Optimized aptamer sequence capable of specifically identifying vibrio parahaemolyticus, and application thereof
A hemolytic Vibrio and aptamer technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, instruments, analytical materials, etc., can solve the problems of library diversity reduction, affecting aptamer binding characteristics, PCR amplification deviation, etc., to achieve Ideal affinity, good specificity, and convenient synthesis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Clipping and Directed Mutation of Adapter Sequences
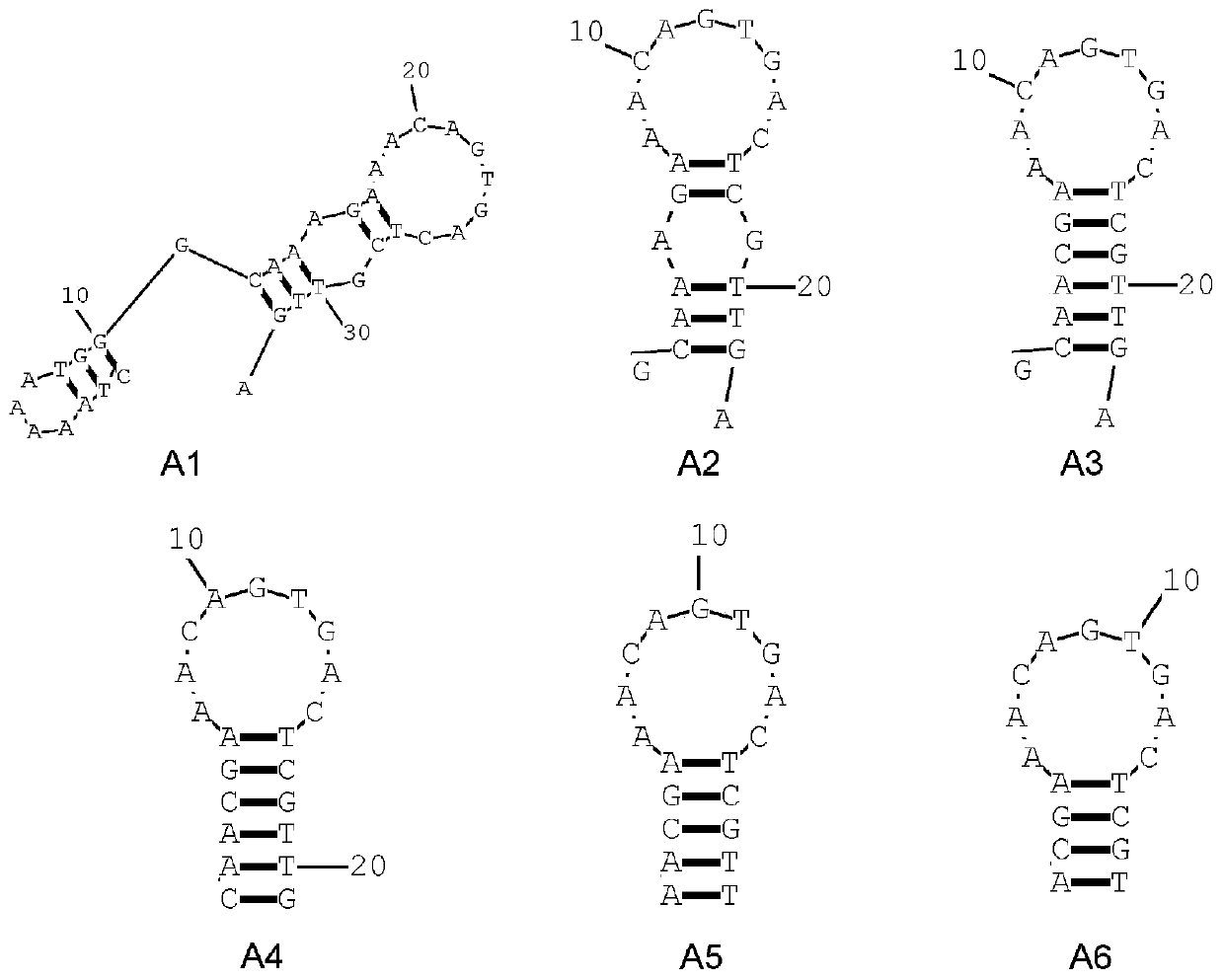
[0038] Clipping and targeted mutation sequence secondary structures such as figure 1shown. A3P is the original aptamer sequence of Vibrio parahaemolyticus screened by SELEX technology, which contains 87 bases. Based on this, the primer regions at both ends are removed to obtain the sequence A1 (SEQ.ID.No.2). Considering that the structure of A1 is relatively complex, part of the nucleotides were trimmed at both ends to obtain the sequence A2 (SEQ.ID.No.3). Base mismatches were observed in the stem region of the A2 sequence, and it was reported that base mismatches may affect the stability of the secondary structure of the aptamer and