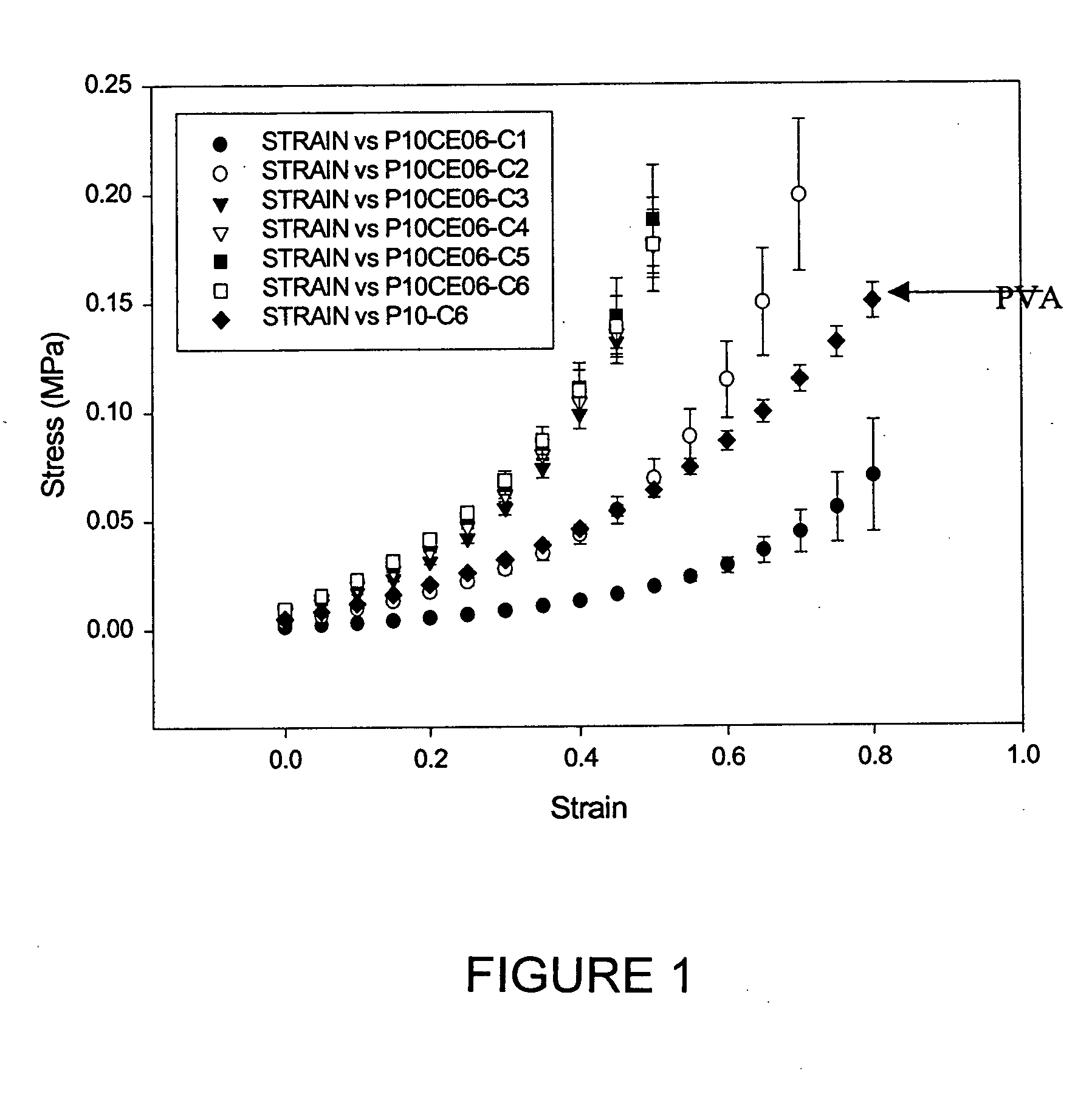
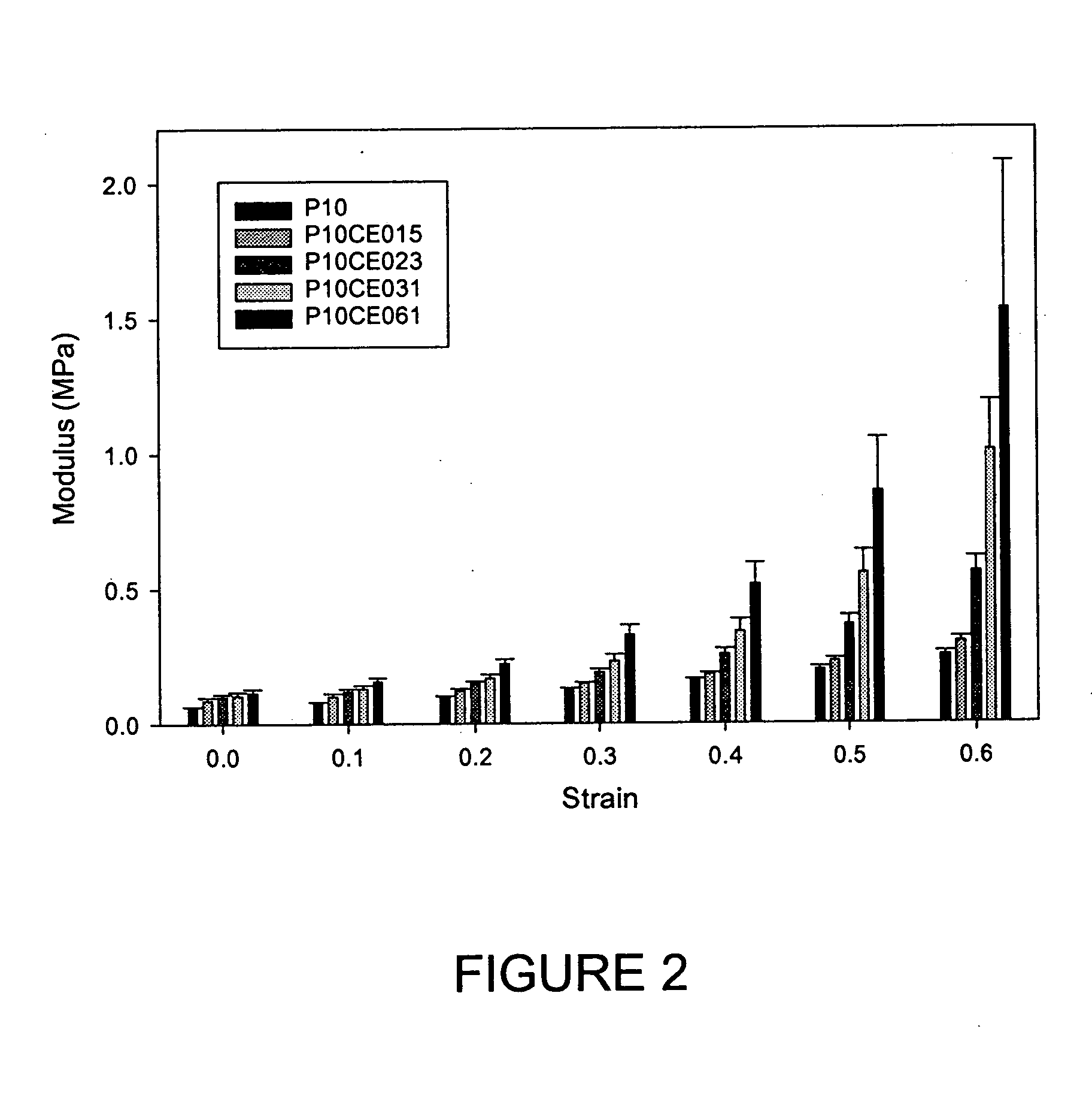
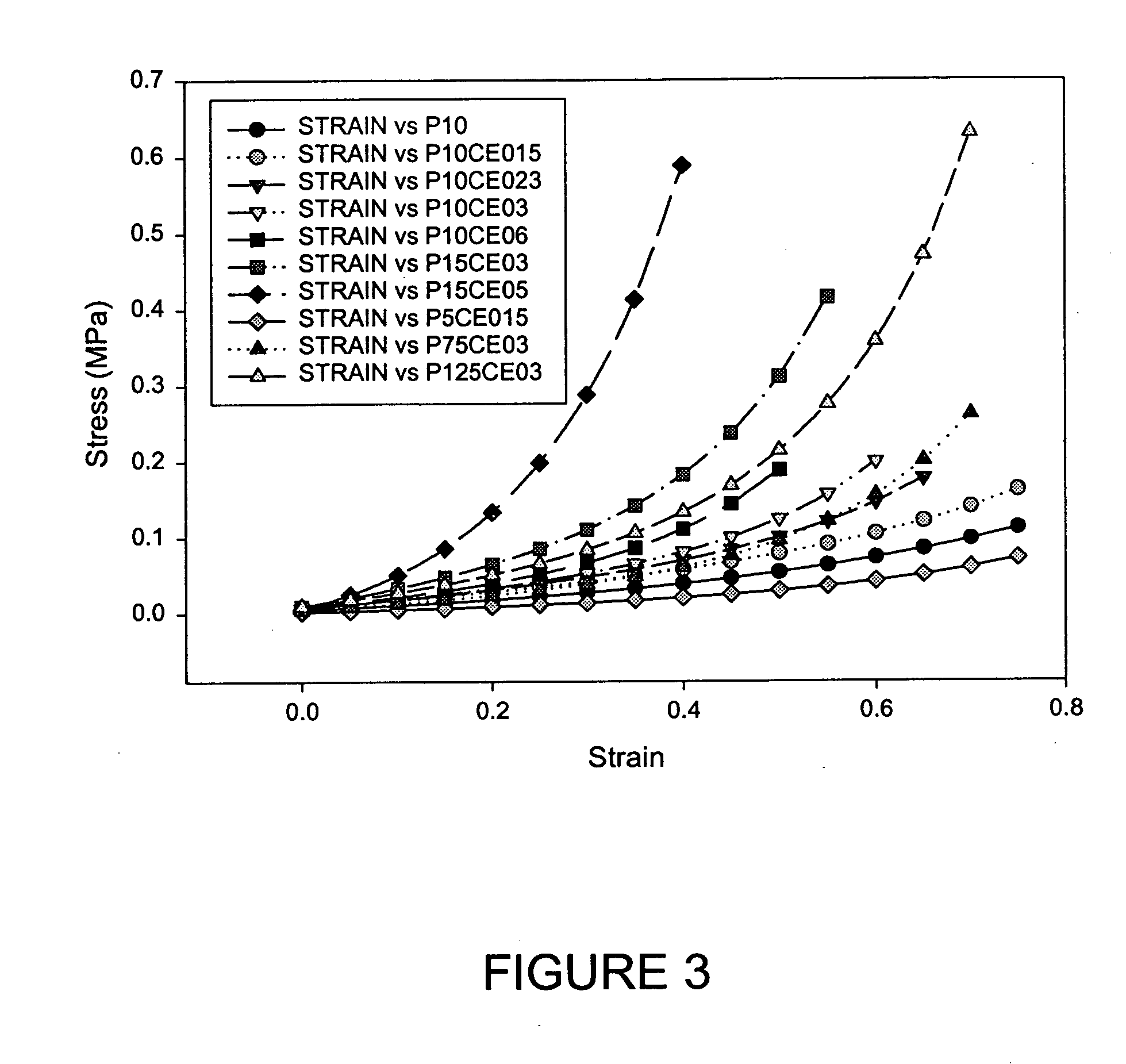
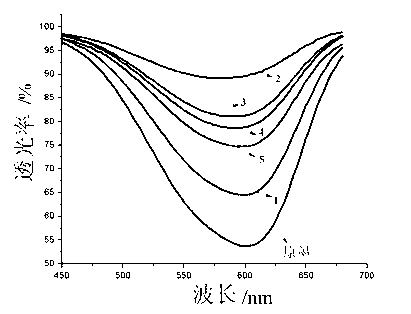
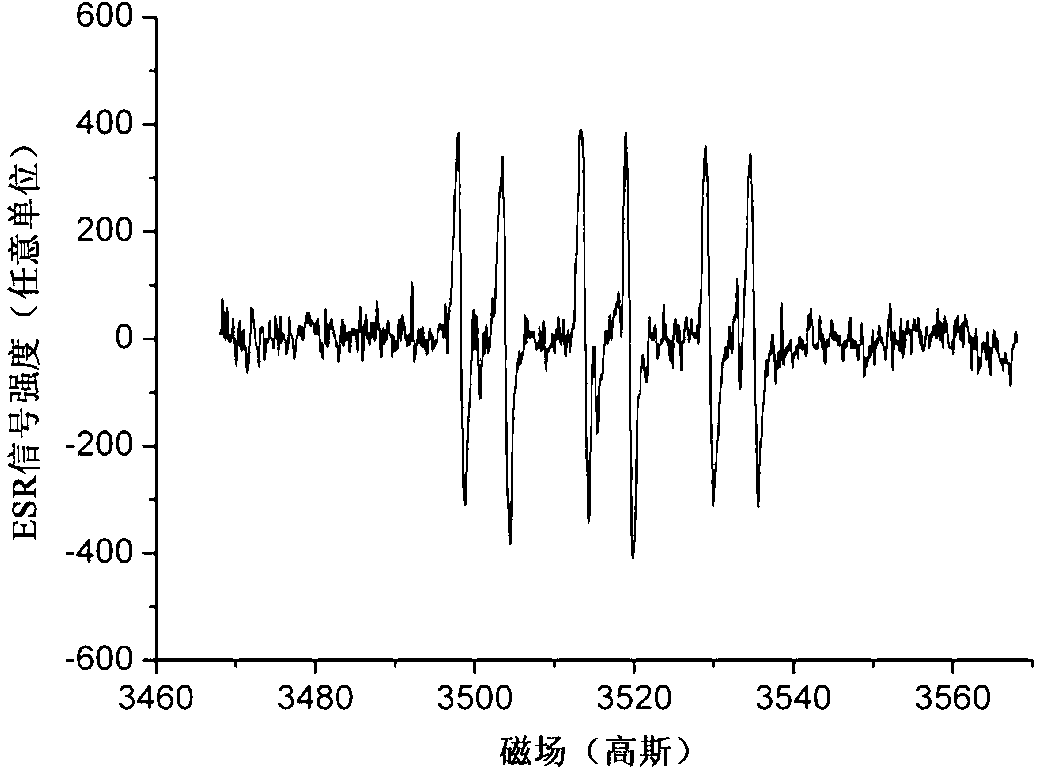
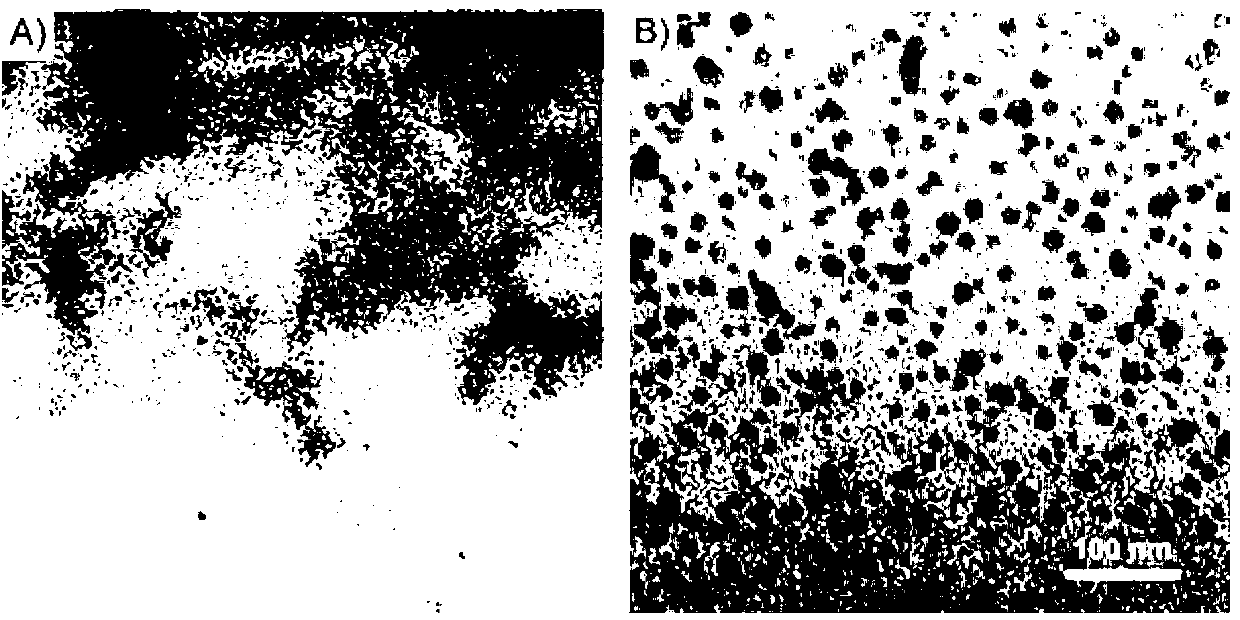
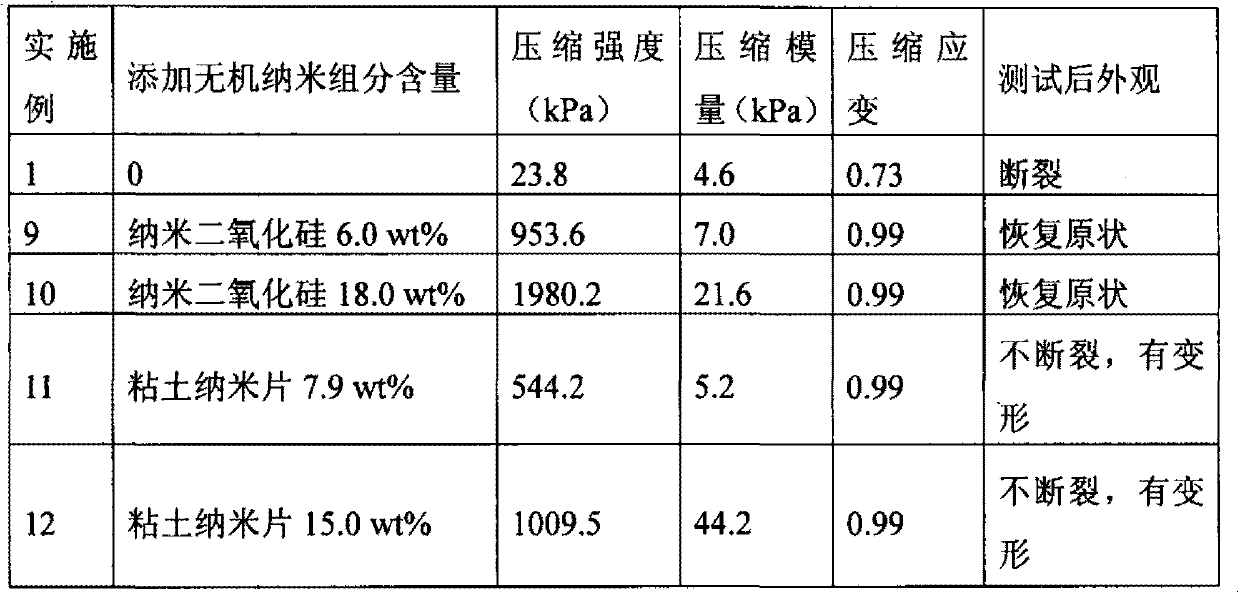
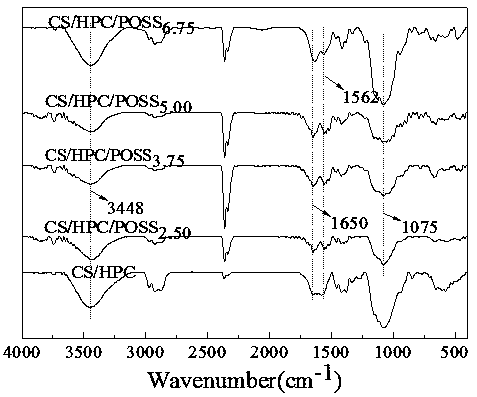
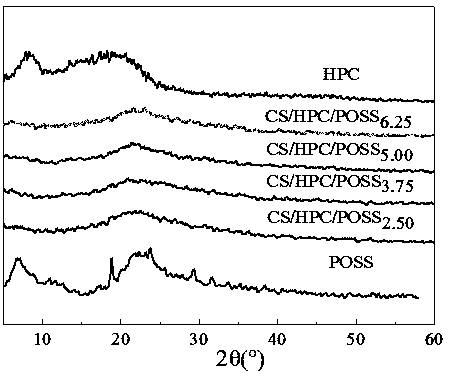
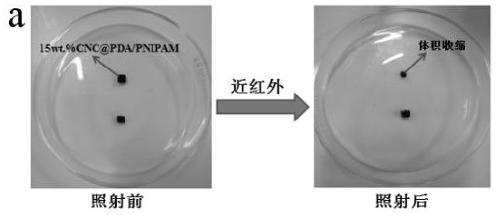
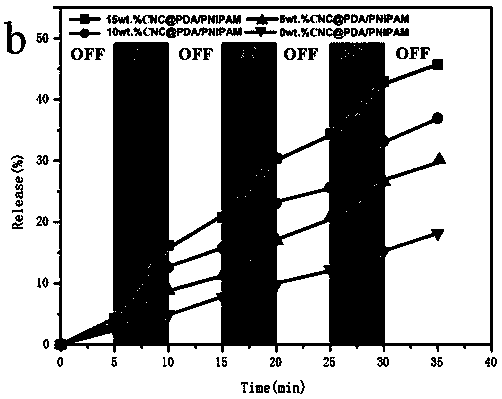
Patents
Literature
205 results about "Nanocomposite hydrogels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
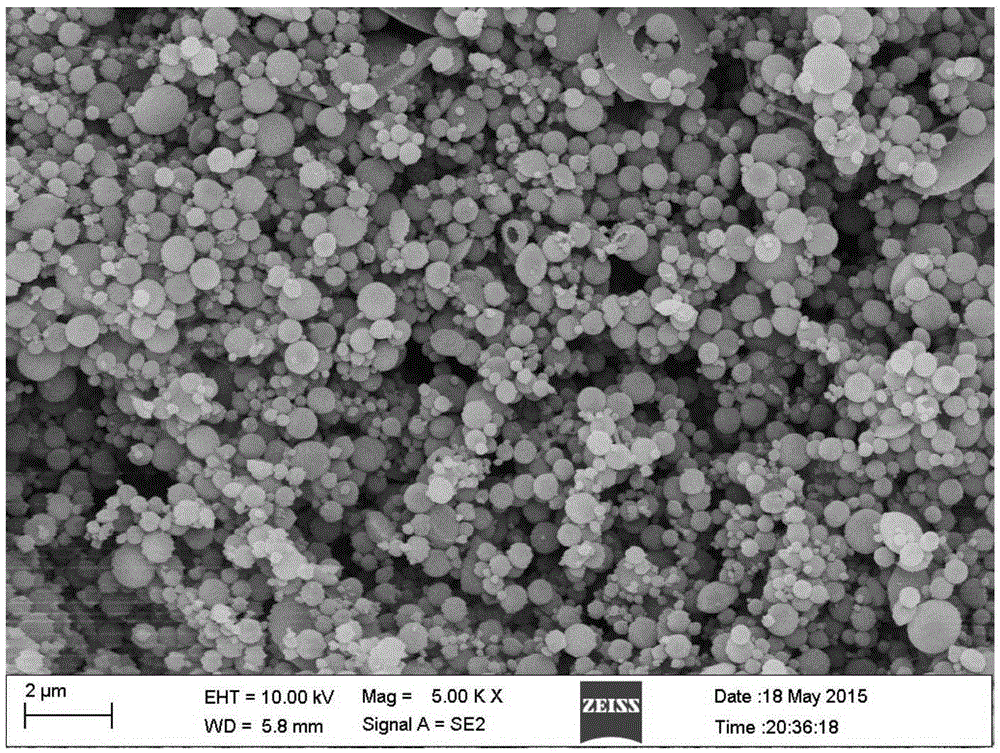
Nanocomposite hydrogels (NC gels) are nanomaterial-filled, hydrated, polymeric networks that exhibit higher elasticity and strength relative to traditionally made hydrogels. A range of natural and synthetic polymers are used to design nanocomposite network. By controlling the interactions between nanoparticles and polymer chains, a range of physical, chemical, and biological properties can be engineered. The combination of organic (polymer) and inorganic (clay) structure gives these hydrogels improved physical, chemical, electrical, biological, and swelling/de-swelling properties that cannot be achieved by either material alone. Inspired by flexible biological tissues, researchers incorporate carbon-based, polymeric, ceramic and/or metallic nanomaterials to give these hydrogels superior characteristics like optical properties and stimulus-sensitivity which can potentially be very helpful to medical (especially drug delivery and stem cell engineering) and mechanical fields.
Poly(vinyl alcohol)-bacterial cellulose nanocomposite
Hydrogel-bacterial cellulose nano-composite materials are created using a hydrogel and never dried bacterial cellulose fibers. Such materials are suitable for a broad range of soft tissue replacement applications. In addition controlled release of bioactive agents properties can be designed into medical devices fabricated from such composite materials.
Owner:AXCELON BIOPOLYMERS COPRORATION
Preparation method of graphene based nano composite hydrogel
The invention relates to a preparation method of a graphene based nano composite hydrogel, and belongs to the field of nano composite hydrogel preparation. An insitu polymerization method is adopted in the invention, which comprises the steps of: (1) preparing graphite into high water-soluble graphite oxide through an improved Hummers method and obtaining graphene emulsions of different varietiesand with different concentrations after peeling and processing; (2) uniformly mixing 1-10g of the graphene emulsions from step (1), 5-10g of water, 0.1-10g of water-soluble monomer, 0.005-0.5g of water-soluble initiator and 1-50[mu]l of catalyst, feeding in nitrogen for 1h to obtain a graphene pre-polymerized solution, and polymerizing under a certain temperature to obtain the graphene based nanocomposite hydrogel. The method of the present invention has a simple technology and is easy for operation; and the obtained nano composite hydrogel has excellent mechanical properties, restorability and environmental responsiveness. Therefore, the graphene based nano composite hydrogel has wide application prospects in biomedicine and machinery industry, etc.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Bioactive nano composite PVA-hydroxyapatite aquagel and its prepn.
