Method for separating and purifying protein through aqueous-two-phase system
A two-phase system, separation and purification technology, applied in peptide preparation methods, chemical instruments and methods, animal/human proteins, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency of protein back extraction, difficult separation and purification of proteins, weak phase separation ability of DES, etc. problems, achieve protein structure and activity retention, high stripping efficiency, and low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] The effect of deep eutectic solvent type and molar ratio on the extraction rate of two-phase system:
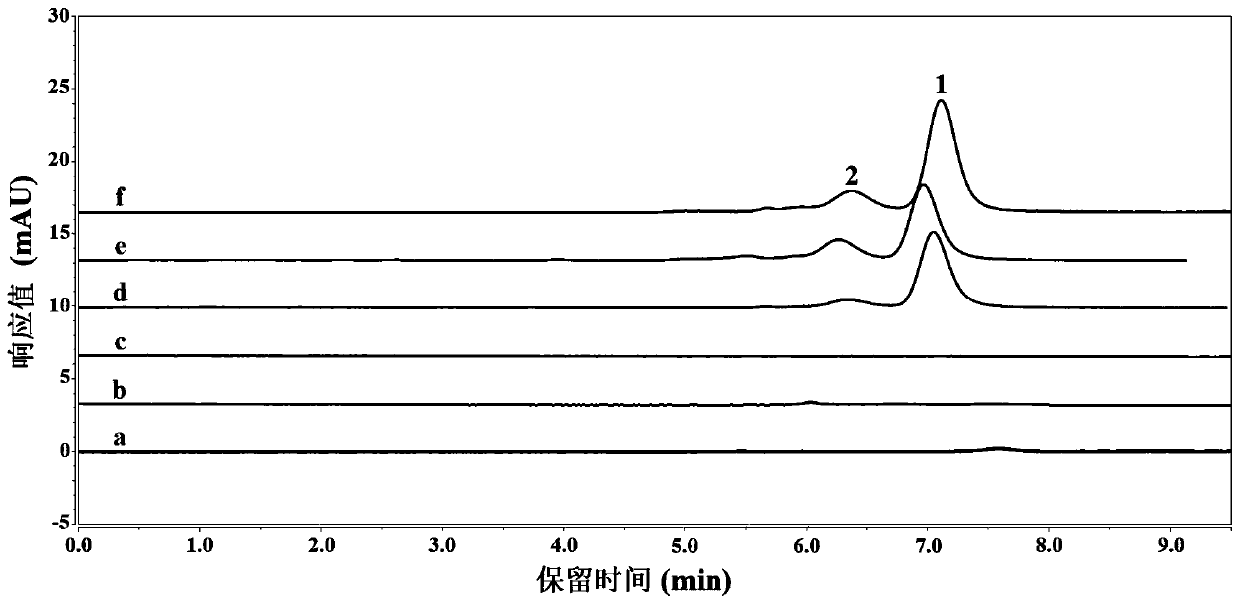
[0052] Aqueous two-phase extraction: Weigh 1.6 g of DES into a 5 mL centrifuge tube, add 2 mL of 0.03 g / mL K containing 10 mg bovine serum albumin (BSA) 2 HPO 4 aqueous solution. Shake at 1000rpm for 10min at 25°C or vortex at 60 W for 10min, and centrifuge at 3000rpm for 5min. At this time, a mutually incompatible liquid-liquid two-phase system is formed, in which the lower layer is the DES phase and the upper layer is the salt phase. Record the volume of the two phases, collect the DES phase and dilute it 20 times with water for UV measurement, take the reference substance comparison method to quantitatively analyze the content of BSA, and calculate the extraction rate. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0053] It can be seen from Table 1 that both ChCl-HFIP DES and tetramethylammonium chloride-HFIP DES have higher protein extraction rates. The extraction rates...
Embodiment 2
[0057] The influence of different extraction conditions on the extraction rate of the two-phase system:
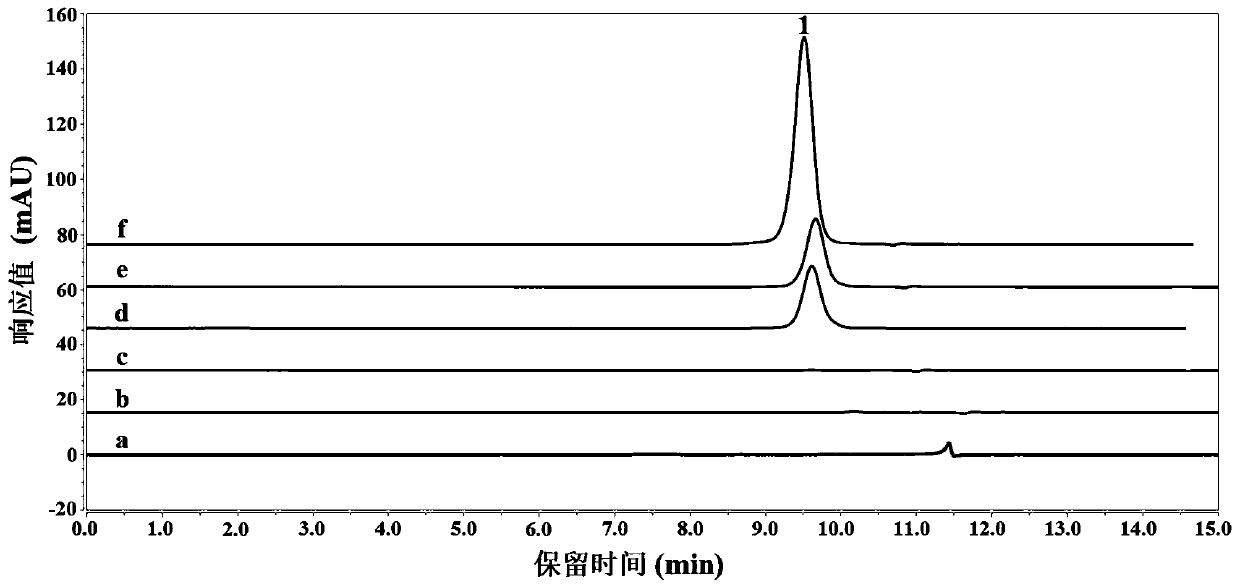
[0058] Aqueous two-phase extraction: Weigh ChCl-HFIP DES with a certain mass molar ratio of 1:2 and place it in a 5mL centrifuge tube, add 2mL of a certain concentration of K containing a certain mass of BSA 2 HPO 4 aqueous solution. Shake at 1000 rpm for a certain time at a certain temperature, and centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 5 minutes. At this time, a mutually incompatible liquid-liquid two-phase system is formed, in which the lower layer is the DES phase and the upper layer is the salt phase. Record the volume of the two phases, collect the DES phase and dilute it with water 15-200 times for UV measurement, take the reference substance comparison method to quantitatively analyze the content of BSA, and calculate the extraction rate. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0059] Extraction rate under different extraction conditions in table 2
[0060]
[0061]
[...