affect the affinity performance of the aptamer, so the stem of A2 Targeted mutagenesis was performed to make it complete base pairing to generate A3 (SEQ.ID.No.4). One nucleotide was trimmed at the 5' and 3' ends of A3 to obtain sequence A4 (SEQ.ID.No.1). Thereafter, on the...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The LNA replacement of embodiment 2 adapter sequences
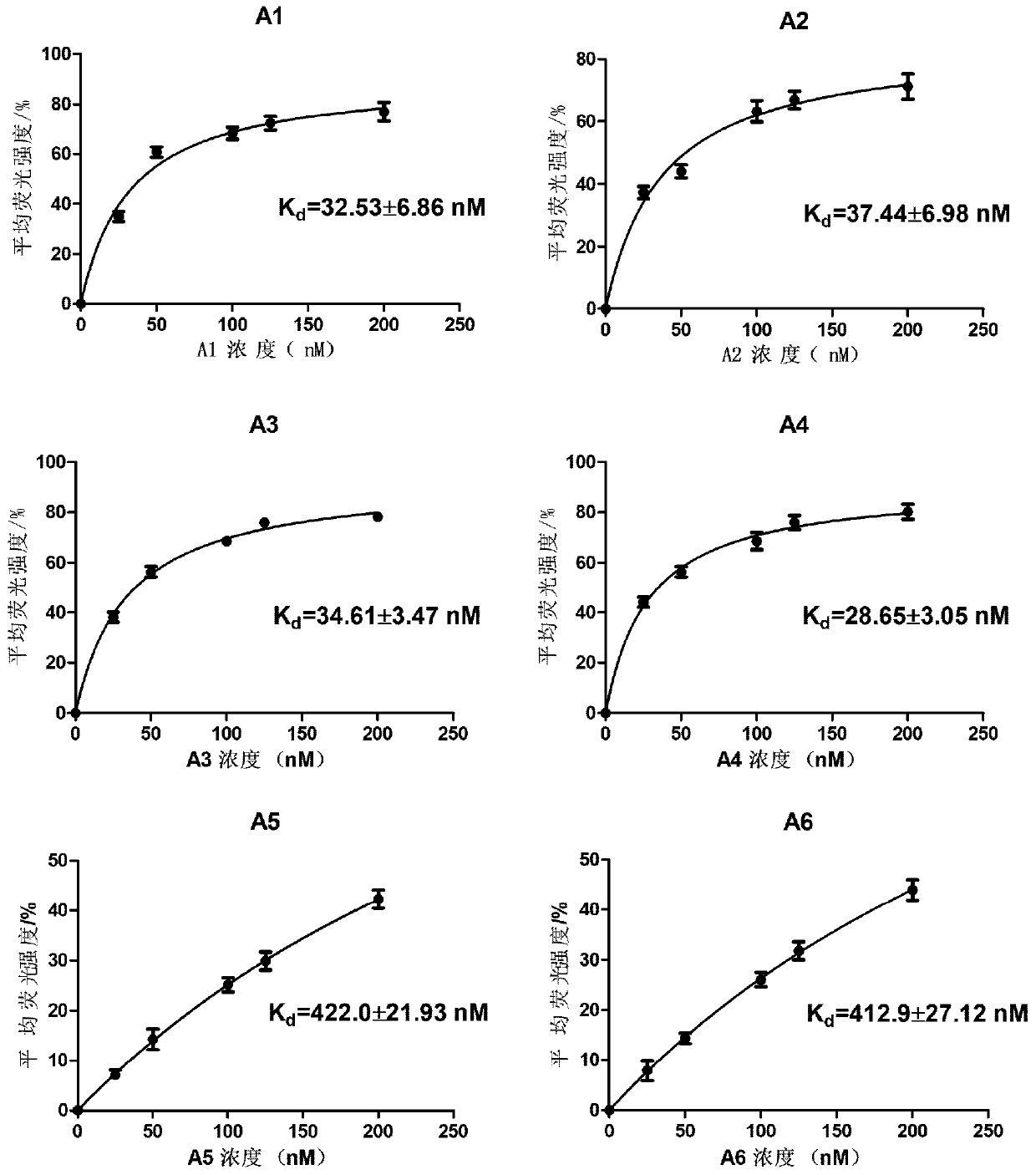
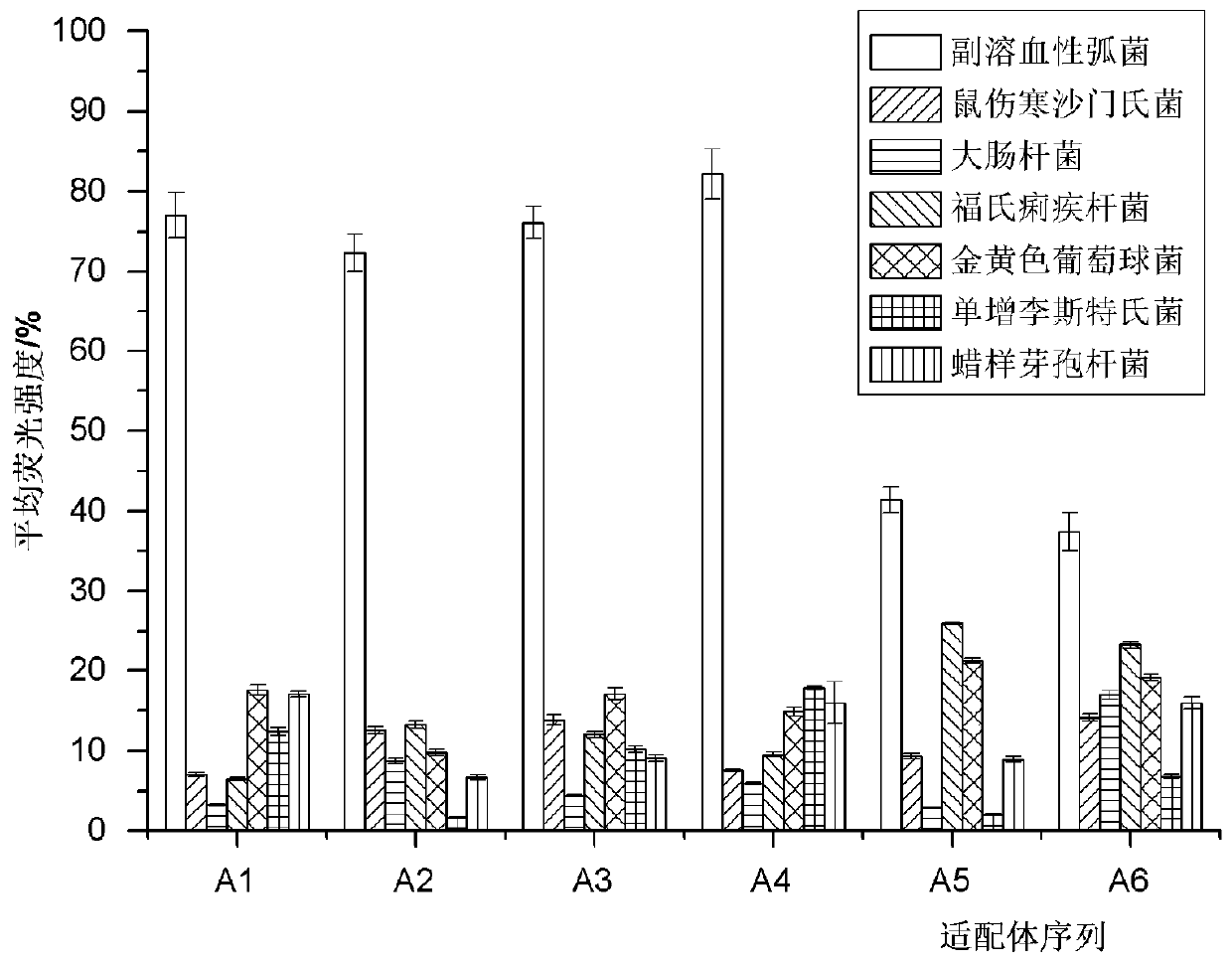
[0044] On the basis of the optimal sequence A4 (SEQ.ID.No.1) obtained by tailoring, the stem region was replaced by LNA in order to obtain an aptamer sequence with good affinity and ideal stability. First, one pair, two pairs, and three pairs of nucleotides are replaced with LNA at the end of the stem of A4 to obtain A4-1 (the first and 21st bases of A4 are replaced by LNA), A4-2 (the first and second bases of A4 1, 2, 20 and 21 bases are substituted by LNA) and A4-3 (the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 19th, 20th and 21st bases of A4 are substituted by LNA), the secondary structure of the sequence is as follows Figure 4 shown. Although their specificity results ( Figure 5 shown) is ideal, but the affinity results (saturation binding curves such as Image 6 As shown, K d The values are summarized in Table 2 below) showing the K for these three sequences d The values are in the same order of magnitude, and the affinity is...
Embodiment 3
[0052] Example 3 Application of aptamer functionalized magnetic beads to capture Vibrio parahaemolyticus in samples
[0053] (1) Preparation of aptamer-functionalized magnetic beads
[0054] The streptavidin-modified magnetic beads were washed and resuspended in 2×B&W buffer to a final concentration of 5 mg / mL. An equal volume of biotinylated optimized aptamer was added to the magnetic bead suspension to a final concentration of 1 μM, followed by incubation at 37°C for 10 min. Magnetic beads were collected using an external magnetic field and washed twice with 1×B&W buffer to remove excess aptamers in the system. The aptamer-coated magnetic beads were stored in PBS buffer at 4°C for future use.
[0055] (2) Determination of capture efficiency of different bacteria by aptamer functionalized magnetic beads
[0056] Take 1mL logarithmic phase (OD 600 =0.3) in a centrifuge tube, and gradiently diluted to an appropriate concentration. The prepared aptamer-coated magnetic beads...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com