The invention refers to a kind of nano complex water gel of bioactive polyvinyl alcohol / the oxhydryl apatite and preparation method which is as follows: prepare the PVA solution by using the purified polyvinyl alcohol; add the grinded and sifted Ca(OH)2 to the pure anhydrous alcohol, then heat the mixture and ultrasonically disperse it to get the alcohol-calcium suspended liquid (or add the metal calcium to the anhydrous alcohol, stir them and make them react to get the calcium alcohol solution); mix said two solutions; then add anhydrous alcohol containing H3PO4 to the mixed solution, and by freezing-melt molding, get the naneo complex water gel of bioactive polyvinyl alcohol. The invention utilizes the hydrophilicity of water-soluble polymer and the static acting force of oxhydryl to make the surface of the generative HA wetting and evenly dispersing.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Polyvinyl alcohol/ inorganic nanocomposite hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses polyvinyl alcohol / inorganic nanocomposite hydrogel, which is characterized by being formed by the following components: 30-90 parts by weight of polyvinyl alcohol and 0.1-20 parts by weight of inorganic nanocomposite particles through a chemical crosslinking gel method, wherein the inorganic nanocomposite particles comprise nano clay, nano mica powder, a nano molecular sieve, nano wollastonite, nano graphite, nanosilicon dioxide or a carbon nano tube. With the adoption of the polyvinyl alcohol / inorganic nanocomposite hydrogel, the mechanical strength of polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel is enhanced on the basis of not influencing the moisture of the hydrogel, the service life is prolonged, the permeability of the polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel is improved, and a channel is reserved for transmission of matters. As the selection of the materials, the production cost is controlled, and the better economic benefit is brought. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the polyvinyl alcohol / inorganic nanocomposite hydrogel. The preparation method is simple and feasible to operate and good in mechanical strength, and can be produced industrially.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP +2
Biocompatible and temperature-sensitive nano composite hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101703805AGood biocompatibilityImprove mechanical propertiesTumor/cancer cellsProsthesisDesorptionBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a biocompatible and temperature-sensitive nano composite hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The hydrogel contains alkyl acrylamide M1 with temperature-sensitive property, inorganic nano-powder M2 and polyhydroxyalkanoate M3 with good biocompatibility, and the mass percentage of the three is 94-60: 