Method for improving coercive force of sintered neodymium iron boron magnet
A technology of NdFeB and coercive force, which is applied in the field of improving the coercive force of sintered NdFeB magnets, can solve the problems of low coercive force and large grain size of sintered NdFeB magnets, and achieve lower sintering temperature, Improve the coercive force of the magnet and promote the effect of liquid phase flow
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Prepare the mixture according to the following formula:
[0038] Pr-Nd alloy: 32wt%; Fe: 66.4wt%; Al: 0.5wt%; Cu: 0.1wt%; B: 1.0wt%.
[0039] Put the prepared mixture into a vacuum quick-setting casting furnace, vacuumize to 1Pa, fill it with argon protection for heating and melting, and then pour the melted liquid on the rotating cooling copper roller to obtain a thickness of about 0.3mm NdFeB alloy cast sheet.
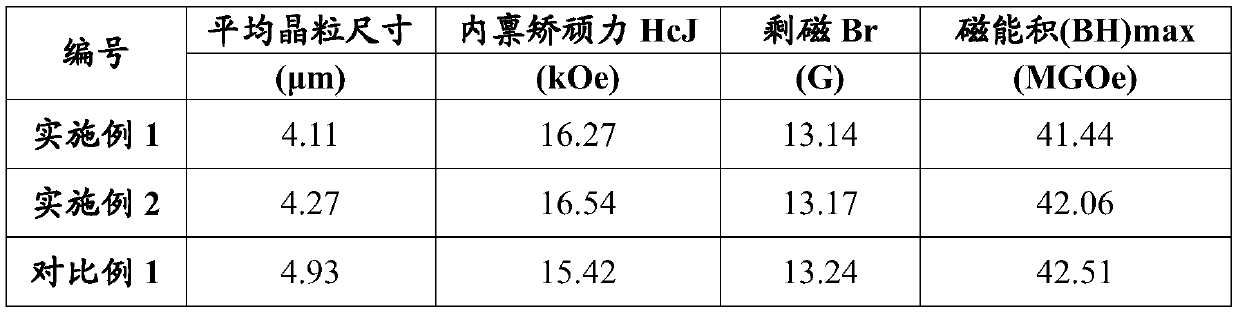
[0040] Hydrogen crushing of NdFeB alloy castings to obtain NdFeB coarse powder, mix NdFeB coarse powder with antioxidant and lubricant for 1 hour, and then obtain NdFeB fine powder with an average particle size D50 of 3.04 μm by jet mill . Mix tungsten powder with a volume ratio of 0.5:100 (average particle diameter D50 is 500nm) and NdFeB fine powder for 1.5h to obtain mixed powder. In a 2T magnetic field, the mixed powder is subjected to orientation molding and isostatic pressing to obtain a compact; the compact is vacuum sintered at 1050°C for 2h, and th...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Prepare the mixture according to the following formula:
[0043] Pr-Nd alloy: 32wt%; Fe: 66.4wt%; Al: 0.5wt%; Cu: 0.1wt%; B: 1.0wt%.
[0044] Put the prepared mixture into a vacuum quick-setting casting furnace, vacuumize to 1Pa, fill it with argon protection for heating and melting, and then pour the melted liquid on the rotating cooling copper roller to obtain a thickness of about 0.3mm NdFeB alloy cast sheet.
[0045] Hydrogen crushing of NdFeB alloy castings to obtain NdFeB coarse powder, mix NdFeB coarse powder with antioxidant and lubricant for 1 hour, and then obtain NdFeB fine powder with an average particle size D50 of 3.04 μm by jet mill . Mix tungsten powder, Cu-Ga alloy and NdFeB fine powder according to the volume ratio of 0.5:0.5:100 for 1.5h to obtain mixed powder; wherein, the average particle diameter D50 of tungsten powder is 500nm, and the average particle size of Cu-Ga alloy The particle size D50 is 1.3 μm, and the Ga content in the Cu-Ga alloy is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com