A method for producing podophyllotoxin from the adventitious roots of P. chinensis
A technology of podophyllotoxin and Peach Seven, which is applied in gardening methods, botanical equipment and methods, plant regeneration, etc. It can solve the problems of farmers' lack of enthusiasm for planting, large consumption of Peach Seven seeds, slow callus growth, etc. problem, to achieve the effects of low browning degree without subculture, short culture period, promotion of accumulation and content improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The acquisition of embodiment 1 sterile seed embryo
[0044]Remove moth-eaten and rotten seeds from fresh peach seven seeds, wash them with water, corrode the seed coats with a little concentrated sulfuric acid until the color turns black, soak them in 0.5% sodium carbonate at room temperature for 20 hours to remove oily, waxy and other hydrophobic components, 80mg / L gibberellin (GA4+7) was soaked at 4°C for 28 hours, and 0.2% mercury chloride surface was disinfected for 6 minutes.
[0045] In the experimental group, the above-mentioned pretreated seeds were blotted dry with sterilized filter paper, and the seed embryos were extruded from the germination hole of the hilum with sterilized needle-nose pliers, and inoculated in MS medium; The pretreatment method of group seeds is the same as above, only the seed embryos are taken out using the following method: the seeds are cut open with a scalpel, and half seeds with embryos are inoculated on MS medium. The two groups ...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Effect of Example 2 Different Hormones on Embryogenic Callus Induction
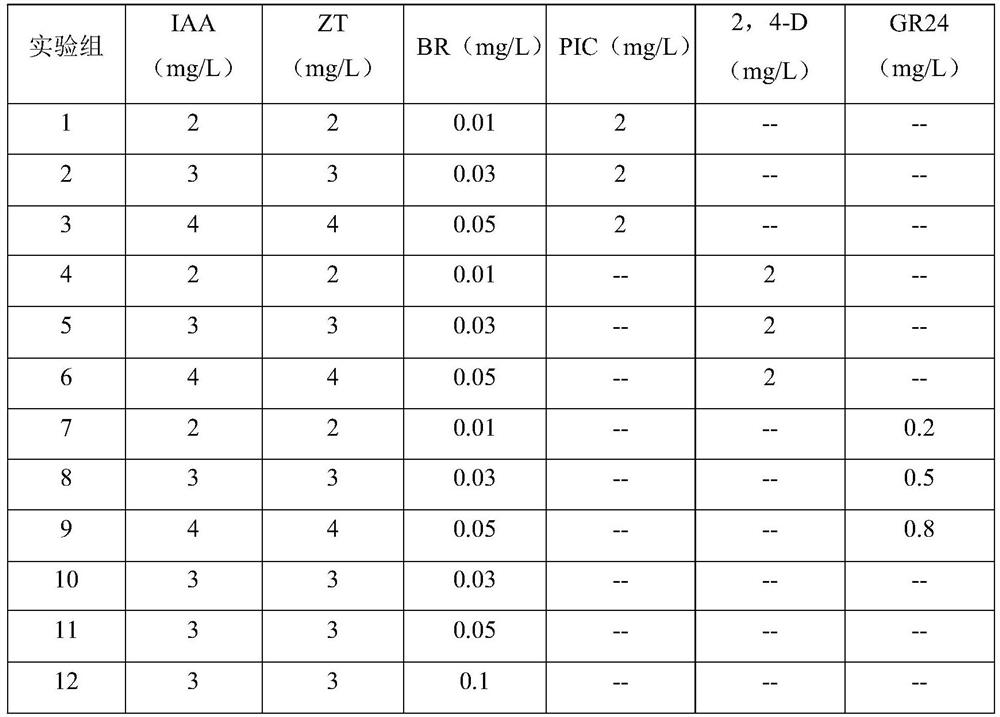
[0049] Using seed embryos as explants, culture them at a temperature of 23°C in the dark for about 40 days until adventitious root primordia are clearly visible and embryogenic callus is obtained. Embryogenic callus induction medium formula: MS basic culture medium, sucrose 50g / L, acid hydrolyzed casein 1g / L, agar 5g / L, biotin 0.2mg / L, pH6.5, and add different hormones for culture , see Table 1 for the ratio of different hormones.
[0050] Table 1 Embryogenic callus induction medium
[0051]
[0052] After the culture, the growth state of the explants was observed, the callus induction rate was calculated, and the number of adventitious root primordia was counted. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0053] test group explant growth status callus induction rate average adventitious root cardinality 1 After about 20 days, the explants expanded obviously 80% callus inductio...
Embodiment 3
[0056] The growth of embodiment 3 adventitious roots
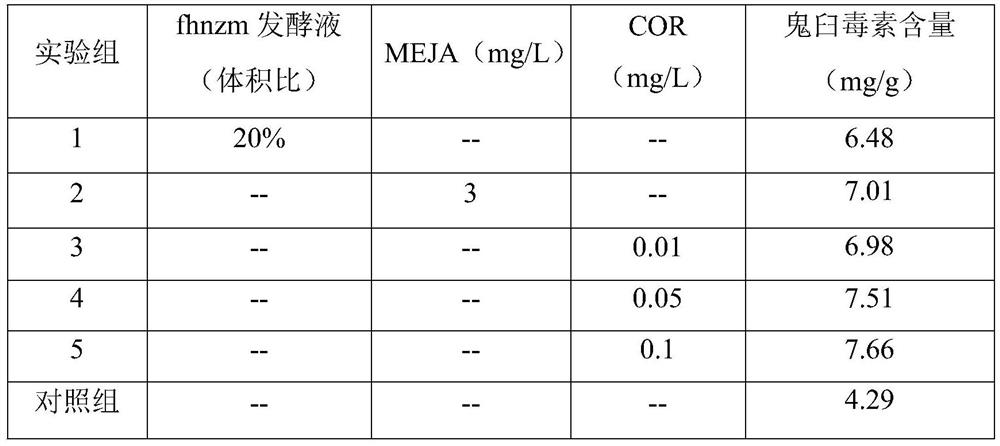
[0057] The callus with root primordia obtained in Example 2 was transferred into the adventitious root growth medium, and cultured for 40 days under dark conditions at a temperature of 20° C., and the length of the adventitious root was 5+1 cm. At this time, the adventitious roots were divided into two groups, and one group continued to grow in the liquid 1 / 2MS medium (sucrose 20g / L) without agar under sterile conditions; Cultivate in a flask, immerse the roots in 0.2g / L of water-soluble fertilizer with a nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content ratio of 20:20:20 (with 0.1g / L of sucrose added), and cover the callus with sterilized peat soil.
[0058] Adventitious root growth medium formula is as follows: 1 / 2MS basic culture medium, sucrose 20g / L, agar 5g / L, naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA) concentration of 0.2mg / L, indoleacetic acid (IAA) concentration of 0.2mg / L.
[0059] The experimental results show that adventitious roo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com