1-20: 5-39. The preparation method comprises the steps that: the M1, the M2 and the M3 are subjected to in-situ free radical polymerization reaction in aqueous solution, and the nano composite hydrogel with biocompatibility and temperature-sensitive property is obtained after soaking and impurity removal. The method has simple and easily controlled preparation process, and can implement automatic desorption of cells by reducing the temperature; the biocompatibility and the temperature-sensitive property of the hydrogel can be adjusted by changing the density of a crosslinker, the dosage of the M3 and the component; and the method can be widely applied in the fields of tissue engineering and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Natural polysaccharide/nano-TiO2 composite light-sensitive antimicrobial hydrogel dressing and radiation synthesis method thereof
The invention provides a natural polysaccharide / nano-TiO2 composite light-sensitive antimicrobial hydrogel dressing which is composed of a backing layer, a hydrogel dressing layer and a strippable layer. A synthesis method of the natural polysaccharide / nano-TiO2 composite light-sensitive antimicrobial hydrogel dressing comprises performing radiation crosslinking on raw materials, namely 10-40% of natural polysaccharide, 0.1-10% of nano-TiO2, 0.1%-5% of radiation sensitizer, 0.1%-3% of pH regulator, 0.1%-3% of surfactant and 60%-95% of water, by use of an electron beam or gamma ray by a radiation dose of 10-150kGy and at a dose rate of 10-80kGy / pass. The natural polysaccharide / nano-TiO2 composite light-sensitive antimicrobial hydrogel dressing is sheared, bagged and sterilized by radiation, and then stored for a long time. The natural polysaccharide / nano-TiO2 composite light-sensitive antimicrobial hydrogel dressing has the advantages that the maximization and optimization of the properties of the composite hydrogel, light-sensitive and antimicrobial properties are united organically, and the multiple-element composite synergic antimicrobial effect of the nano-TiO2-natural polysaccharide hydrogel is also realized; meanwhile, the composite hydrogel dressing has the characteristics of air permeability, no bonding with tissues, good flexibility and the like, and thus is suitable for protecting and treating various wounds.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Anisotropic nanocomposite hydrogel
ActiveUS20090252800A1Increased anisotropyIncrease stiffnessPowder deliveryOn/in organic carrierCelluloseActive agent
Anisotropic nanocomposite hydrogel materials are created using a process in which a hydrogel-forming material is crosslinked in the presence of nanoscale cellulose and subsequently thermally cycled under an applied tensile strain. Such materials are capable of exhibiting high mechanical and viscoelastic anisotropy, increased stiffness when subjected to large strain, and are suitable for a broad range of soft tissue replacement applications. In addition controlled release of bioactive agents properties can be designed into medical devices fabricated from such nanocomposite materials.