Embodiment 3
[0064] The influence of different stripping conditions on the stripping rate:
[0065] 1. Aqueous two-phase extraction:
[0066] Weigh 1.33 g of ChCl-HFIP DES with a molar ratio of 1:2 and place it in a 5 mL centrifuge tube, add 2 mL of 0.022 g / mL K containing 5 mg BSA 2 HPO 4 aqueous solution. Shake at 1000rpm for 5min at 25°C and centrifuge at 3000rpm for 5min. At this time, a mutually incompatible liquid-liquid two-phase system is formed, in which the lower layer is the DES phase and the upper layer is the salt phase. Record the volume of the two phases, collect the DES phase and dilute it 20 times with water for UV measurement, and use the reference substance comparison method to quantitatively analyze the content of BSA. The extraction rate is 99.20%-100.00%, and almost all of the BSA is extracted into the DES phase.
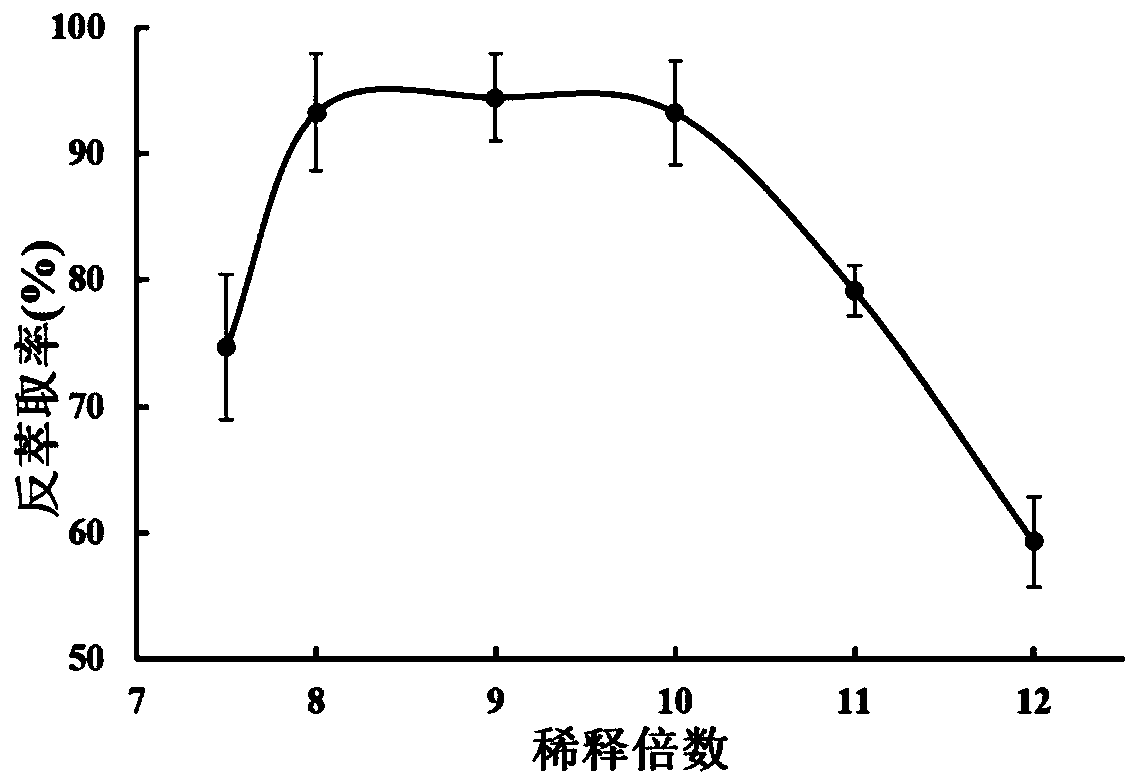
[0067] 2. Back extraction protein:
[0068] The DES phase after protein extraction was placed in a 5 mL centrifuge tube, diluted 7.5, 8, 9, 10, 11, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com