After dialysis, a nanocellulose solution was obtained;
[0034] (2) Dissolve 2.0 g of dopamine hydrochloride in 20 g of the nanocellulose suspension with a mass fraction of 10.0% obtained in step (1), adjust pH=8.5 with hydrochloric acid, and react at room temperature for 24 h. After that, an appropriate amount of deionized water was added to the nanocellulose to prepare a nanocellulose solution with a mass fraction of 8.0%.
[0035] (3) Add 0.4 g of N-isopropylacrylamide to 0.4 g of the cellulose solution obtained in step (2), and then add 0.004 g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide cross-linking agent, Magnetic stirring for 30-40min, the near-infrared responsive cellulose / N-isopropylacrylamide hydrogel can be obtained ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] (1) According to the mass ratio of cellulose raw material to sulfuric acid of 1:50, add microcrystalline cellulose raw material to 50 wt % sulfuric acid solution, and ultrasonically obtain nanocellulose for 3 hours at a temperature of 60 °C. After dialysis, the nanocellulose solution was obtained;
[0040] (2) Dissolve 2.0 g of dopamine hydrochloride in 20 g of the nanocellulose suspension with a mass fraction of 10.0% obtained in step (1), adjust pH=8.5 with hydrochloric acid, and react at room temperature for 24 h. After that, an appropriate amount of deionized water was added to the nanocellulose to prepare a nanocellulose solution with a mass fraction of 8.0%.
[0041] (3) Take 0.4g of N-isopropylacrylamide and add it to 0.8g of the cellulose solution obtained in step (2), then add 0.004g of N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide cross-linking agent, magnetically After stirring for 30-40min, the near-infrared responsive cellulose / N-isopropylacrylamide hydrogel can be obtained...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com