Owner:AXCELON BIOPOLYMERS COPRORATION
High-gel strength, salt resistant amphoteric ion type nano-composite hydrogel and preparing method
The invention relates to high-strength-gel and salt-resistant zwitterionic nano-composite hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The hydrogel consists of a polymer matrix accounting for 60 to 100 weight percent of the gel and inorganic components accounting for 0 to 40 weight percent of the gel. The preparation method is that prepolymerization reaction solution is firstly prepared; the inorganic components are dispersed and stripped in deionized water to form even and stable colloidal dispersion; and then monomer is dissolved in the deionized water to prepare into monomer solution with 30 percent to 100 percent of mass concentration; when being stirred, the monomer solution is added into the colloidal dispersion, and then a crosslinking agent, an initiator and a catalyst are added in to prepare the prepolymerization reaction solution; under the nitrogen condition and 20 DEG C to 60 DEG C, the prepolymerization reaction solution is polymerized for 12 to 30 hours to obtain a polymerization product; and then the polymerization product is treated for 3 to 7 days under 40 DEG C to 60 DEG C; the mechanical strength of the gel after the obtained hydrogel absorbs water is up to 225mJ / g, and the salt absorbing magnification is up to 140g / g.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nanometer composite hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a nanometer compound aquagel and preparing method, which comprises the following steps: polymerizing the prepolymer liquid at 25-35 deg.c for 20-30 h to obtain the product. The monomer is selected from acrylamide. The crosslink is selected from hectorite of modified sodium pyrophosphate. The general formula of chemical structure is Mg5.34Li0.66Si8O20 (OH) 4Na0.66.
Owner:SUZHOU NUOYIMAN IND
Method for preparing nano-composite hydrogel with excellent mechanical performances
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano composite hydrogel with good mechanical property, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: firstly, an anhydrous monomer and physical crosslinking agent inorganic clay are dispersed in deionized water, nitrogen enters into a closed container under the condition of normal temperature and normal pressure, and then the mixture is stirred; secondly, an initiator is added, stirring is continued under the condition of normal temperature and normal pressure, and a hydrogel solution is prepared; and thirdly, the solution undergoes free radical polymerization reaction at a certain temperature, and then a reactant is immersed in the deionized water so as to prepare the nano composite hydrogel with good mechanical property. The method has the advantages that: not only the preparation technique is simple but also the gel prepared simultaneously has good transparency, hydroscopic and swelling capacity, and mechanical property.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
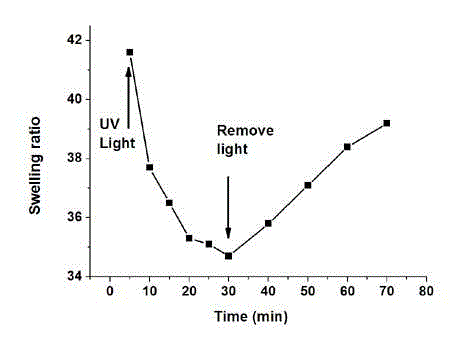
Preparation method of temperature, pH and ultraviolet multi-stimuli-responsive semi-interpenetrating network nanocomposite hydrogel
The invention relates to a preparation method of a semi-interpenetrating network nanocomposite hydrogel which can respond to variations in temperature, pH and ultraviolet to realize volume transition. The preparation method of the gel is as follows: taking temperature-sensitive monomers, namely N-isopropylacrylamide and azo type water soluble monomers, namely 4-((4-acryloxy) phenyl azo) benzoic acid as copolymerization monomers, taking modified nano-clay as a cross-linking agent, dissolving the monomers and the cross-linking agent in a cellulose type macromolecular water solution, uniformly stirring, and then performing oxidation, reduction and catalytic free radical polymerization in an ice bath under the protection of nitrogen for preparation. The gel uses nano-laponite cross-linked monomers to constitute a framework of the gel and takes cellulose type macromolecules as semi-interpenetrating macromolecules. The obtained hydrogel has the advantages of excellent mechanical properties, high swelling rate and fast and controllable stimulus response. The gel has the potential to be applied to the field of sustained release of medicaments.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
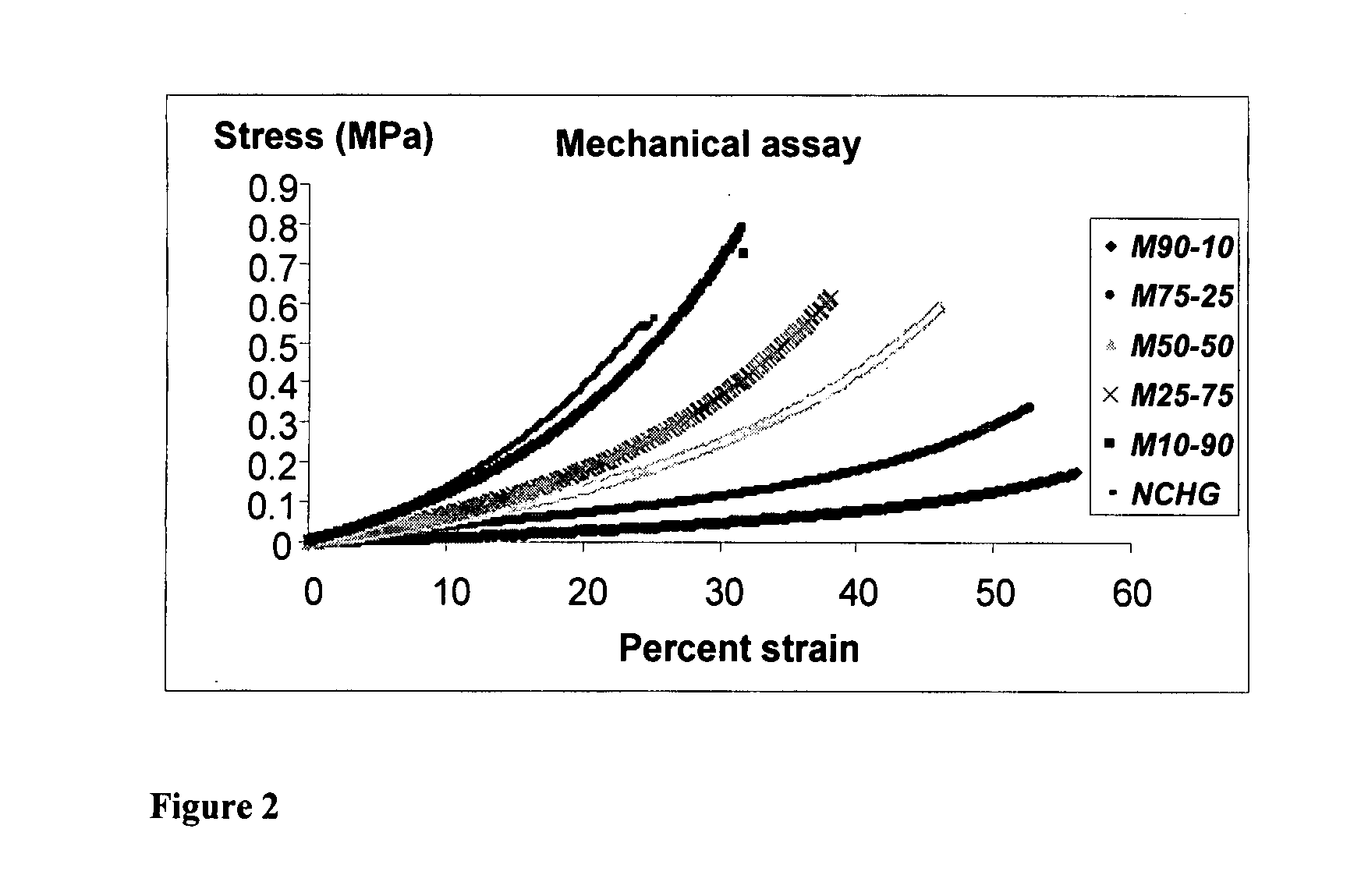
Synthesis of biocompatible nanocomposite hydrogels as a local drug delivery system
InactiveUS20070212419A1Slow drug releaseHigh compressive strengthOrganic active ingredientsBiocide(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylateModel system
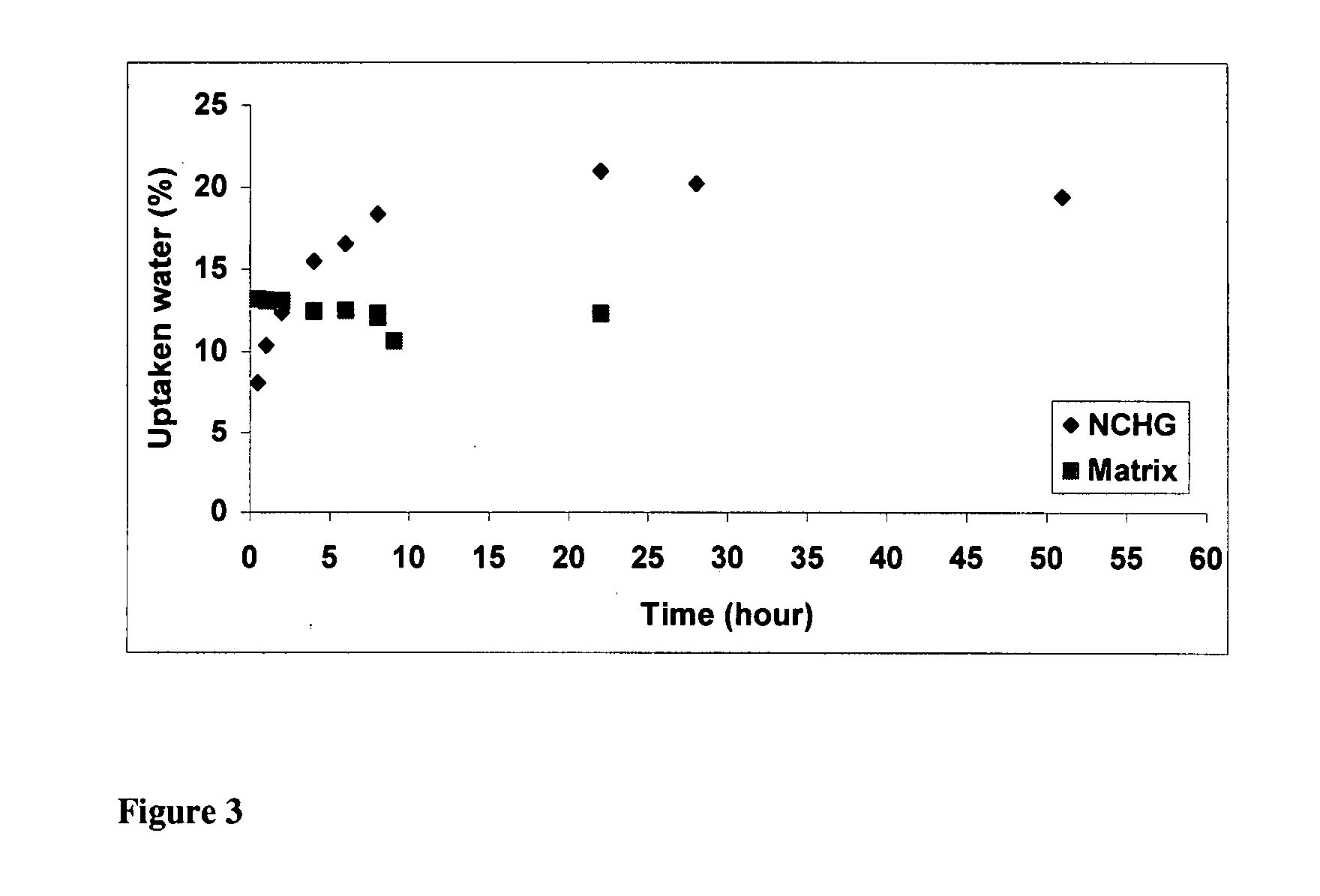
Nanocomposite biocompatible hydrogels (NCHGs) may be synthesised as model systems for in situ cured local drug delivery devices for treatment of inter alia periodontal infections. The composite includes the following components: nanoparticles (NPs), a matrix gel, and chlorhexidine (CHX) or other antibacterial drug. The NPs were obtained by free radical initiated copolymerization of the monomers, 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and polyethyleneglycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA), in aqueous solution. The same monomers were used to prepare crosslinked matrices by photopolymerization. NCHGs were obtained by mixing NPs, monomers, and drug in an aqueous solution then crosslinked by photopolymerization.
Owner:BAKO JOZSEF +6
Transparent bacterial cellulose nanocomposite hydrogels
InactiveUS20130011385A1High mechanical strengthEnhanced interactionOrganic active ingredientsBiocidePolymer scienceWater insoluble
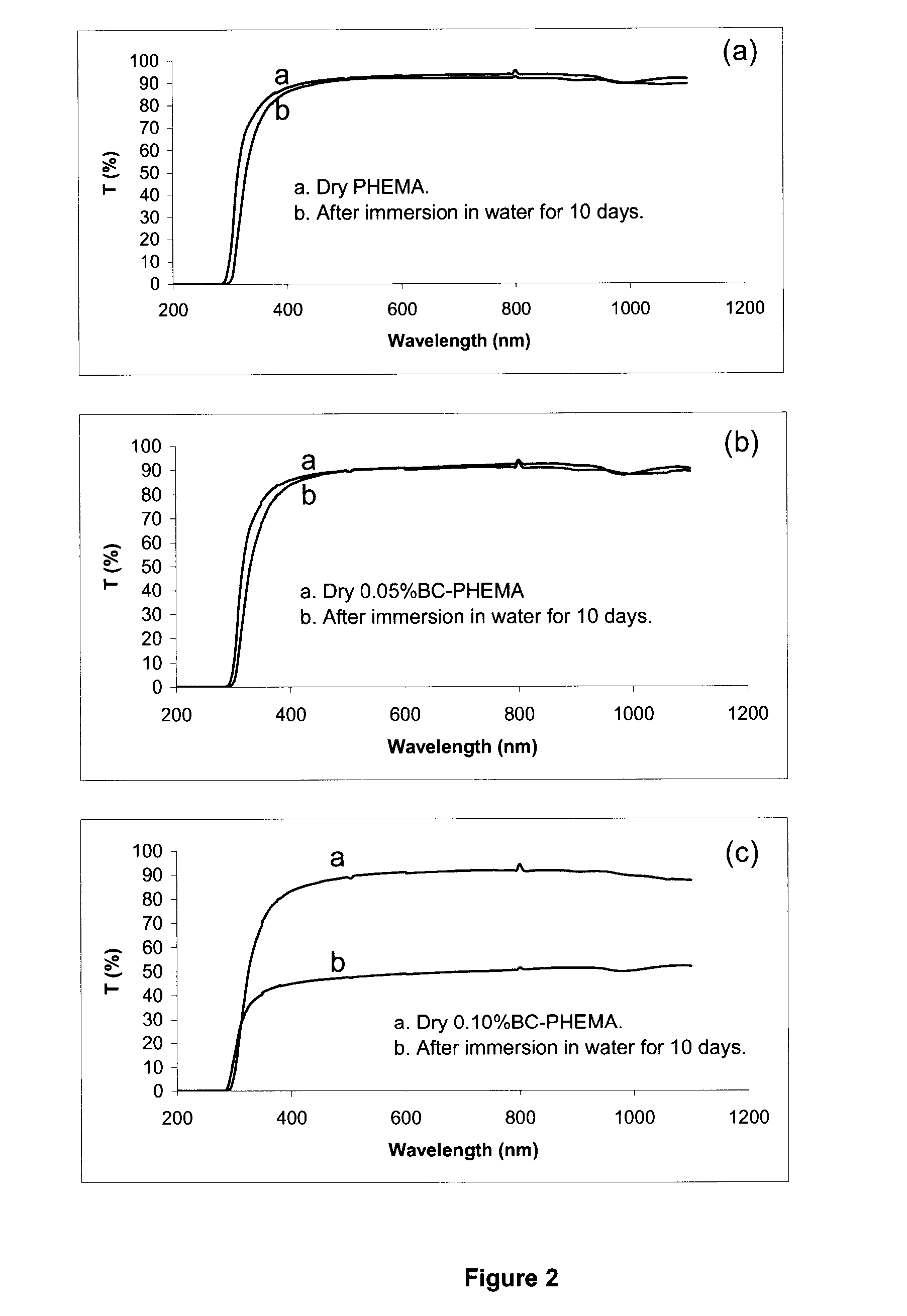
A transparent polymeric nanocomposite hydrogel is provided, wherein the polymeric nanocomposite hydrogel is made from a water insoluble polymer, i.e. poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) or / and crosslinked PHEMA and a water insoluble nanofiber, i.e., bacterial cellulose (BC). Disclosed is a synthetic route for polymeric nanocomposites hydrogels. The preferred polymeric nanocompositions are produced through free radical polymerization of HEMA monomer in the presence of bacterial cellulose with an assistance of ultrasound to enhance the mixing of bacterial cellulose, initiator, and the monomers. The polymeric nanocomposite hydrogel is then formed by immersion of the dry polymeric nanocomposite in water. Disclosed is a high transmittance polymer nanocomposite hydrogel with a preferred BC loading less than 0.1%, water content of about 40% in weight, good mechanical integrity and strength. The disclosed polymer nanocomposite hydrogel and compositions pertain to hydrogel applications, particularly contact lenses and optic components for biosensor.
Owner:AXCELON BIOPOLYMERS COPRORATION
PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) composite aquagel with bioactivity and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) composite aquagel with bioactivity and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: mixing a PVA water solution and a PEO (polyoxyethylene) solution, adding a Ca-ethanol suspension or calcium ethoxide solution, adding anhydrous alcohol containing H3PO4, freezing, and defreezing to obtain the PVA composite aquagel with bioactivity. The invention has the advantages of no biotoxicity of raw materials, low cost, mild reaction conditions, and safe and simple technique, and satisfies the environmental requirements; high number-average molecular weight PEO with favorable biocompatibility and lubricating property is introduced into a nano HA / PVA composite aquagel, so the high number-average molecular weight PEO molecular chain forms polymer brushes on the aquagel surface to lower the friction force of the aquagel surface; and thus, the material can be conveniently applied to joint prosthesis cartilage replacement materials.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ion type nano-composite hydrogel and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an ion type nano-composite hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving acrylamide monomer, nano inorganic clay and gelatin in deionized water, stirring for 10 to 30 minutes in an inert atmosphere; adding auxiliary cross-linking agent and catalyst, stirring for 5 to 10 minutes in the inert atmosphere, and then adding an initiating agent; carrying out a free radical polymerization for 12 to 36 hours at a temperature of 0 to 30 DEG C; immersing reaction product in the deionized water at the temperature of 20 to 60 DEG C, changing deionized water at regular intervals of 5 to 8 hours, continuing for 48 to 72 hours to obtain the ion type nano-composite hydrogel. The preparation method has simple process and controllable condition; the prepared gel has excellent biocompatibility, mechanical property and optical property, and can be widely used in the field of tissue engineering.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
3D bioprinting ink, preparation method of ink, tissue engineering scaffold and preparation method of scaffold
InactiveCN110665063AHigh strengthRelieve painAdditive manufacturing apparatusTissue regenerationComputer printingBiology
The invention discloses 3D bioprinting ink, a preparation method of the ink, a tissue engineering scaffold and a preparation method of the scaffold. The ink contains the following five components: gelatin, sodium alginate, nano-scale magnesium lithium silicate, deionized water and human mesenchymal stem cells. The preparation method of the ink comprises the following steps: firstly dissolving thesterile gelatin and the sodium alginate into the sterile deionized water in order to prepare a mixed prepolymer solution of 140-200 mg / ml gelatin and 20-60 mg / ml sodium alginate; dissolving the sterile magnesium lithium silicate into the sterile deionized water to prepare 20-60 mg / mL magnesium lithium silicate colloid; mixing the two gel in equal volume to prepare a nanocomposite hydrogel which can be used for 3D bioprinting; and finally, uniformly mixing the pre-cultured human mesenchymal stem cells and the nano-composite hydrogel to obtain the nano composite bio-ink with a final cell concentration of 3 x 10<6> / mL. The functionalized, biomimetic tissue engineering bone scaffold with osteogenesis inducing ability is prepared by using the bio-ink as a raw material and adopting a squeeze type 3D bioprinter through printing, and has potential clinical application value
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Quantum dot/TiO2 nano-composite hydrogel soft reactor and in-situ radiation preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106215952AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh mechanical strengthBiocidePhysical/chemical process catalystsNanocomposite hydrogelsElectron
The invention discloses a quantum dot / TiO2 nano-composite hydrogel soft reactor and an in-situ radiation preparation method thereof. According to the in-situ radiation preparation method, physically crosslinked TiO2 composite hydrogel utilizing natural polysaccharides as a base material is prepared by virtue of cycle freezing, and after a quantum dot precursor and TiO2 nano-composite hydrogel are blended, quantum dots prepared through in-situ radiation of electron beams can be uniformly assembled to the surface of nano-TiO2 to effectively modify and sensitize the surface of nano-TiO2, so as to form a hydrogel 'soft reactor' catalytic material in which a quantum dot / TiO2 composite is effectively loaded into a hydrogel skeleton. Due to the organic unification of adsorption, photocatalysis, antibiosis and sterilization, the hydrogel soft reactor which is excellent in mechanical strength, high in expansion response speed and shrinkage response speed, capable of easily loading catalysts and stable in performance can be obtained. The quantum dot / TiO2 nano-composite hydrogel 'soft reactor'catalytic material prepared by virtue of the in-situ radiation preparation method can be widely popularized and applied to the fields of environmental sewage treatment, photocatalysis, antibiosis, sterilization and the like.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Sericin-based semi-interpenetrating temperature-sensitive nano-composite hydro-gel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a sericin-based semi-interpenetrating temperature-sensitive nano-composite hydro-gel and a preparation method thereof. The hydro-gel comprises a sericin polypeptide chain part, an inorganic nano-soapstone particle part and a polymer formed after an alkylacrylamide monomer is polymerized. In the hydro-gel, a semi-interpenetrating network technology is mainly adopted, and by combining the physical crosslinking effect of inorganic nano-soapstone particles, the sericin, the inorganic nano-soapstone particles and in-situ free radical of the alkylacrylamide monomer are polymerized. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dispersing the inorganic nano-soapstone particles; preparing a reaction prepolymerization solution; preparing gel; and purifying the gel. The sericin-based semi-interpenetrating temperature-sensitive nano-composite hydro-gel has rich raw material sources, simple preparation method, low cost, high swelling degree and excellent cell compatibility, can be adjusted according to the content of sericin, and has a wide application prospect in artificial skin, artificial cartilage, cell culture stent, bioreactor and other biomedical aspects.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
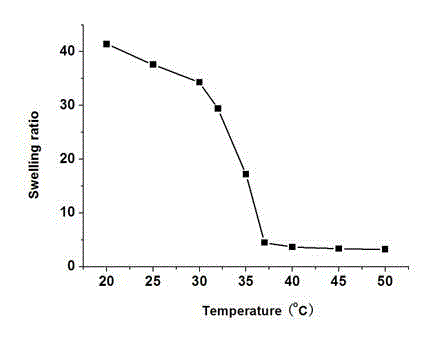
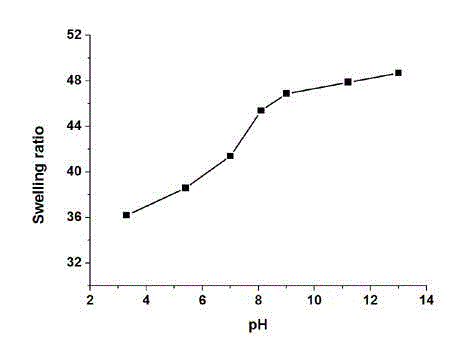
Preparation method of high-strength nano-composite hydrogel with rapid dual responses of pH and temperature
The invention relates to a preparation method of high-strength nano-composite hydrogel capable of rapidly responding to pH and temperature. The preparation method taking dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate as a monomer, inorganic nanometer clay and N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide as co-crosslinking agents, and a nanometer cellulose whisker as a gel composite reinforcer comprises the following steps of: stirring the components, carrying out uniform ultrasonic oscillation, carrying out photo-initiation free radical polymerization in 0 DEG C ice-bath, then reacting at -18 DEG C for 24 hours to obtain the final gel product. The hydrogel prepared by the method has the dual responses of temperature and pH and excellent mechanical performance and can rapidly swell and deswell; and the lowest transformation temperature of the hydrogel is close to temperature of human bodies; raw materials are cheap; the preparation method is simple; and the high-strength nano-composite hydrogel has the potential of application in fields such as sustained release of medicines and tissue engineering.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of nano meso-porous silicon composite hydrogel with controlled release function
InactiveCN106492220AHigh activityKeep aliveAerosol deliveryInorganic non-active ingredientsControl releaseBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a preparation method of nano meso-porous silicon composite hydrogel with a controlled release function. The preparation method includes the steps that micromolecular medicine is loaded in meso-porous silicon nano-particles; an oxidized hyaluronic acid and carboxymethyl chitosan solution is prepared, and the medicine-carrying nano-particles are added into the hyaluronic acid solution to be ultrasonically treated and then stirred to be uniform; a medicine-carrying nano composite hydrogel carrier is prepared. The prepared nano composite hydrogel has good mechanical performance, biocompatibility, biodegradability and medicine slow release effects, and has potential of being applied to the fields of tissue engineering and biological medicine treatment. In addition, the preparation method of the nano composite hydrogel is simple, cost is low, and large-scale production can be achieved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of chemically crosslinked nanocomposite hydrogel
The invention relates to a preparation method of a chemically crosslinked nanocomposite hydrogel, which comprises the following steps: (1) adding water, hydrophobic monomers and a surfactant into a container, raising the temperature to a certain temperature, adding a water-soluble initiator, carrying out reaction for 1h-2h, adding acetone solution of a polymerizable photoinitiator into a system, completing the adding within 6h, stopping heating, obtaining nano-microspheres with photo-initiation activity and carrying out dialysis on the prepared microspheres in distillated water for 72h; and (2) adding emulsion of the microspheres with the photo-initiation activity in the concentration of 5%-40% after the dialysis of the step (1) into water-soluble monomers for light radiation. The preparation method has the advantages of simpleness, wide sources of raw materials, high polymerization efficiency and fast polymerization speed, and is applicable to industrial production; and the obtained nanocomposite hydrogel has excellent mechanical properties and good stability.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
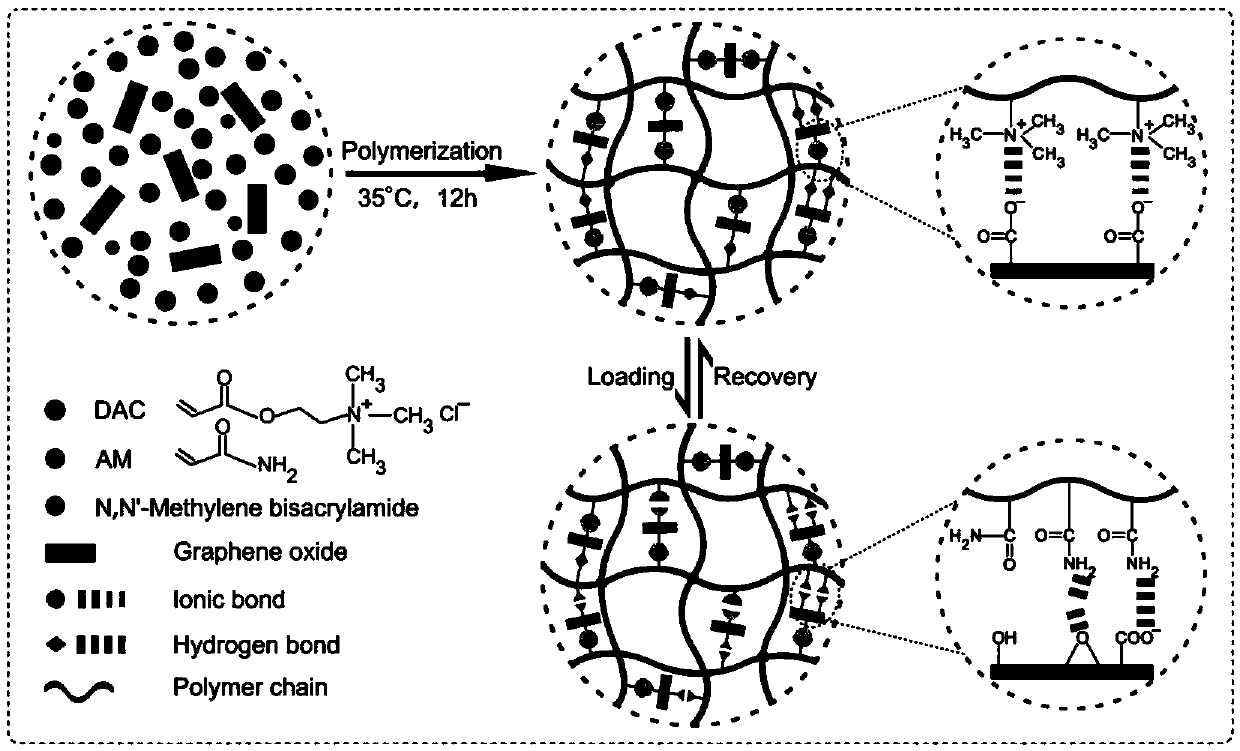
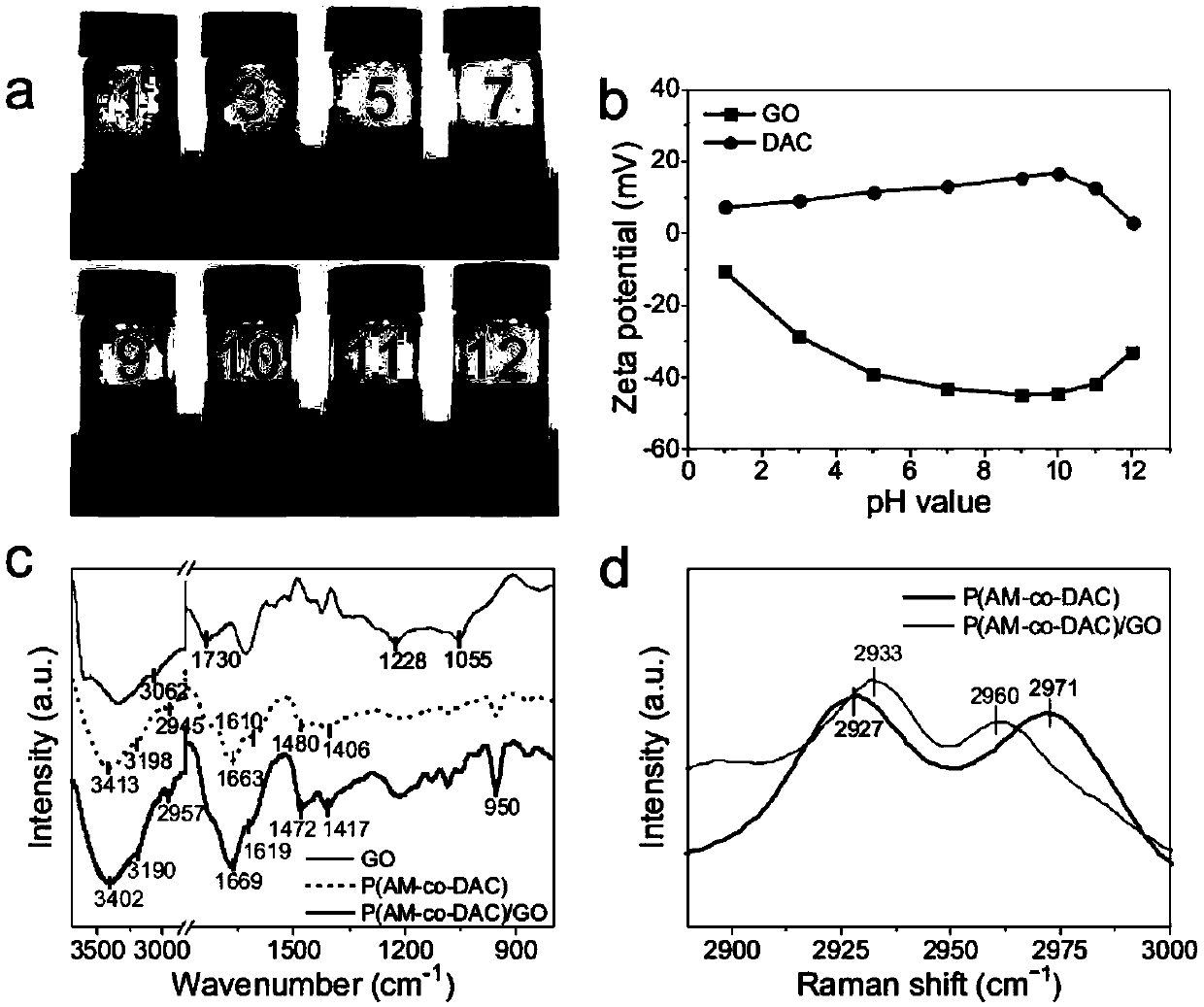
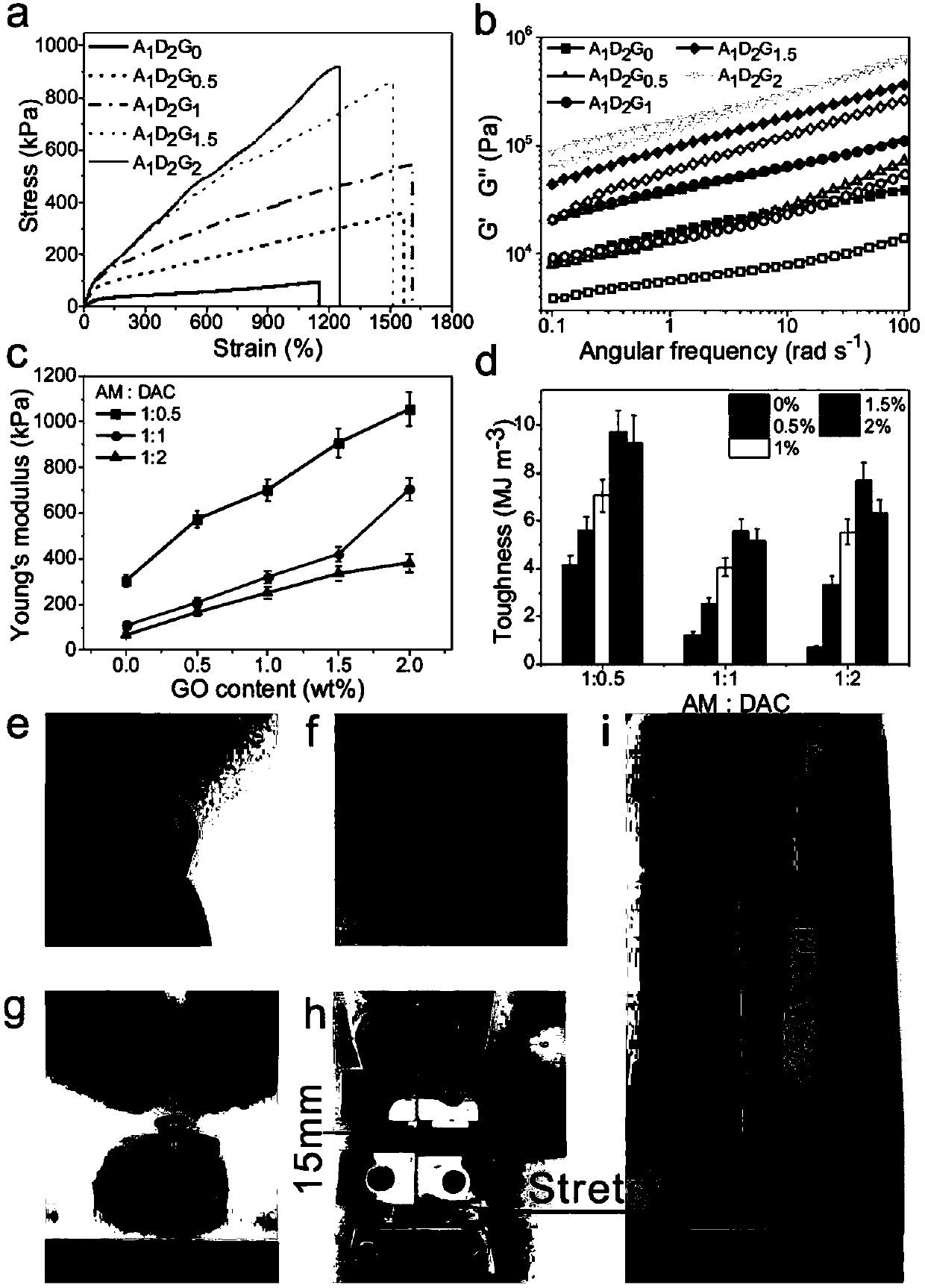
Tough stretchable compressible polymer/graphene oxide nano composite hydrogel with excellent self-repairing performance
InactiveCN107814869AImprove self-healing efficiencyImprove mechanical propertiesYoung's modulusMechanical property
The invention provides tough stretchable compressible polymer / graphene oxide nano composite hydrogel and the tough stretchable compressible polymer / graphene oxide nano composite hydrogel has excellentself-repairing performance. Under the existence of graphene oxide, by free radical polymerization of acrylamide (AM) and acryloyloxyethyl trimethyl ammonium chloride (DAC), the cationic polyacrylamide / graphene oxide (GO) hydrogel is prepared. Mechanical performance and self-repairing capacity can be regulated by content of GO and a mass ratio of the AM to the DAC. An ionic bond between the DAC and the GO and a hydrogen bond between the AM and the GO can effectively dissipate energy and reconstruct a network. The obtained composite hydrogel has high rigidity (Young modulus: to 1.1MPa), high toughness (to 9.3MJm<-3>) and high fatigue resistance, and a high self-repairing rate (tensile strength of over 92%, tensile strain of over 99% and toughness of over 93%). The tough stretchable compressible polymer / graphene oxide nano composite hydrogel are simple in step, convenient to operate and high in practicality.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
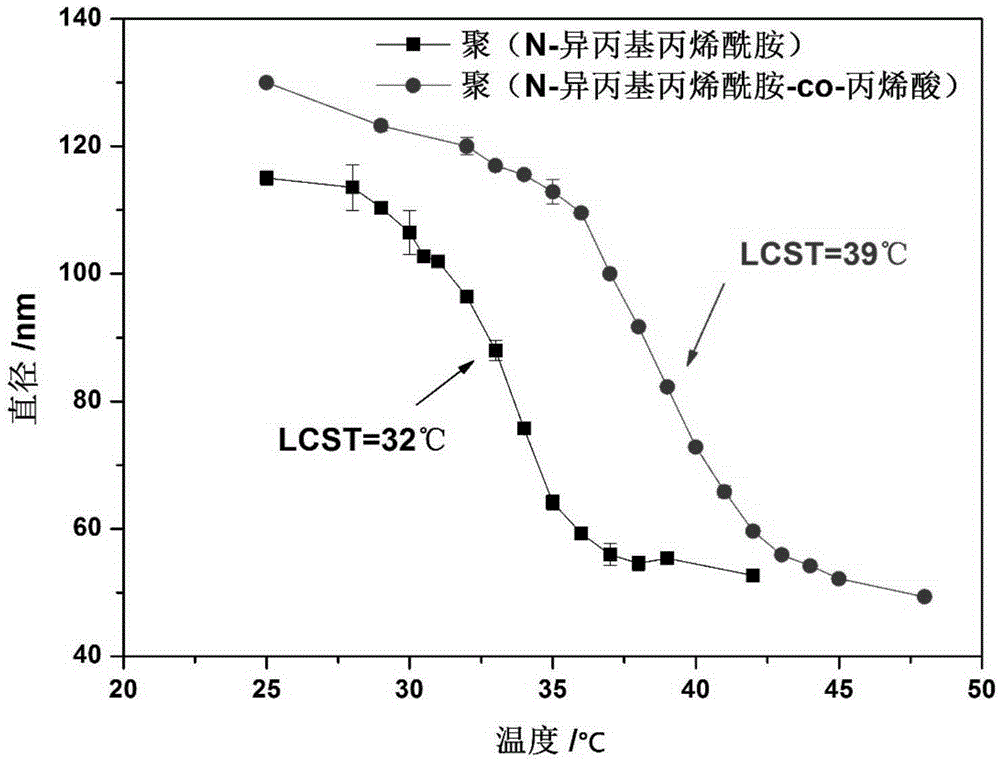
Thermosensitive dual-administration nanocomposite hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical fields of biomedical materials and medical apparatus, and in particular relates to a thermosensitive dual-administration nanocomposite hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the thermosensitive dual-administration nanocomposite hydrogel comprises the following steps: preparing a poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) nano microsphere and loading a growth factor, preparing a poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) nano microsphere and loading an anti-inflammatory drug, and preparing the thermosensitive dual-administration nanocomposite hydrogel. The finished product takes sodium alginate as a matrix phase and uses two poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) based thermosensitive nano gel microspheres which have different LCSTs and are respectively loaded with the anti-inflammatory drug and the growth factor as a dispersion phase; and by controlling the temperature of the composite hydrogel to be higher than or lower than LCST of the nano microspheres, the release of the anti-inflammatory drug and the release of the growth factor are controlled, so that controlled release of the anti-inflammatory drug and the growth factor in inflammatory stage and proliferative stage of a deep wound repairing process is achieved.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Process for producing poly(vinyl alcohol)-bacterial cellulose nanocomposite
Owner:AXCELON BIOPOLYMERS COPRORATION
High-strength silicon dioxide and clay dual nano-composite hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104530294AImprove mechanical propertiesSimple preparation processSilicon oxideSilicon dioxide
The invention relates to a high-strength silicon dioxide and clay dual nano-composite hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method is characterized by comprising the following steps: adding a monomer and a silicon dioxide precursor into clay aqueous dispersion liquid with mass percentage concentration of 1-15%, and stirring at normal temperature until uniformly dispersing; then adding an initiating agent, and stirring to be uniform; and reacting mixed liquid for 5-48 hours at 20-90 DEG C until a nano-composite hydrogel is formed, wherein the mass of the clay accounts for 1-30% of the mass of the monomer, the mass of the silicon dioxide precursor accounts for 1-50% of the mass of the monomer, and the mass of the initiating agent accounts for 0.5-2% of the mass of the monomer. The dual nano-composite hydrogel provided by the invention is simple in preparation method and high in gel strength, and ensures that the needs of more fields can be met.
Owner:XINJIANG UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing hydrogel by enzymatic free radical polymerization
InactiveCN103342823AMild reaction conditionsSimple and fast operationPeroxidaseNanocomposite hydrogels
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydrogel by enzymatic free radical polymerization. According to the method, peroxidase, a beta-dicarbonyl compound and hydrogen peroxide are combined as an enzymatic free radical initiating system for providing free radicals for polymerization. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing an aqueous solution containing the peroxidase, the beta-dicarbonyl compound and alkene monomers in a using process; and then, adding hydrogen peroxide in the aqueous solution, adjusting the component concentration of a peroxidase / beta-dicarbonyl compound / hydrogen peroxide ternary initiating system, and controlling to obtain the hydrogel within 20 seconds to 30 minutes under the room temperature. The method for preparing the hydrogel by enzymatic free radical polymerization is realized in a water phase, gentle in reaction condition, simple and convenient to operate, quick and controllable in hydrogel forming time and capable of preparing the high-strength nanometer composite hydrogel material, and therefore, the method has an obvious application prospect in the fields including immobilized enzyme carriers, medicament controlled release, artificial cartilages, tissue engineering scaffold materials and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for preparing nano composite hydrogel with magnetic function
The invention relates to a method for preparing nano composite hydrogel with magnetic function. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) adding inorganic clay into deionized water, stirring to completely strip the clay, adding a water-soluble monomer, an initiator and a catalyst, mixing uniformly to obtain a prepolymer solution, and polymerizing the obtained prepolymer solution at the temperature of between 5 and 30 DEG C for 24 to 120 hours to obtain nano composite hydrogel; and (2) dissolving a bivalent iron salt and a trivalent iron salt into deionized water, adding 1 to 10 grams of the nano composite hydrogel, soaking for 24 to 120 hours at the temperature of between 5 and 30 DEG C under the protection of nitrogen to obtain soaked hydrogel, preparing 0.5 to 5mol / L co-precipitator, adding the soaked hydrogel, reacting for 1 to 12 hours under the protection of nitrogen, and thus obtaining the nano composite hydrogel with magnetic function. The preparing method is simple, wide in raw material source and low in cost; and the obtained nano composite hydrogel has excellent magnetic performance and high application value.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Injectable organosilicone/chitosan nanocomposite hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108404221AInjectable propertiesSelf-healingPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisSelf-healingMechanical property
The invention discloses injectable organosilicone / chitosan nanocomposite hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: selecting water-soluble aminated polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS); uniformly mixing the POSS with a chitosan solution; mixing the mixture with a second macromolecular aqueous solution carrying analdehyde group; carrying out a Schiff base reaction on amino groups contained in the POSS and chitosan and aldehyde-based macromolecules in order to generate the organosilicone / chitosan nanocompositehydrogel. The POSS is dispersed uniformly in a chitosan system. The organosilicone / chitosan nanocomposite hydrogel prepared by the invention has reversible response to pH, has mechanical property being greatly improved compared with the traditional chitosan hydrogel, and has injectability and self-healing performance. The preparation method and process of the hydrogel are simple, and no toxic organic small molecular crosslinking agent is used. The hydrogel is environmentally friendly, is suitable for large-scale preparation and can be applied in the field of biomedical materials.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Cellulose/N-isopropylacrylamide medicine controllable release hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109998988AGood biocompatibilityAchieve the purpose of modificationOrganic active ingredientsDrug photocleavageControl releaseDopamine
The invention belongs to the technical field of cellulose hydrogel and particularly relates to a cellulose / N-isopropylacrylamide medicine controllable release hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. Dopamine is added to a cellulose solution, the surface of cellulose is modified, and the cellulose can wrap a cellulose macromolecule framework, so that the cellulose has the mechanical force reinforcement function and also has the photoresponse characteristic. Meanwhile, N-isopropylacrylamide is dispersed in the modified cellulose solution, through free radical solution polymerization, the hydrogel is formed, and accordingly the cellulose hydrogel is endowed with the near-infrared response characteristic and thermosensitivity. The nano composite hydrogel has certain potential application value in the fields of intelligent medicine control release materials and biomedical application.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Preparing method of carboxymethyl chitosan/graphene oxide/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanocomposite hydrogel
The invention relates to a preparing method of carboxymethyl chitosan / graphene oxide / poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanocomposite hydrogel. In preparation, the method includes the steps of conducting even mixing to obtain carboxymethyl chitosan / graphene oxide / N-isopropylacrylamide dispersion liquid containing photoinitiator, adding an activating agent to obtain a mixed solution, making the mixed solution react under the room temperature and nitrogen protection conditions to obtain carboxymethyl chitosan / graphene oxide crosslinked and cured hydrogel, and finally conducting ultraviolet irradiationto obtain the carboxymethyl chitosan / graphene oxide / poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) nanocomposite hydrogel. The finally prepared nanocomposite hydrogel has the pH / temperature dual-response characteristic, has the water content of 80-92%, the maximum compressive strength of 0.6-0.8 MPa and the fracture strain of 75-85%, has the advantage of good biocompatibility, and has potential application value inthe fields of drug release, molecular devices and the like.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com